|
Basilica Of St Stephen, Jerusalem
The St. Stephen's Basilica () or simply the Church of St. Stephen, also known by its French name, Saint-Étienne, is the name given to a Catholic church located outside the walls of the Old City of Jerusalem, on the road leading north to Nablus. It is next to the convent of St. Stephen, home to the French Bible and Archaeology School (École biblique et archéologique française de Jérusalem), and the convent church. An Saint Stephen#Location of the martyrdom, old tradition sees this place as the place where the martyrdom of Saint Stephen took place, the martyr deacon mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles, book of Acts (). A rival site connected to a later, post-Byzantine tradition is located in the Kidron Valley. History The first time a sanctuary was built to commemorate the martyrdom was in the fifth century, when Aelia Eudocia, Empress Eudocia initiated the building of a structure on the site of the current basilica, a chapel dedicated to St. Stephen, where she was eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
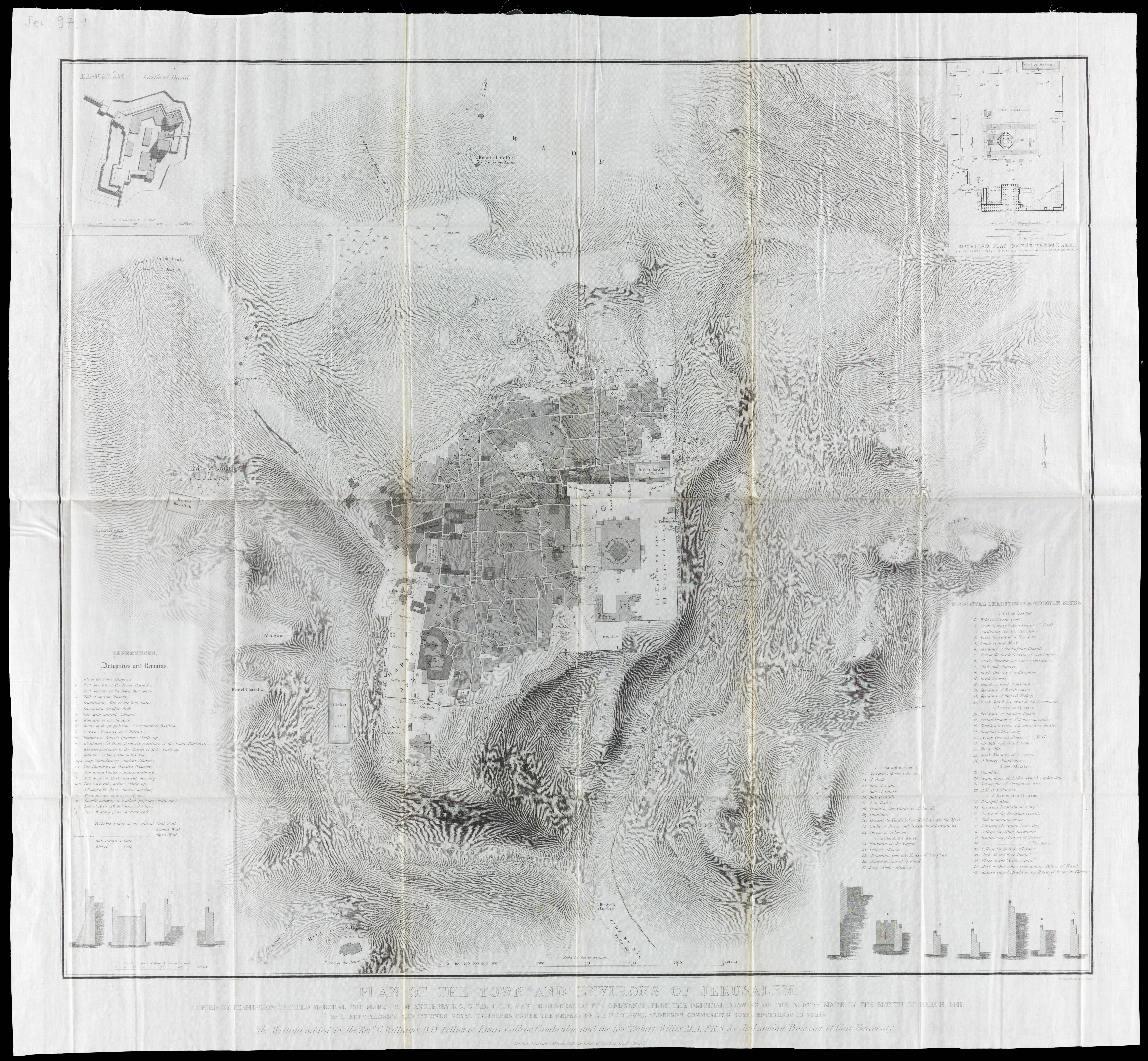
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and is considered Holy city, holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city; Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there, while Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Neither claim is widely Status of Jerusalem, recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Siege of Jerusalem (other), besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David (historic), City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt and it was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word ''pasha'' comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford English Dictionary attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (sir), which were established in usage much earlier, the title ''pasha'' came into Ottoman Empire, Ottoman usage right after the reign of Osman I (d. 1324), though it had been used before the Ottomans by some Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian Turkish rulers of the same era. Old Turkish had no fixed distinction betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Churches In Jerusalem
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the ''basilica'' architectural form. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Churches Completed In 1900
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible * Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People * Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Jerusalem
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Churches In Jerusalem
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD * Roman people, the people of Roman civilization * Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible * Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People * Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters * Roman (sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manar Al-Athar
Manar al-Athar is a photo archive based at the Faculty of Classics at the University of Oxford which aims to provide high-quality open-access images of archaeological sites and buildings. The archive's collection focuses on areas of the Roman Empire which later came under Islamic rule, namely the Levant, North Africa, Turkey, Georgia and Armenia. As of June 2022, the archive holds more than 83,000 unique images. Particular strengths include Late antiquity, as well as the transition from paganism to Christianity and later to Islam. The archive licenses its images under a Creative Commons CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license; the images can be used for any non-commercial purpose, including in academic publications, and are jointly labelled in English and Arabic to encourage usage by academics and students around the world. History Manar al-Athar was founded in 2012 by Judith McKenzie, archaeologist and Associate Professor of Late Antique Egypt and the Holy Land at the University of Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Biblique, Jerusalem (5251802201)
École or Ecole may refer to: * an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée) * École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France * École, Savoie, a French commune * École-Valentin, a French commune in the Doubs département * Grandes écoles, higher education establishments in France * The École The École, formerly Ecole Internationale de New York, is an intimate and independent French-American school, which cultivates an internationally minded community of students from 2 to 14 years old in New York City’s vibrant Flatiron Distric ..., a French-American bilingual school in New York City * Ecole Software, a Japanese video-games developer/publisher {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In Palestine
The Catholic Church in Palestine is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. There are over 80,000 Catholics in the State of Palestine (including Jerusalem) mostly in the agglomeration between Ramallah and Bethlehem, including the West Bank suburbs of Jerusalem. Adherents are mostly of the Latin Church, but there are also small communities of the Melkite Catholic Patriarchate of Antioch and Jerusalem, belonging to the Melkite Catholic Church, as well as the Maronite Church. All three are in full communion with the Holy See as part of the worldwide Catholic Church. There are two archbishops of Jerusalem, one for each jurisdiction. The jurisdiction of the Latin Patriarchate of Jerusalem in Jerusalem and the Palestinian territories includes 17 parishes, two of which are in Jerusalem. The current Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem is Pierbattista Pizzaballa. See also * Catholic Church in Israel * Catholic Church in the Middle East * Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombs Of The Kings (Jerusalem)
The Tombs of the Kings ( ''Keveri HaMlakhim''; ; ) are a Catacombs, rock-cut funerary complex in East Jerusalem believed to be the burial site of Queen Helene of Adiabene (died c. 50–56 CE), hence: Helena's Monuments. The tombs are located north of Jerusalem's Old City (Jerusalem), Old City walls in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood (Hebrew: ; Arabic: ) The grandeur of the site led to the belief that the tombs had once been the burial place of the kings of Judah, hence the name Tombs of the Kings; but the tombs are now associated with Helena of Adiabene, Queen Helena of Adiabene."Ancient Jerusalem's Funerary Customs and Tombs: Part Three, L. Y. Rahmani, The Biblical Archaeologist, Vol. 45, No. 1 (Winter, 1982), pp. 43–53 According to this theory, Queen Helena chose the site to bury her son Isates and others of her dynasty. More recent research by noted French scholar and Dominican friar Jean-Baptiste Humbert has concluded that the tomb was likely designed for Herod Agrippa I, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed Hasmonean royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Roman Empire during the First Jewish–Roman War as general of the Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in AD 67 to the Roman army led by military commander Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Roman emperor. In response, Vespasian decided to keep him as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became emperor in AD 69, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the Emperor's family name of '' Flavius''. Flavius Josephus fully defected to the Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena Of Adiabene
Helena of Adiabene ( ''Hellēnī''; died c. 50–56 CE) was a queen mother of Adiabene, a vassal state of the Parthian Empire. With her husband-brother Monobaz I, she was the mother of Izates II and Monobaz II. Helena became a convert to Judaism about the year 30 CE. According to Josephus, Helena was the daughter of King Izates. Moses of Chorene makes her the chief wife of Abgar V, king of Edessa. Sources of information What is known of Helena is based on the writings of Josephus, Movses Khorenatsi, Kirakos Gandzaketsi, and the Talmud. Josephus, although younger, was almost contemporary with Helena, living in Jerusalem at the time when she lived and was buried there, and he wrote substantial parts of his work from first-hand knowledge. The earliest parts of the Talmud, while based on older sources, were compiled and redacted from around 200 onward. Biography Helena of Adiabene was noted for her generosity; during a famine at Jerusalem in 45–46 CE, she sent to Alexandri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |