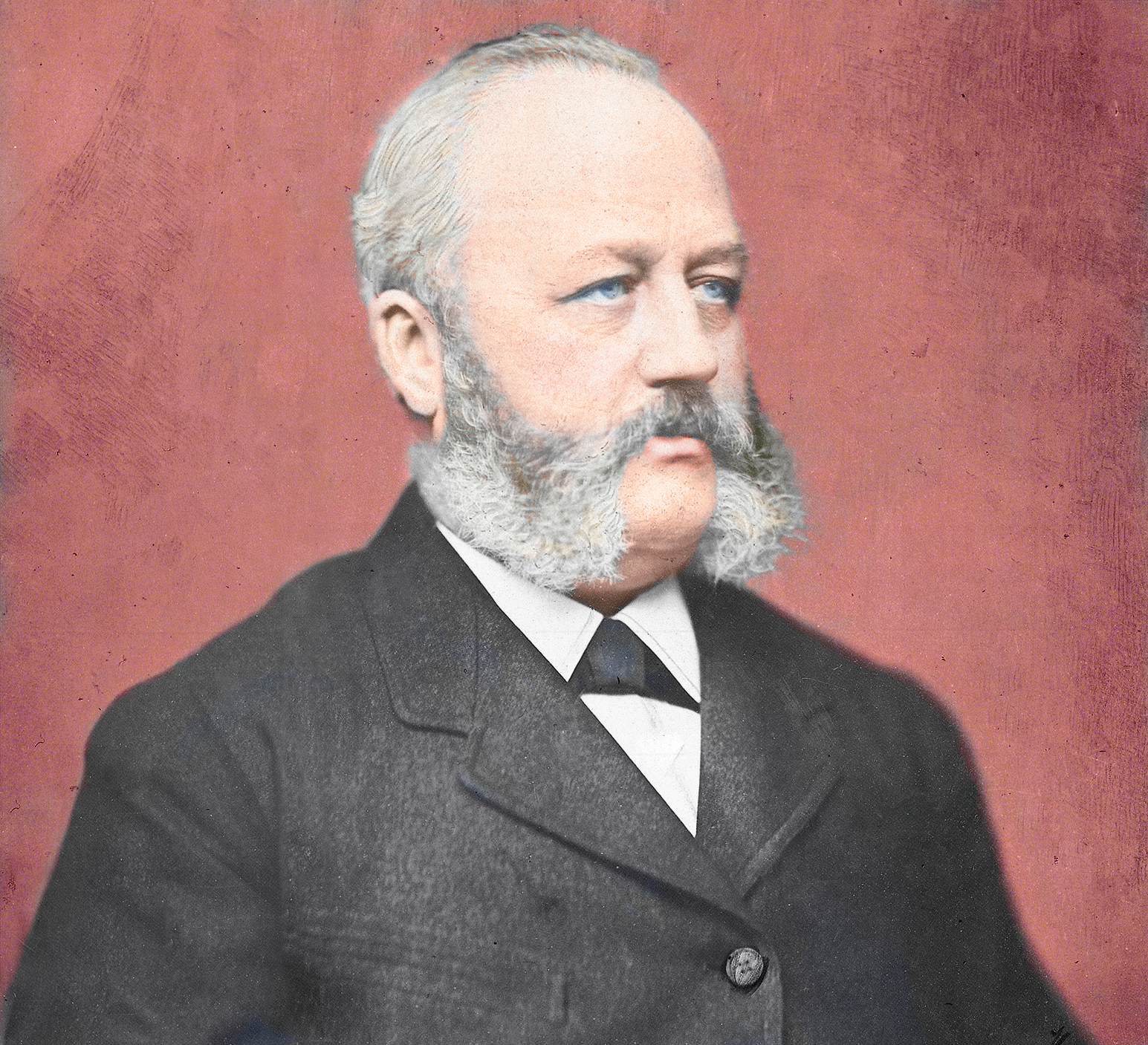|
Barmen
Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal. Barmen, together with the neighbouring town of Elberfeld founded the first electric suspended monorail tramway system, the Wuppertal Schwebebahn, Schwebebahn ''floating tram''. History Barmen was a pioneering centre for both the early Industrial Revolution on the European mainland, and for the socialist movement and its theory. It was the location of one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany, KZ Wuppertal-Barmen, later better known as Kemna concentration camp. Oberbarmen (Upper Barmen) is the eastern part of Barmen, and Unterbarmen (Lower Barmen) the western part. One of its claims to fame is the fact that Friedrich Engels, co-author of ''The Communist Manifesto'', was born in Barmen. Another of its claims is the fact that Bayer AG was founded there by Friedrich Bayer and master dyer Johann Friedrich Weskott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany, with a population of 355,000. Wuppertal is the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and List of cities in Germany by population, 17th-largest in Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of Elberfeld, Barmen, Ronsdorf, Cronenberg, Wuppertal, Cronenberg and Vohwinkel Schwebebahn, Vohwinkel, and was initially called "Barmen-Elberfeld" before adopting its present name in 1930. It is the capital and largest city of the Bergisches Land. The city straddles the densely populated banks of the River Wupper, a tributary of the Rhine. Wuppertal is located between the Ruhr (Essen) to the north, Düsseldorf to the west, and Cologne to the southwest, and over time has grown together with Solingen, Remscheid and Hagen. The stretching of the city in a long band along the narrow Wupper Valley leads to a spatial impression of Wuppertal being larger than it actually is. The city is known for its steep slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barmen (1870)
Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal. Barmen, together with the neighbouring town of Elberfeld founded the first electric suspended monorail tramway system, the Wuppertal Schwebebahn, Schwebebahn ''floating tram''. History Barmen was a pioneering centre for both the early Industrial Revolution on the European mainland, and for the socialist movement and its theory. It was the location of one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany, KZ Wuppertal-Barmen, later better known as Kemna concentration camp. Oberbarmen (Upper Barmen) is the eastern part of Barmen, and Unterbarmen (Lower Barmen) the western part. One of its claims to fame is the fact that Friedrich Engels, co-author of ''The Communist Manifesto'', was born in Barmen. Another of its claims is the fact that Bayer AG was founded there by Friedrich Bayer and master dyer Johann Friedrich Weskott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barmen Declaration
__NOTOC__ The Barmen Declaration or the Theological Declaration of Barmen 1934 (German: ''Die Barmer Theologische Erklärung'') was a document adopted by Christians in Nazi Germany who opposed the German Christian movement. In the view of the delegates to the Synod that met in the city of Wuppertal-Barmen in May 1934, the German Christians had corrupted church government by making it subservient to the state and had introduced Nazi ideology into the German Protestant churches that contradicted the Christian gospel. The Barmen Declaration includes six theses: # The only source of revelation is the Word of God — Jesus Christ. Any other possible sources (earthly powers, for example) will not be accepted. # Jesus Christ is the only Lord of all aspects of personal life. There should be no other authority. # The message and order of the church should not be influenced by the current political convictions. # Leadership in the church is not dominion, it is in service of its ministr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ;"Engels" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 28 November 1820 – 5 August 1895) was a German philosopher, political theorist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He was also a businessman and Karl Marx's lifelong friend and closest collaborator, serving as the co-founder of Marxism. Born in Barmen in the Kingdom of Prussia, Engels was the son of a wealthy textile manufacturer. Despite his Bourgeoisie, bourgeois background, he became a staunch critic of capitalism, influenced by his observations of industrial working conditions in Manchester, England, as published in his early work ''The Condition of the Working Class in England'' (1845). He met Marx in 1844, after which they jointly authored works including ''The Holy Family (book), The Holy Family'' (1844), ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Confessing Church
The Confessing Church (, ) was a movement within German Protestantism in Nazi Germany that arose in opposition to government-sponsored efforts to unify all of the Protestant churches into a single pro-Nazi German Evangelical Church. See drop-down essay on "Unification, World Wars, and Nazism" Demographics The following statistics (as of January 1933 unless otherwise stated) are an aid in understanding the context of the political and theological developments discussed in this article. *Number of Protestants in Germany: 45 million *Number of free church Protestants: 150,000 *Largest regional Protestant church: Evangelical Church of the Old Prussian Union (), with 18 million members, the church strongest in members in the country at the time. *Number of Protestant pastors: 18,000 **Number of Protestant pastors who strongly adhered to the beliefs of the " German Christian" church faction as of 1935: 3000 **Number of Protestant pastors who strongly adhered to the beliefs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Julius Kemna
Julius Kemna (December 8, 1837 – June 8, 1898) was a German machine manufacturer and industrialist. He was the founder of Kemna Bau. Biography Early life Julius Kemna was born the only son of Johann Abraham Kemna and Carolina Wilhelmina (Wilhelmine) van Hees on December 8, 1837 in Barmen Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal. Barmen, together with the neighbouring town of Elberfeld founded the first electric .... The family of Johann Abraham Kemna, a wine wholesaler from Barmen and Royal Prussian purveyor to the court (1810–1878), can be traced back to the 15th century, where they lived in the Kemna manor. Kemna's mother, Carolina Wilhelmina van Hees (1814-1880), was the niece of the well known Barmer school founder Susanna Sophia Antoinetta van Hees and granddaughter of the first pharmacist in Barmen Johann Hermann von Hees. Kemna associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
KZ Wuppertal-Barmen
Kemna concentration camp () was one of the early Nazi concentration camps, created by the Third Reich to incarcerate their political opponents (ostensibly in protective custody) after the Nazi Party first seized power in 1933. The camp was established in a former factory on the Wupper river in the Kemna neighborhood of the Barmen quarter of Wuppertal. It was run by the SA group in Düsseldorf. The purpose of the early concentration camps was to repress and terrorize opponents of the new regime, primarily communists, but also socialists, dissenting Christians, and trade unionists. Unlike later concentration camps, the prisoners and the guards at Kemna were from the same cities and in many cases, knew each other and were already enemies from the German Revolution of 1918–1919 and subsequent political battles of the 1920s. Torture was practiced and the screams of the men were audible to people living and working nearby, and severely injured men were taken to nearby hospitals, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elberfeld
Elberfeld is a municipal subdivision of the Germany, German city of Wuppertal; it was an independent town until 1929. History The first official mentioning of the geographic area on the banks of today's Wupper River as "''elverfelde''" was in a document of 1161. Etymologically, ''elver'' is derived from the old Low German word for "river." (See etymology of the name of the German Elbe#Etymology, Elbe River; cf. North Germanic languages, North Germanic ''älv''.) Therefore, the original meaning of "elverfelde" can be understood as "field on the river." Elverfelde received its town charter in 1610. In 1726, Elias Eller and a pastor, Daniel Schleyermacher, founded a Philadelphian Society. They later moved to Ronsdorf in the Duchy of Berg, becoming the Zionites (Germany), Zionites, a fringe sect. In 1826 Friedrich Harkort, a famous German industrialist and politician, had a type of suspension railway built as a trial and ran it on the grounds of what is today the tax office at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wuppertal Schwebebahn
The Wuppertaler Schwebebahn () is a suspension railway in Wuppertal, Germany. The line was originally called in () named after its inventor, Eugen Langen. It is the oldest electric elevated railway with hanging cars in the world. Being grade-separated, it is considered rapid transit. Langen first offered the technology to the cities of Berlin, Munich, and Wrocław, Breslau which all turned it down. However, the towns of Barmen, Elberfeld, and Wuppertal-Vohwinkel station, Vohwinkel along the banks of the river Wupper were intrigued by the technology’s ability to connect their communities. The elevated tracks and stations were built between 1897 and 1903; the first track opened in 1901. The railway line is credited with growth of the original cities and their eventual merger into Wuppertal. The ' is still in use as a local public transport line, moving 25 million passengers annually, per the 2008 annual report. New rail cars were ordered in 2015, called Generation 15, and the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Julius Richard Petri
Julius Richard Petri (; 31 May 185220 December 1921) was a German microbiologist who is generally credited with inventing the device known as the Petri dish, which is named after him, while working as assistant to bacteriologist Robert Koch. Life and career Petri was born in the town of Barmen (now a district of the city of Wuppertal), Germany, on 31 May 1852. He came from a distinguished family of scholars, and was the eldest son of Philipp Ulrich Martin Petri (18171864), a professor in Berlin, and Louise Petri. Petri's grandfather, Viktor Friedrich Leberecht Petri (1782–1857), was also a scholar, being both a director and professor at the Collegium Carolinum in Brunswick (Braunschweig), Germany. Petri initially studied medicine at the Kaiser Wilhelm Academy for Military Physicians (18711875) and received his medical degree in 1876. He continued his studies at the Charité Hospital in Berlin where his thesis on the chemistry of protein urine tests earned him his doctorate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bayer AG
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include: pharmaceuticals, consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the EURO STOXX 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer (1825–1880) and dyer Friedrich Weskott (1821–1876). The company was established as a dyestuffs producer, but the versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand its business into other areas. In 1899, Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. Aspirin is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 34th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ferdinand Sauerbruch
Ernst Ferdinand Sauerbruch (; 3 July 1875 – 2 July 1951) was a German surgeon. His major work was on the use of negative-pressure chambers for surgery. Biography Sauerbruch was born in Barmen (now a district of Wuppertal), Germany. He studied medicine at the Philipps University of Marburg, the University of Greifswald, the Friedrich Schiller University of Jena, and the University of Leipzig, from the last of which he graduated in 1902. He went to Breslau in 1903, where he developed the Sauerbruch chamber, a pressure chamber for operating on the open thorax, which he demonstrated in 1904. This invention was a breakthrough in thorax medicine and allowed heart and lung operations to take place at greatly reduced risk. As a battlefield surgeon during World War I, he developed several new types of limb prostheses, which for the first time enabled simple movements to be executed with the remaining muscle of the patient. Sauerbruch worked at the Ludwig Maximilian University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |