|
Basque Grammar
This article provides a sketch of Basque grammar. Basque is the language of the Basque people of the Basque Country or Euskal Herria, which borders the Bay of Biscay in Western Europe. Noun phrases The Basque noun phrase is structured quite differently from those in most Indo-European languages. Articles, determiners and quantifiers Determiners and quantifiers play a central role in Basque noun phrase structure. Articles are best treated as a subset of the determiners. The articles ''-a, -ak, -ok, -(r)ik'', demonstratives ''hau, hori, hura'' and some of the quantifiers follow the noun they determine or quantify. Other determiners and quantifiers, including ''beste'' 'other', the interrogatives and numerals above one or two (depending on dialect) precede the noun. A normal noun phrase with a common noun as head must contain exactly one determiner or exactly one quantifier but not both, as in the above examples. However, the numerals may co-occur with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque Language
Basque ( ; ) is a language spoken by Basques and other residents of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Basque is classified as a language isolate (unrelated to any other known languages), the only one in Europe. The Basques are indigenous to and primarily inhabit the Basque Country. The Basque language is spoken by 806,000 Basques in all territories. Of them, 93.7% (756,000) are in the Spanish area of the Basque Country and the remaining 6.3% (50,000) are in the French portion. Native speakers live in a contiguous area that includes parts of four Spanish provinces and the French Basque Country, three "ancient provinces" in France. Gipuzkoa, most of Biscay, a few municipalities on the northern border of Álava and the northern area of Navarre formed the core of the remaining Basque-speaking area before measures were introduced in the 1980s to stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
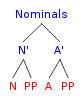
Nominal (linguistics)
In linguistics, the term ''nominal'' refers to a category used to group together nouns and adjectives based on shared properties. The motivation for nominal grouping is that in many languages nouns and adjectives share a number of Morphology (linguistics), morphological and Syntax, syntactic properties. The systems used in such languages to show agreement can be classified broadly as gender systems, noun class systems or Grammatical case, case marking, classifier systems, and mixed systems. Typically an affix related to the noun appears attached to the other Part of speech, parts of speech within a sentence to create agreement. Such morphological agreement usually occurs in parts within the noun phrase, such as determiners and adjectives. Languages with overt nominal agreement vary in how and to what extent agreement is required. History The history of research on ''nominals'' dates back to European studies on Latin and Bantu in which agreement between ''nouns'' and ''adjectives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Polarity Item
In grammar and linguistics, a polarity item is a lexical item that is associated with affirmation or negation. An affirmation is a positive polarity item, abbreviated PPI or AFF. A negation is a negative polarity item, abbreviated NPI or NEG. The linguistic environment in which a polarity item appears is a licensing context. In the simplest case, an affirmative statement provides a licensing context for a PPI, while negation provides a licensing context for an NPI. However, there are many complications, and not all polarity items of a particular type have the same licensing contexts. In English As examples of polarity items, consider the English lexical items ''somewhat'' and ''at all'', as used in the following sentences: # I liked the film somewhat. # I didn't like the film at all. # *I liked the film at all. # *I didn't like the film somewhat. As can be seen, ''somewhat'' is licensed by the affirmative environment of sentence (1), but it is forbidden (anti-licensed) by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemma (morphology)
In morphology and lexicography, a lemma (: lemmas or lemmata) is the canonical form, dictionary form, or citation form of a set of word forms. In English, for example, ''break'', ''breaks'', ''broke'', ''broken'' and ''breaking'' are forms of the same lexeme, with ''break'' as the lemma by which they are indexed. ''Lexeme'', in this context, refers to the set of all the inflected or alternating forms in the paradigm of a single word, and ''lemma'' refers to the particular form that is chosen by convention to represent the lexeme. Lemmas have special significance in highly inflected languages such as Arabic, Turkish, and Russian. The process of determining the ''lemma'' for a given lexeme is called lemmatisation. The lemma can be viewed as the chief of the principal parts, although lemmatisation is at least partly arbitrary. Morphology The form of a word that is chosen to serve as the lemma is usually the least marked form, but there are several exceptions such as the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Default (computer Science)
A default, in computer science, refers to the preexisting value of a user-configurable setting that is assigned to a software application, computer program or device. Such settings are also called factory settings, or factory presets, especially for electronic devices. Default values are standards values that are universal to all instances of the device or model and intended to make the device as accessible as possible "out of the box" without necessitating a lengthy configuration process prior to use. The user only has to modify the default settings according to their personal preferences. In many devices, the user has the option to restore these default settings for one or all options. Such an assignment makes the choice of that setting or value more likely, this is called the default effect. Examples Application software preferences One use of default parameters is for initial settings for application software. For example, the first time a user runs an application it may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head (linguistics)
In linguistics, the head or nucleus of a phrase is the word that determines the syntax, syntactic category of that phrase. For example, the head of the noun phrase "boiling hot water" is the noun (head noun) "water". Analogously, the head of a compound (linguistics), compound is the word stem, stem that determines the semantic category of that compound. For example, the head of the compound noun "handbag" is "bag", since a handbag is a bag, not a hand. The other elements of the phrase or compound Grammatical modifier, modify the head, and are therefore the head's ''dependent (grammar), dependents''. Headed phrases and compounds are called ''endocentric'', whereas ''exocentric'' ("headless") phrases and compounds (if they exist) lack a clear head. Heads are crucial to establishing the direction of branching (linguistics), branching. Head-initial phrases are right-branching, head-final phrases are left-branching, and head-medial phrases combine left- and right-branching. Basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an object or subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined according to how its members combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or isolated areas. The non-standard dialects of a language with a writing system will operate at different degrees of distance from the standardized written form. Standard and nonstandard dialects A ''standard dialect'', also known as a "standardized language", is supported by institutions. Such institutional support may include any or all of the following: government recognition or designation; formal presentation in schooling as the "correct" form of a language; informal monitoring of everyday Usage (language), usage; published grammars, dictionaries, and textbooks that set forth a normative spoken and written form; and an extensive formal literature (be it prose, poetry, non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral (linguistics)
In linguistics, a numeral in the broadest sense is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity. Some theories of grammar use the word "numeral" to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner that specify the quantity of a noun, for example the "two" in "two hats". Some theories of grammar do not include determiners as a part of speech and consider "two" in this example to be an adjective. Some theories consider "numeral" to be a synonym for "number" and assign all numbers (including ordinal numbers like "first") to a part of speech called "numerals". Numerals in the broad sense can also be analyzed as a noun ("three is a small number"), as a pronoun ("the two went to town"), or for a small number of words as an adverb ("I rode the slide twice"). Numerals can express relationships like quantity (cardinal numbers), sequence (ordinal numbers), frequency (once, twice), and part (fraction). Identifying numerals Numerals may be attributive, as in ''two dogs'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogatives
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', '' who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of them start with '' wh-'' (compare Five Ws). Most may be used in both direct (''Where is he going?'') and in indirect questions (''I wonder where he is going''). In English and various other languages the same forms are also used as relative pronouns in certain relative clauses (''The country where he was born'') and certain adverb clauses (''I go where he goes''). It can also be used as a modal, since question words are more likely to appear in modal sentences, like (''Why was he walking?'') A particular type of interrogative word is the interrogative particle, which serves to convert a statement into a yes–no question, without having any other meaning. Examples include ''est-ce que'' in French, ли ''li'' in Russian, ''czy'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantifier (linguistics)
In formal semantics, a generalized quantifier (GQ) is an expression that denotes a set of sets. This is the standard semantics assigned to quantified noun phrases. For example, the generalized quantifier ''every boy'' denotes the set of sets of which every boy is a member: \ This treatment of quantifiers has been essential in achieving a compositional semantics for sentences containing quantifiers. Type theory A version of type theory is often used to make the semantics of different kinds of expressions explicit. The standard construction defines the set of types recursively as follows: #''e'' and ''t'' are types. #If ''a'' and ''b'' are both types, then so is \langle a,b\rangle #Nothing is a type, except what can be constructed on the basis of lines 1 and 2 above. Given this definition, we have the simple types ''e'' and ''t'', but also a countable infinity of complex types, some of which include: \langle e,t\rangle;\qquad \langle t,t\rangle;\qquad \langle\langle e,t\rangl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |