|
Battle Of Cabeza De Las Marías
The Battle of Cabeza de Las Marías and Las Hicoteas (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Batalla de Cabeza de Las Marías y Las Hicoteas'') were the first military engagements of the Dominican War of Independence and were fought between the 13 and 18 March 1844, at Cabeza de Las Marías, near Neyba, Baoruco Province and Las Hicoteas, near Azua de Compostela, Azua Province. A force of roughly 500 Dominican troops, a portion of the Army of the South, led by General Manuel de Regla Mota, encountered an outnumbering force of roughly 10,000 troops of the Haitian Army led by General Souffrand and was routed, fleeing to Azua de Compostela. References Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Battle of Cabeza de Las Marias Dominican War of Independence Conflicts in 1844 Battles involving Haiti, Cabeza de Las Marías Battles of the Dominican War of Independence, Cabeza de Las Marías 1844 in the Dominican Republic March 1844 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican War Of Independence
The Dominican War of Independence () was a war of independence that began when the Dominican Republic declared independence from the Republic of Haiti on February 27, 1844 and ended on January 24, 1856. Before the war, the island of Hispaniola had been united for 22 years when the newly independent nation, previously known as the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, was unified with the Republic of Haiti in 1822. The criollo class within the country overthrew the Spanish crown in 1821 before unifying with Haiti a year later. The First Dominican Republic was proclaimed at the Puerta de la Misericordia after the blunderbluss shot by the patrician Matías Ramón Mella in the early morning of February 27, 1844 and by the raising of the tricolor flag at the Puerta del Conde by the patrician Francisco del Rosario Sánchez, both inspired by the ideals of their leader, Juan Pablo Duarte, ending the 22 years of Haitian rule. In response, Charles Rivière-Hérard issued the first Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neyba
Neiba (also spelt ''Neyba'') is a city in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It is the capital city of the Baoruco province, and is located 180 kilometres west of the national capital, Santo Domingo, close to the shore of Lake Enriquillo, the largest lake in the West Indies. History Before the conquest and colonization of Hispaniola, the place was a nitainato belonging to the Chiefdom of Jaragua. Founded in 1546 as a town from a cattle herd on the west side, years later it was depopulated together with the Villa de San Juan, being refounded in 1735 when it was repopulated and its neighbors enjoyed their lands that were from the Azua district. On March 13, 1844, a confrontation between Haitian and Dominican troops took place in the municipality in the so-called Battle of the Baptism of Blood, held in the now municipality of Galván, Bahoruco Province. The municipality was also the scene of the restoration struggles, where the first war day began with the assault on the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
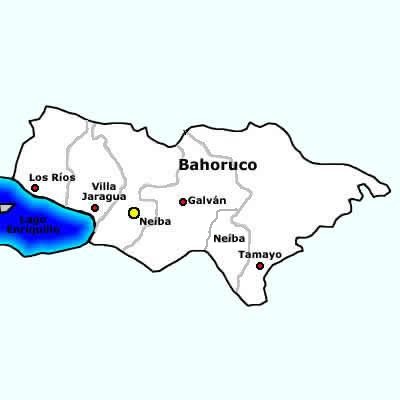
Baoruco Province
Baoruco, alternatively spelt Bahoruco (), is a Provinces of the Dominican Republic, province of the Dominican Republic located in the southwest of the country, part of the Enriquillo Region, along with the provinces of Barahona, Independencia and Pedernales. Before 1952 it included what is now Independencia Province. Important features are the Sierra de Neiba mountain range and Lake Enriquillo. Municipalities and municipal districts The province is divided into the following Municipalities of the Dominican Republic, municipalities (''municipios'') and municipal districts (''distrito municipal'' - D.M.) within them: *Galván, Dominican Republic, Galván *Los Ríos, Dominican Republic, Los Ríos **Las Clavellinas city (D.M.) *Neiba **El Palmar, Dominican Republic, El Palmar (D.M.) *Tamayo (Dominican Republic), Tamayo **Cabeza de Toro (D.M.) **Montserrat, Baoruco, Montserrat (D.M.) **Santana, Baoruco, Santana (D.M.) **Uvilla, Baoruco, Uvilla (D.M.) *Villa Jaragua The following is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azua De Compostela
Azua de Compostela, also known simply as Azua, is a city, municipality (''municipio'') and capital of Azua Province in the southern region of Dominican Republic. Founded in 1504, Azua is one of the oldest European settlements in the Americas. The town is located 100 kilometres west of the national capital, Santo Domingo. History The territory was part of the chiefdom of Maguana, one of the five Taino chiefdoms in the island. Christopher Columbus encountered great difficulties that forced him and his companions to take refuge in the Bay of Ocoa, in the eastern part of the Azua territory. There he met the resistance of the Great (Cacique) of Azua Cuyocagua, whom the Admiral tried to subdue without success. The town of Azúa de Compostela was officially founded in 1504 by Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar (conqueror of Cuba), during the government of Don Nicolás de Ovando. The famous conqueror of Mexico Hernán Cortés also resided in the town for several years (1504–1511). During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azua Province
Azua () is a province which is collectively one of the thirty-two provinces of the Dominican Republic. It is divided into 10 municipalities (the same as Santiago) and its capital city is Azua de Compostela. It is bordered by the provinces of La Vega to the north-east, San José de Ocoa and Peravia to the east, Barahona and Baoruco to the west and San Juan to the north-west. To the south, Azua has a significant coastline of the Caribbean Sea. Azua is known for its diverse geography and climate, with the southern part of the province having an arid climate that is not the typical tropical-like that is found in other parts of the Caribbean. Geography The southern part of the province is located in the Llanura or Llano de Azua (also known as the "Plena de Azua"), a coastal plain surrounded by mountains that act as barriers to the water-laden winds so that the lower parts of the province are very arid. Azua had the Sierra de Ocoa, which is the southern end of the Cordillera Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Dominican Republic (up To 1844)
The national flag of the Dominican Republic is one of the official national symbols of the nation, along with the coat of arms and the national anthem. The blue on the flag stands for liberty, the white for salvation, and the red for the blood of heroes. The civil flag follows the same design, but without the charge in the center. The flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte. Description As described by Article 21 of the Dominican Constitution, the flag features a centered white Saint George's cross that extends to the edges and divides the flag into four rectangles; the top ones are blue (hoist side) and red, and the bottom ones are red (hoist side) and blue. The national coat of arms, featuring a shield with the flag, design and supported by a bay laurel branch (left) and a palm frond (right), is at the center of the cross. Above the shield, a blue ribbon displays the national motto ''Dios, Patria, Libertad'' (English: God, Homeland, Liberty). Below the shield, the words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and a Dominican Republic–Haiti border, land border with Haiti to the west, occupying the Geography of the Dominican Republic, eastern five-eighths of Hispaniola which, along with Saint Martin (island), Saint Martin, is one of only two islands in the Caribbean shared by two sovereign states. In the Antilles, the country is the List of Caribbean islands by area, second-largest nation by area after Cuba at and List of Caribbean countries by population, second-largest by population after Haiti with approximately 11.4 million people in 2024, of whom 3.6 million reside in the Greater Santo Domingo, metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola prior to European colonization of the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean, and with an estimated population of 11.4 million, is the most populous Caribbean country. The capital and largest city is Port-au-Prince. Haiti was originally inhabited by the Taíno people. In 1492, Christopher Columbus established the first European settlement in the Americas, La Navidad, on its northeastern coast. The island was part of the Spanish Empire until 1697, when the western portion was Peace of Ryswick, ceded to France and became Saint-Domingue, dominated by sugarcane sugar plantations in the Caribbean, plantations worked by enslaved Africans. The 1791–1804 Haitian Revolution made Haiti the first sovereign state in the Caribbean, the second republic in the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel De Regla Mota
Manuel de Regla Mota y Álvarez (November 21, 1795May 1, 1864) was a Dominican Republic, Dominican military figure and politician. Mota served as the 5th president of the Dominican Republic from May 26, 1856, until October 8, 1856. Prior to that he served as the country's vice president under Pedro Santana. Birth Born on November 21, 1795, in Baní, Peravia, Dominican Republic. He is the son of Antonio Mota and María Álvarez. Political and military career When the country's independence was declared in 1844, De Regla had already managed to develop a successful military career and served as colonel of the National Militias. Once the First Dominican Republic was proclaimed, the separatist movement commissioned him to lead the first contingent of troops in the cities of Baní and San Cristóbal, Dominican Republic, San Cristóbal with the mission of defending the border line of the island. In his new role, he met Pedro Santana, named the country's first president, who became hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José María Cabral
General José María Cabral y Luna (born Ingenio Nuevo; December 12, 1816 – February 28, 1899) was a Dominican Republic, Dominican military figure and politician. He served as the first President of the Dominican Republic, Supreme Chief of the Dominican Republic from August 4, 1865, to November 15 of that year and again officially as president from August 22, 1866, until January 3, 1868. In his military career he stood out for his work commanding the troops that defeated Haiti in the Battle of Santomé (December 22, 1855), and even in the Cibaeño Revolution. After the annexation of Santo Domingo to Spain, decreed by General and President Pedro Santana in 1861, José María Cabral joined Francisco del Rosario Sánchez to fight against the annexation and restore the Republic. Once the country's independence was recovered in 1865, José María Cabral assumed the presidency of the second Dominican Republic. At the end of the same year, Buenaventura Báez took power, but was overt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1844
Conflict may refer to: Social sciences * Conflict (process), the general pattern of groups dealing with disparate ideas * Conflict continuum from cooperation (low intensity), to contest, to higher intensity (violence and war) * Conflict of interest, involvement in multiple interests which could possibly corrupt the motivation or decision-making * Cultural conflict, a type of conflict that occurs when different cultural values and beliefs clash * Ethnic conflict, a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups * Group conflict, conflict between groups * Intragroup conflict, conflict within groups * Organizational conflict, discord caused by opposition of needs, values, and interests between people working together * Role conflict, incompatible demands placed upon a person such that compliance with both would be difficult * Social conflict, the struggle for agency or power in something * Work–family conflict, incompatible demands between the work and family roles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |