|
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the electronic output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is analogous to the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting, the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency. A baseband signal may have frequency components going all the way down to the DC bias, or at least it will have a high ratio bandwidth. A modulated baseband signal is called a passband signal. This occupies a higher range of frequencies and has a lower ratio and fractional bandwidth. Various uses Baseband signal A ''baseband signal'' or ''lowpass signal'' is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseband Processor
A baseband processor (also known as baseband radio processor, BP, or BBP) is a device (a chip or part of a chip) in a network interface controller that manages all the radio functions (all functions that require an antenna); however, this term is generally not used in reference to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth radios. A baseband processor typically uses its own RAM and firmware. Baseband processors are typically fabricated using CMOS (complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) or RF CMOS technology, and are widely used in radio-frequency (RF) and wireless communications. Overview Baseband processors typically run a real-time operating system (RTOS) as their firmware, such as ENEA's OSE, Nucleus RTOS (iPhone 3G/3GS/iPad), ThreadX (iPhone 4), and VRTX. There are more than a few significant manufacturers of baseband processors, including Broadcom, Icera, Intel Mobile Communications (former Infineon wireless division), MediaTek, Qualcomm, Spreadtrum, and ST-Ericsson. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For example, a 3 kHz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pass Filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter. In optics, high-pass and low-pass may have different meanings, depending on whether referring to the frequency or wavelength of light, since these variables are inversely related. High-pass frequency filters would act as low-pass wavelength filters, and vice versa. For this reason, it is a good practice to refer to wavelength filters as ''short-pass'' and ''long-pass'' to avoid confusion, which would correspond to ''high-pass'' and ''low-pass'' frequencies. Low-pass filters exist in many different forms, including electronic circuits such as a '' hiss filter'' used in audio, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandlimited2
Bandlimiting is the process of reducing a signal’s energy outside a specific frequency range, keeping only the desired part of the signal’s spectrum. This technique is crucial in signal processing and communications to ensure signals stay clear and effective. For example, it helps prevent interference between radio frequency signals, like those used in radio or TV broadcasts, and reduces aliasing distortion (a type of error) when converting signals to digital form for digital signal processing. Bandlimited signals A bandlimited signal is a signal that, in strict terms, has no energy outside a specific frequency range. In practical use, a signal is called bandlimited if the energy beyond this range is so small that it can be ignored for a particular purpose, like audio recording or radio transmission. These signals can be either random (unpredictable, also called stochastic) or non-random (predictable, known as deterministic). In mathematical terms, a bandlimited signal rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Coding
In telecommunications, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often using differential signaling). * the line-coded signal (the '' baseband signal'') u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, campus, or building, and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed. LANs facilitate the distribution of data and sharing network devices, such as printers. The LAN contrasts the wide area network (WAN), which not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves Leased line, leased telecommunication circuits or Internet links. An even greater contrast is the Internet, which is a system of globally connected business and personal computers. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies used for local area networks; historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring, and LocalTalk. Cabling Most wired network infrastructures utilize Category 5 cable, Category 5 or Category 6 cable, Category 6 twisted pair cabling with RJ45 (telecommunications), RJ45 compatible terminations. This medium provides physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
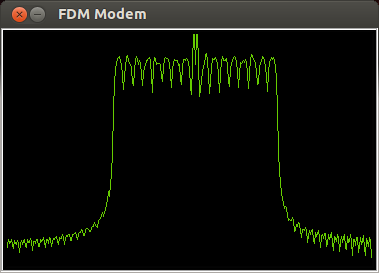
Frequency Division Multiplexing
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel. The most common example of frequency-division multiplexing is radio and television broadcasting, in which multiple radio signals at different frequencies pass through the air at the same time. Another example is cable television, in which many television channels are carried simultaneously on a single cable. FDM is also used by telephone systems to transmit multiple telephone calls through high capacity trunklines, communications satellites to transmit multiple channels of data on uplink and down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10BASE5
10BASE5 (also known as thick Ethernet or thicknet) was the first commercially available variant of Ethernet. The technology was standardized in 1982 as IEEE 802.3. 10BASE5 uses a thick and stiff coaxial cable up to in length. Up to 100 stations can be connected to the cable using vampire taps and share a single collision domain with 10 Mbit/s of bandwidth shared among them. The system is difficult to install and maintain. 10BASE5 was superseded by much cheaper and more convenient alternatives: first by 10BASE2 based on a thinner coaxial cable (1985), and then, once Ethernet over twisted pair was developed, by 10BASE-T (1990) and its successors 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T. In 2003, the IEEE 802.3 working group deprecated 10BASE5 for new installations. Name origination The name ''10BASE5'' is derived from several characteristics of the physical medium. The ''10'' refers to its transmission speed of 10 Mbit/s. The ''BASE'' is short for baseband signaling (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Physical Layer
The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer. An implementation of a specific physical layer is commonly referred to as PHY. The Ethernet physical layer has evolved over its existence starting in 1980 and encompasses multiple physical media interfaces and several orders of magnitude of speed from to . The physical medium ranges from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber with a standardized reach of up to 80 km. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers. Many Ethernet adapters and switch ports support multiple speeds by using autonegotiation Autonegotiation is a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100BASE-TX
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of . The prior Ethernet speed was . Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The ''100'' in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of , while the ''BASE'' refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash (''T'' or ''F'') refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character (''X'', ''4'', etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where ''X'' is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet is an extension of the 10-megab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |