|
Behavior-altering Parasites And Parasitoids
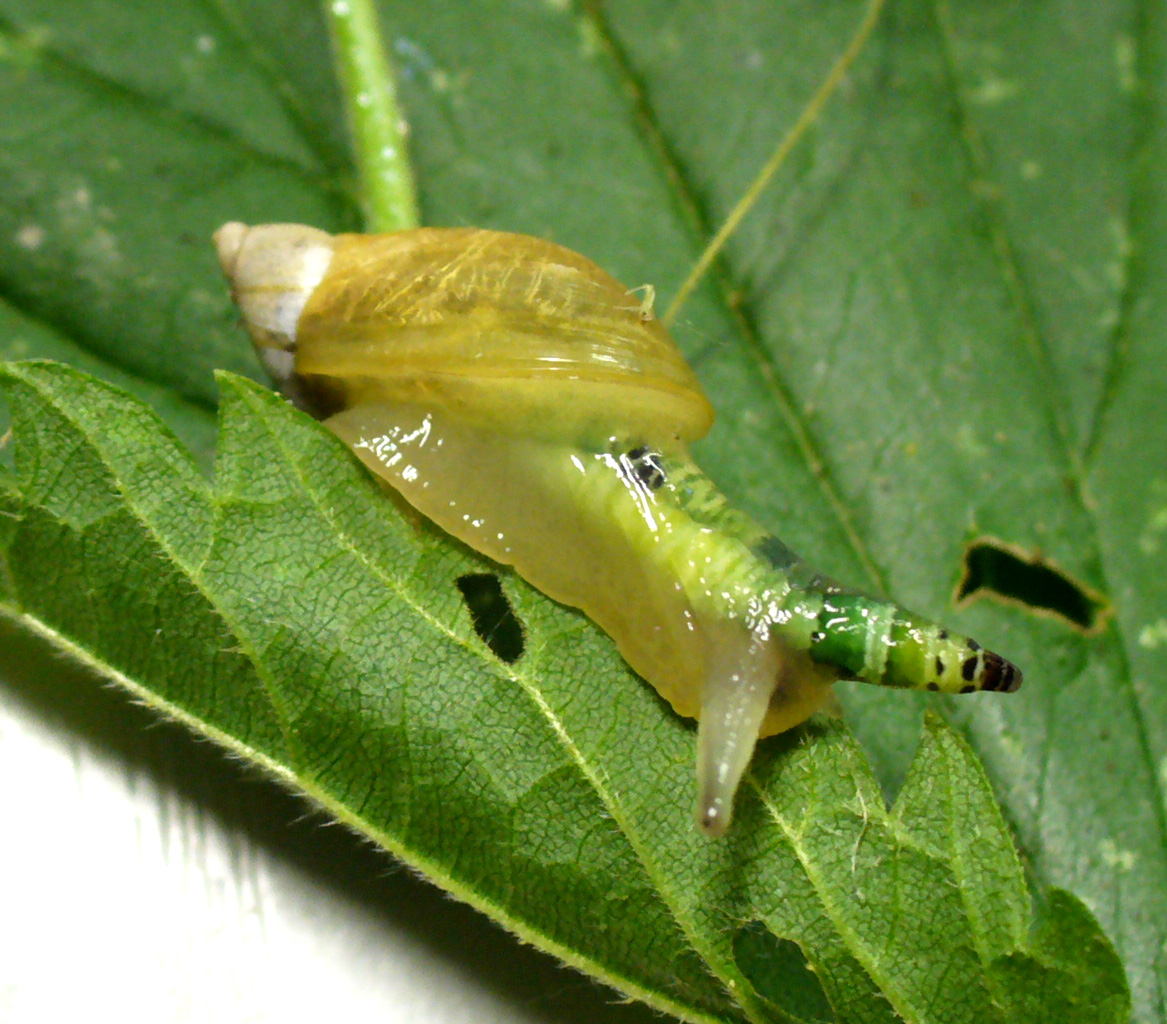
Behavior-altering parasites are parasites capable of causing changes in the behavior of their hosts species to enhance their transmission, sometimes directly affecting the hosts' decision-making and behavior control mechanisms. By way of example, a parasite that reproduces in an intermediate host may require, as part of their life cycle, that the intermediate host be eaten by a predator at a higher trophic level, and some parasites are capable of altering the behavior of the intermediate host to make such predation more likely; a mechanism that has been called parasite increased trophic facilitation or parasite increased trophic transmission. Examples can be found in bacteria, protozoa, viruses, and animals. Parasites may also alter the host behavior to increase protection of the parasites or their offspring; the term bodyguard manipulation is used for such mechanisms. Among the behavioral changes caused by parasites is carelessness, making their hosts easier prey.Moore, J. (2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle cramp which is accompanied by a sudden burst of pain. A muscle cramp is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. It is typically caused by ion imbalance or muscle fatigue. There are other causes of involuntary muscle contractions, and some of these may cause a health problem. A series of spasms, or permanent spasms, is referred to as a "spasmism". Description and causes Spasms occur when the part of the brain that controls movement malfunctions, causing involuntary muscle activity. A spasm may be a muscle contraction caused by abnormal nerve stimulation or by abnormal activity of the muscle itself. Causes The cause of spasms is often unknown, but it can be due to an inherited genetic problem, a side effect of medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch (music), pitch and sound pressure, volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' (: larynges) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throatʼ. Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a respiratory epithelium, ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The laryngeal cavity, cavity of the larynx extends from its tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lingual lipase and amylase), and antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Saliva has specialized purposes for a variety of animal species beyond predigestion. Certain swifts construct nests with their sticky saliva. The foundation of bird's nest soup is an aerodramus nest. Venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyssavirus
''Lyssavirus'' (from the Greek ''lyssa'' "rage, fury, rabies" and the Latin '' vīrus'') is a genus of RNA viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', order '' Mononegavirales''. Mammals, including humans, can serve as natural hosts. The genus ''Lyssavirus'' includes the causative agent (rabies virus) of rabies. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * ''Lyssavirus aravan'', Aravan virus * ''Lyssavirus australis'', Australian bat lyssavirus * ''Lyssavirus bokeloh'', Bokeloh bat lyssavirus * ''Lyssavirus caucasicus'', West Caucasian bat virus * ''Lyssavirus duvenhage'', Duvenhage virus * ''Lyssavirus formosa'', Taiwan bat lyssavirus * ''Lyssavirus gannoruwa'', Gannoruwa bat lyssavirus * ''Lyssavirus hamburg'', European bat lyssavirus 1 * ''Lyssavirus helsinki'', European bat lyssavirus 2 * ''Lyssavirus ikoma'', Ikoma lyssavirus * ''Lyssavirus irkut'', Irkut virus * ''Lyssavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abnormal sensations at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, violent movements, uncontrolled excitement, fear of water, an inability to move parts of the body, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Once symptoms appear, the result is virtually always death. The time period between contracting the disease and the start of symptoms is usually one to three months but can vary from less than one week to more than one year. The time depends on the distance the virus must travel along Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerves to reach the central nervous system. Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including the rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus. It is spread when an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm. Viral production / replication Viruses multiply only in living cells. The host cell must provide the energy and synthetic machinery and the low-molecular-weight precursors for the synthesis of viral proteins and nucleic acids. Virus replication occurs in seven stages: # Attachment # Entry (penetration) # Uncoating # Replication # Assembly # Maturation # Release (liberation stage). Attachment It is the first step of viral replication. Some viruses attach to the cell membrane of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baculoviridae
''Baculoviridae'' is a family of viruses. Arthropods, among the most studied being Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera, serve as natural hosts. Currently, 85 Virus classification, species are placed in this family, assigned to four genera. Baculoviruses are known to infect insects, with over 600 host species having been described. Immature (larval) forms of lepidopteran species (moths and butterflies) are the most common hosts, but these viruses have also been found infecting sawfly, sawflies, and mosquitoes. Although baculoviruses are capable of entering mammalian cells in culture, they are not known to be capable of replication in mammalian or other vertebrate animal cells. Starting in the 1940s, they were used and studied widely as biopesticides in crop fields. Baculoviruses contain a cccDNA, circular, double-stranded DNA, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) genome ranging from 80 to 180 Base pair#Length measurements, kbp. Historical influence The earliest records of baculoviruses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |