|
Battle Of Žalgiris
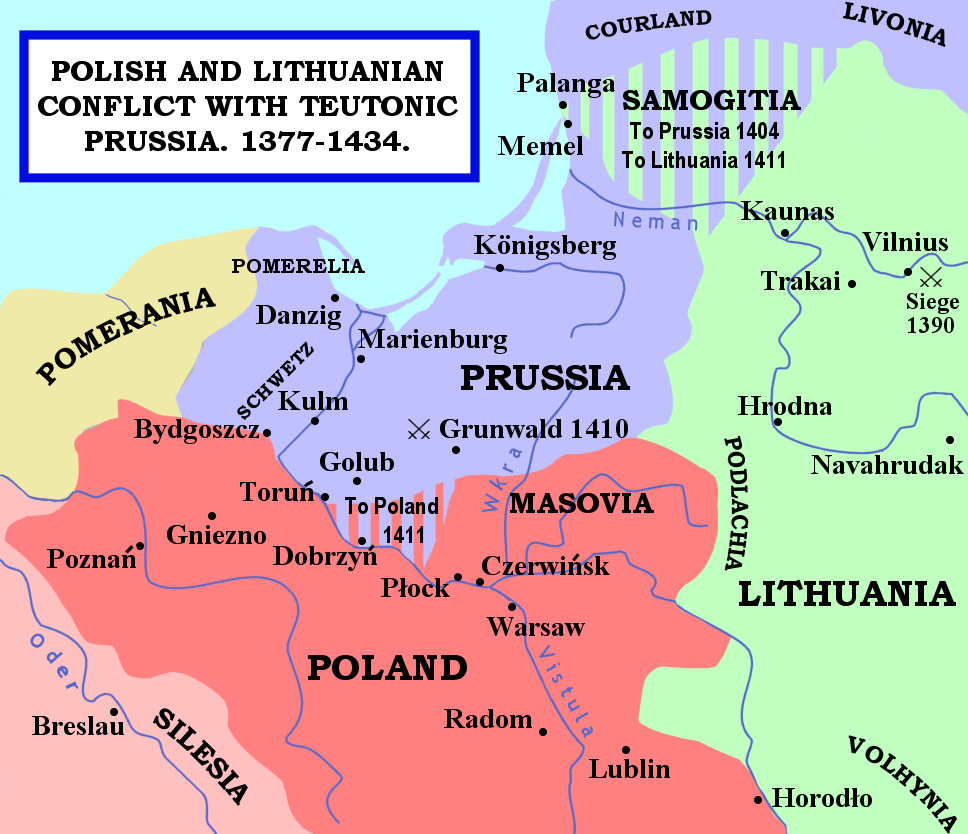
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), and Grand Duke Vytautas, decisively defeated the German Teutonic Order, led by Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen. Most of the Teutonic Order's leadership was killed or taken prisoner. Although defeated, the Teutonic Order withstood the subsequent siege of the Malbork Castle and suffered minimal territorial losses at the Peace of Thorn (1411), with other territorial disputes continuing until the Treaty of Melno in 1422. The order, however, never recovered their former power, and the financial burden of war reparations caused internal conflicts and an economic downturn in the lands controlled by them. The battle shifted the balance of power in Central and Eastern Europe and marked the rise of the Polish–Lithuanian union as the dominant r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War
The Polish–Lithuanian — Teutonic War, also known as the Great Teutonic War, occurred between 1409 and 1411 between the Teutonic Knights and the allied History of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Inspired by the local Samogitian uprising, the war began with a Teutonic invasion of Poland in August 1409. As neither side was ready for a full-scale war, Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia brokered a nine-month truce. After the truce expired in June 1410, the military-religious monks were decisively defeated in the Battle of Grunwald, one of the largest battles in medieval Europe. Most of the Teutonic leadership was killed or taken prisoner. Although they were defeated, the Teutonic Knights Siege of Marienburg (1410), withstood the siege on their capital in Marienburg (Malbork) and suffered only minimal territorial losses in the Peace of Thorn (1411). Territorial disputes lasted until the Peace of Melno of 1422. However, the Knights never recovered their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lands Of The Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of Bohemia, an Prince-elector, electorate of the Holy Roman Empire according to the Golden Bull of 1356, the Margraviate of Moravia, the duchies of Silesia, and the two Lusatias, known as the Margraviate of Upper Lusatia and the Margraviate of Lower Lusatia, as well as other territories throughout its history. This agglomeration of states nominally under the rule of the Bohemian kings was referred to simply as Bohemia. They are now sometimes referred to in scholarship as the Czech lands, a direct translation of the Czech abbreviated name. The joint rule of ''Corona regni Bohemiae'' was legally established by decree of King Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV issued on 7 April 1348, on the foundation of the original Cze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło (),Other names include (; ) (see also Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło) was Grand Duke of Lithuania beginning in 1377 and starting in 1386, becoming King of Poland as well. As Grand Duke, he ruled Lithuania from 1377 to 1381 and from 1382 to 1401, at which time he became the Supreme Duke of Lithuania in exchange for naming his cousin Vytautas as the new Grand Duke. Władysław II initially served as King of Poland alongside his wife Jadwiga of Poland, Jadwiga until her death in 1399, and then the sole ruler until his own death in 1434. Raised a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and baptized as Ladislaus () in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he Christianization of Lithuania, converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context. The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean world, the Latin West of the Roman Empire, and "Western Christendom". Beginning with the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery, roughly from the 15th century, the concept of ''Europe'' as "the Western world, West" slowly became distinguished from and eventually replaced the dominant use of "Christendom" as the preferred endonym within the area. By the Age of Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution, the concepts of "Eastern Europe" and "Western Europe" were more regularly used. The distinctiveness of Western Europe became most apparent during the Cold War, when Europe was divided for 40 years by the Iron Curtain into the Western Bloc and Eastern Bloc, each characterised by distinct political and economical systems. Historical divisions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protection by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. International and national laws of war Protocol I, Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) is a 1977 amendment Protocol (diplomacy), protocol to the Geneva Conventions. Article 47 of the protocol provides the most widely accepted internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Sambia
The Diocese of Samland (Sambia) (, ) was a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in Samland (Sambia) in medieval Prussia. It was founded in 1243 by papal legate William of Modena. Its seat was Königsberg, until 1523 the episcopal residence was in Fischhausen. The bishopric became Lutheran in the 16th century during the Protestant Reformation and was eventually dissolved following the establishment of Ducal Prussia, a Protestant vassal duchy of the Kingdom of Poland. The territory of the defunct bishopric of Samland came nominally under the jurisdiction of the Roman Catholic bishopric of Warmia in the 17th century, and the title of bishop of Samland was occasionally used by Warmian bishops. From 1617 to 1773, the Bishops of Warmia were the Catholic Apostolic administrators of Sambia. In 1821 Pope Pius VII formally dissolved the Diocese, and merged its territory with the Diocese of Warmia. Most of the area of the medieval bishopric of Sambia became a part of the Russian Kal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Pomesania
The Bishopric of Pomesania (; ) was a Catholic diocese in the Prussian regions of Pomesania and Pogesania, in modern northern Poland until the 16th century, then shortly a Lutheran diocese, and became a Latin titular see. The former Cathedral and Castle of Pomesanian Cathedral Chapter complex in Kwidzyn is listed as a Historic Monument of Poland. Catholic diocese It was founded as one of four Roman Catholic dioceses in Prussia in 1243 by the papal legate William of Modena. The bishops, whose seat was Riesenburg ( Prabuty), ruled one third of diocesan territory as his temporality. The diocesan cathedral chapter met in the fortified cathedral of Marienwerder (Kwidzyn). In the 1280s the Teutonic Order succeeded to impose the simultaneous membership of all capitular canons in the Order thus winning influence in the diocese and in the capitular elections of the bishops. So the temporality of Pomesania's bishop did not develop the status of a prince-bishopric and was ruled as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Warmia
The Prince-Bishopric of Warmia (; ) was a semi-independent ecclesiastical state, ruled by the incumbent ordinary of the Warmia see and comprising one third of the then diocesan area. The Warmia see was a Prussian diocese under the jurisdiction of the Archbishopric of Riga that was a protectorate of the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights (1243–1464) and a protectorate and part of the Kingdom of Poland—later part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1464–1772), confirmed by the Peace of Thorn in 1466. The other two thirds of the diocese were under the secular rule of the Teutonic Knights until 1525 and Ducal Prussia thereafter, both entities also being a protectorate and part of Poland from 1466. It was founded as the Bishopric of Ermland by William of Modena in 1243 in the territory of Prussia after it was conquered by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. The diocesan cathedral chapter constituted in 1260. While in the 1280s the Teutonic Order su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Oels
The Duchy of Oleśnica (, ) or Duchy of Oels () was one of the duchies of Silesia with its capital in Oleśnica in Lower Silesia, Poland. Initially ruled by the Silesian Piasts, it was acquired by the Münsterberg (Ziębice) dukes of the Podiebrad family from 1495 and was inherited by the House of Württemberg in 1649. Conquered by Prussia in 1742, it was enfeoffed to the Welf dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg from 1792 until its dissolution in 1884. History Initially part of the Piast Duchy of Silesia, the Oleśnica area became part of the Duchy of Głogów in 1294, following an armed conflict between Duke Henry III of Głogów and his cousin Henry V the Fat, Duke of Wrocław. After the death of Duke Henry III in 1309, it gained significant autonomy during the division of the Głogów lands and the creation of the Duchy of Oleśnica for Henry's son Bolesław in 1313, succeeded by his brother Konrad I in 1321. Dukes Bolesław and Konrad I still claimed to be heirs of the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerania-Stettin
The Duchy of Pomerania-Stettin, also known as the Duchy of Stettin, and the Duchy of Szczecin, was a feudal duchy in Farther Pomerania within the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was Stettin (Szczecin). It was ruled by the Griffin dynasty.B. Dopierała, ''Polskie losy Pomorza Zachodniego'', p. 40, 58-59. It existed in the eras of the High and Late Middle Ages, and the early modern period, between 1160 and 1264, between 1295 and 1523, and between 1532 and 1625. The state was formed in 1160, in the partition of the Duchy of Pomerania, with duke Bogusław I, as its first ruler. In 1264, Barnim I, Duke of Stettin, had unified duchies of Pomerania-Stettin and Pomerania-Demmin, re-establishing the Duchy of Pomerania.Jan Maria Piskorski, ''Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten'', p. 61. The state was again formed in 1295, in the partition of the Duchy of Pomerania, with Otto I as its ruler.E. Rymar, ''Rodowód książąt pomorskich'', p. 170.K. Kozłowski, J. Podralski, ''Gryfici. Książęta Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding territories from Muslim rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which culminated in the Siege of Jerusalem (1099), capture of Jerusalem in 1099, these expeditions spanned centuries and became a central aspect of European political, religious, and military history. In 1095, after a Byzantine request for aid,Helen J. Nicholson, ''The Crusades'', (Greenwood Publishing, 2004), 6. Pope Urban II proclaimed the first expedition at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos, AlexiosI Komnenos and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in Western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. Participants came from all over Europe and had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusades, crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant order of chivalry, chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |