|
Banská Štiavnica
Banská Štiavnica (; ; , ) is a town in central Slovakia, in the middle of an immense caldera created by the collapse of an ancient volcano. For its size, the caldera is known as the Štiavnica Mountains. Banská Štiavnica has a population of less than 10,000. It is a completely preserved medieval town. Because of their historical value, the town and its surroundings were proclaimed by the UNESCO to be a World Heritage Site on December 11, 1993. History The fate of Banská Štiavnica has been closely linked to the exploitation of its abundant resources of silver ore. According to evidence from excavations, the site was settled during the Neolithic period. The first mining settlement was founded by Celts in the 3rd century BC. It was probably occupied by the Celtic Cotini tribe. Roman authors mentioned mining activities of the Cotini, who had lived in present-day central Slovakia until they were deported to Pannonia within the Marcomannic Wars by Rome. The site was also settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities And Towns In Slovakia
This is an alphabetical list of the 2,891 (singular , "municipality") in Slovakia. They are grouped into 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts (, singular ), in turn grouped into 8 Regions of Slovakia, regions (, singular ); articles on individual districts and regions list their municipalities. The average area of Slovak municipalities is about and an average population of about 1,888 people. * Ábelová * Abovce * Abrahám * Abrahámovce, Bardejov District * Abrahámovce, Kežmarok District * Abramová * Abranovce * Adamovské Kochanovce * Adidovce * Alekšince * Andovce * Andrejová * Ardanovce * Ardovo * Arnutovce * Báb, Nitra District, Báb * Babie * Babín * Babiná * Babindol * Babinec, Slovakia, Babinec * Bacúch * Bacúrov * Báč * Bačka, Slovakia, Bačka * Bačkov, Trebišov District, Bačkov * Bačkovík * Baďan * Bádice * Badín * Báhoň * Bajany * Bajč * Bajerov * Bajerovce * Bajka * Bajtava * Baka, Slovakia, Baka * Balá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Greek Catholic Church
The Slovak Greek Catholic Church or Byzantine Catholic Church in Slovakia, is a ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic church based in Slovakia. As a Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites, particular church of the Catholic Church, it is in full communion with the Holy See. The church is organised as a single ecclesiastical province with one Metropolis (religious jurisdiction), metropolitan see. Its liturgical rite is the Byzantine Rite. In 2008 in Slovakia alone, the Greek Catholic Church in Slovakia had some 350,000 faithful, 374 priests and 254 parishes. In 2017, the Catholic Church counted 207,320 Greek Catholics in Slovakia worldwide, representing roughly one percent of all Eastern Catholics. History Since the unanimous acceptance of the Union of Uzhhorod on the territory that includes present day eastern Slovakia in 1646, the history of the Slovak Greek Catholic Church was intertwined with that of the Ruthenian Greek Catholic Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It included the modern regions western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Background In the Early Iron Age, Transdanubia was inhabited by the Pannonians or Pannonii, a collection of Illyrians, Illyrian tribes. The Celts invaded in the Late Iron Age and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman historian Pompeius Trogus writes that the Celts were met with heavy resistance from the locals and were not able to overrun the southern part of Transdanubia. Some tribes advanced as far as Delphi, with the Scordisci settling in Syrmia (279 BC) upon being forced to withdraw. The arrival of the Celts in Transdanubia disrupted the flow of amber from the Balti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
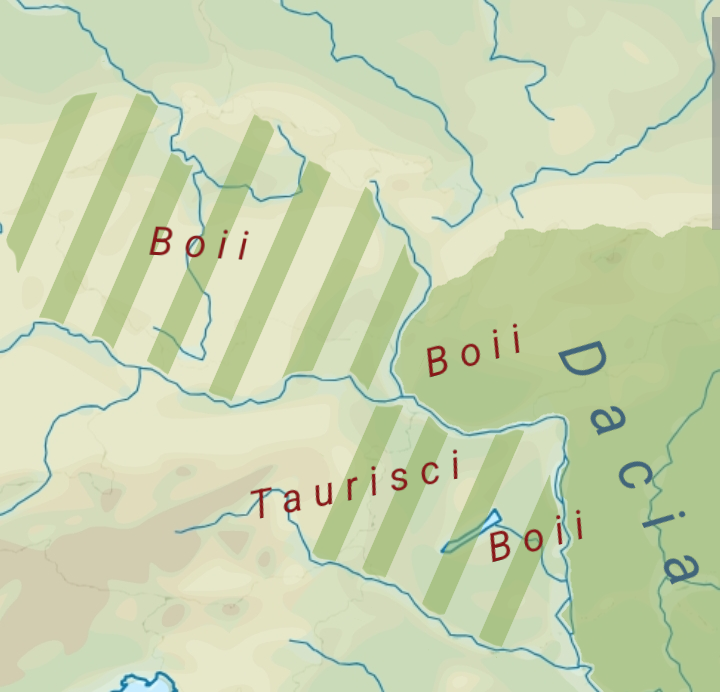
Cotini
The Cotini, sometimes spelled Gotini (because it is found in some manuscript copies of Tacitus), were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland, and Slovakia. The spelling "Gotini" is only known from one classical source, the '' De Origine et situ Germanorum'' of Tacitus. (Tacitus clearly distinguishes the Gotini from the similarly named Gotones, whom he discusses in the immediately following passage.) Tacitus described the Gotini as speaking a Gaulish language and working, to their degradation, in mining. Like their neighbours in the mountains, the Osi, they had to pay tribute to both the neighbouring Quadi and Sarmatians. Although the Gotini lived in the midst of Suevic peoples, in geographical Germania, they were not Germanic in their language. Probably resident in the area of modern western Slovakia, Moravia, and southern Poland, they may have constituted all or part of the archaeologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site is nominated by its host country and determined by the UNESCO's World Heritage Committee to be a unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable, having a special cultural or physical significance, and to be under a sufficient system of legal protection. World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains or wilderness areas, and others. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humankind and serve as evidence of humanity's intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Štiavnica Mountains
The Štiavnica Mountains (also Štiavnické Mountains; , ) are a volcanic mountain range southern central Slovakia. They are part of Inner Western Carpathians and the Slovenské stredohorie Mountains. The area is protected by Štiavnica Mountains Protected Landscape Area. They are bordered by the Kremnica Mountains (''Kremnické vrchy'') in the north, Pliešovce and Krupina basins (''Krupinská kotlina'') in the east, Danubian Hills (''Podunajská pahorkatina'') in the south and Pohronský Inovec, Vtáčnik and Žiar Basin (''Žiarska kotlina'') in the west. The highest point is Sitno (1,009 m). Štiavnica Mountains are an immense caldera created by the collapse of an ancient volcano. Due to their volcanic origin, they are mineral-rich, with around 140 kinds of minerals. In the past, silver mining flourished in the area around the town of Banská Štiavnica Banská Štiavnica (; ; , ) is a town in central Slovakia, in the middle of an immense caldera created by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a Volcanic crater, crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |