|
Bambusoideae
Bamboos are a diverse group of mostly evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family, in the case of '' Dendrocalamus sinicus'' having individual stalks ( culms) reaching a length of , up to in thickness and a weight of up to . The internodes of bamboos can also be of great length. '' Kinabaluchloa wrayi'' has internodes up to in length. and ''Arthrostylidium schomburgkii'' has internodes up to in length, exceeded in length only by papyrus. By contrast, the stalks of the tiny bamboo ''Raddiella vanessiae'' of the savannas of French Guiana measure only in length by about in width. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, but it most likely comes from the Dutch or Portuguese language, which originally borrowed it from Malay or Kannada. In bamboo, as in other grasses, the internodal regions of the stem are usually hollow and the vascular bundles in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials ( bamboo, thatch, and straw); oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olyreae
Olyreae is a tribe of grasses in the bamboo subfamily ( Bambusoideae). Unlike the other two bamboo tribes, Olyreae are herbaceous and do not have a woody stem. Their sister group are the tropical woody bamboos ( Bambuseae). Olyreae grow in the understorey of humid tropical forests. They are mainly distributed in the Neotropics around the Amazon Basin The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries ... but there is also one species from Africa, '' Olyra latifolia'', and one from New Guinea, '' Buergersiochloa bambusoides''. The tribe is divided into three subtribes with 21 genera: References Bambusoideae Poaceae tribes {{Bamboo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raddiella
''Raddiella'' is a genus of Neotropical plants in the grass family native to South America, Panama and Trinidad. ;Species # '' Raddiella esenbeckii'' (Steud.) C.E.Calderón ex Soderstr. - Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Venezuela, French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad, Panama # '' Raddiella kaieteurana'' Soderstr. - Venezuela ( Bolívar), Suriname, Guyana, Brazil (Pará) # '' Raddiella lunata'' Zuloaga & Judz. - Rondônia, Mato Grosso # '' Raddiella malmeana'' (Ekman) Swallen - Pará, Mato Grosso # '' Raddiella minima'' Judz. & Zuloaga - Pará, Mato Grosso # '' Raddiella molliculma'' (Swallen) C.E.Calderón ex Soderstr. - Caquetá # '' Raddiella potaroensis'' Soderstr. - Venezuela ( Bolívar), Guyana # '' Raddiella vanessiae'' Judz. - French Guiana French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Surinam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinabaluchloa
''Kinabaluchloa'' is a genus of Southeast Asian bamboos in the grass family. ;Species * '' Kinabaluchloa nebulosa'' K.M.Wong - Sabah, Brunei * '' Kinabaluchloa wrayi'' (Stapf) K.M.Wong - Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ... References Bambusoideae Bambusoideae genera Flora of Borneo Flora of Peninsular Malaysia Flora of Thailand Flora of Vietnam {{Bamboo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arundinarieae
Arundinarieae is a tribe of bamboo in the grass family (Poaceae) containing a single subtribe, Arundinariinae, and 31 genera. These woody bamboos occur in areas with warm temperate climates in southeastern North America, Subsaharan Africa, South Asia and East Asia East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja .... The tribe forms a lineage independent of the tropical woody bamboos ( Bambuseae) and the tropical herbaceous bamboos ( Olyreae). Genera References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q9159167, from2=Q3756834 Bambusoideae Poaceae tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bambuseae
The Bambuseae are the most diverse tribe of bamboos in the grass family ( Poaceae). They consist of woody species from tropical regions, including some giant bamboos. Their sister group are the small herbaceous bamboos from the tropics in tribe Olyreae, while the temperate woody bamboos ( Arundinarieae) are more distantly related. The Bambuseae fall into two clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...s, corresponding to species from the Neotropics ( subtribes Arthrostylidiinae, Chusqueinae, and Guaduinae) and from the Paleotropics (subtribes Bambusinae, Hickeliinae, Melocanninae, and Racemobambosinae). Subtribes and genera The 73 genera are placed in eleven subtribes: * subtribe Arthrostylidiinae: *:'' Actinocladum'', '' Alvimia'', '' Arthrostylidium' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or ) is a Western Romance language of the Indo-European language family originating from the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the official language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tomé and Príncipe, and has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau. Portuguese-speaking people or nations are known as Lusophone (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Gallaecian language, Celtic phonology. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 17 million second language speakers, Portuguese has approximately 267 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the List of languages by number of native speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay ( , ; , Jawi alphabet, Jawi: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken primarily by Malays (ethnic group), Malays in several islands of Maritime Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula on the mainland Asia. The language is an official language of Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore. Indonesian language, Indonesian, a standardized variety of Malay, is the official language of Indonesia and one of the working languages of East Timor. Malay is also spoken as a regional language of Malays (ethnic group), ethnic Malays in Indonesia and the Thai Malays, southern part of Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 60 million people across Maritime Southeast Asia. The language is pluricentric and a ISO 639 macrolanguage, macrolanguage, i.e., a group of Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible speech varieties, or dialect continuum, that have no traditional name in common, and which may be considered distinct languages by their speakers. Several varieties of it ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada Language
Kannada () is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for 15 million speakers in Karnataka. It is the official and administrative language of Karnataka. It also has Languages with legal status in India, scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's Classical languages of India, designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Press, 2012, Kannada was the court language of a number of dynasties and empires of South India, Central India and the Deccan Plateau, namely the Kadamba dynasty, Western Ganga dynasty, Nolamba dynasty, Chalukya dynasty, Rashtrakutas, Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
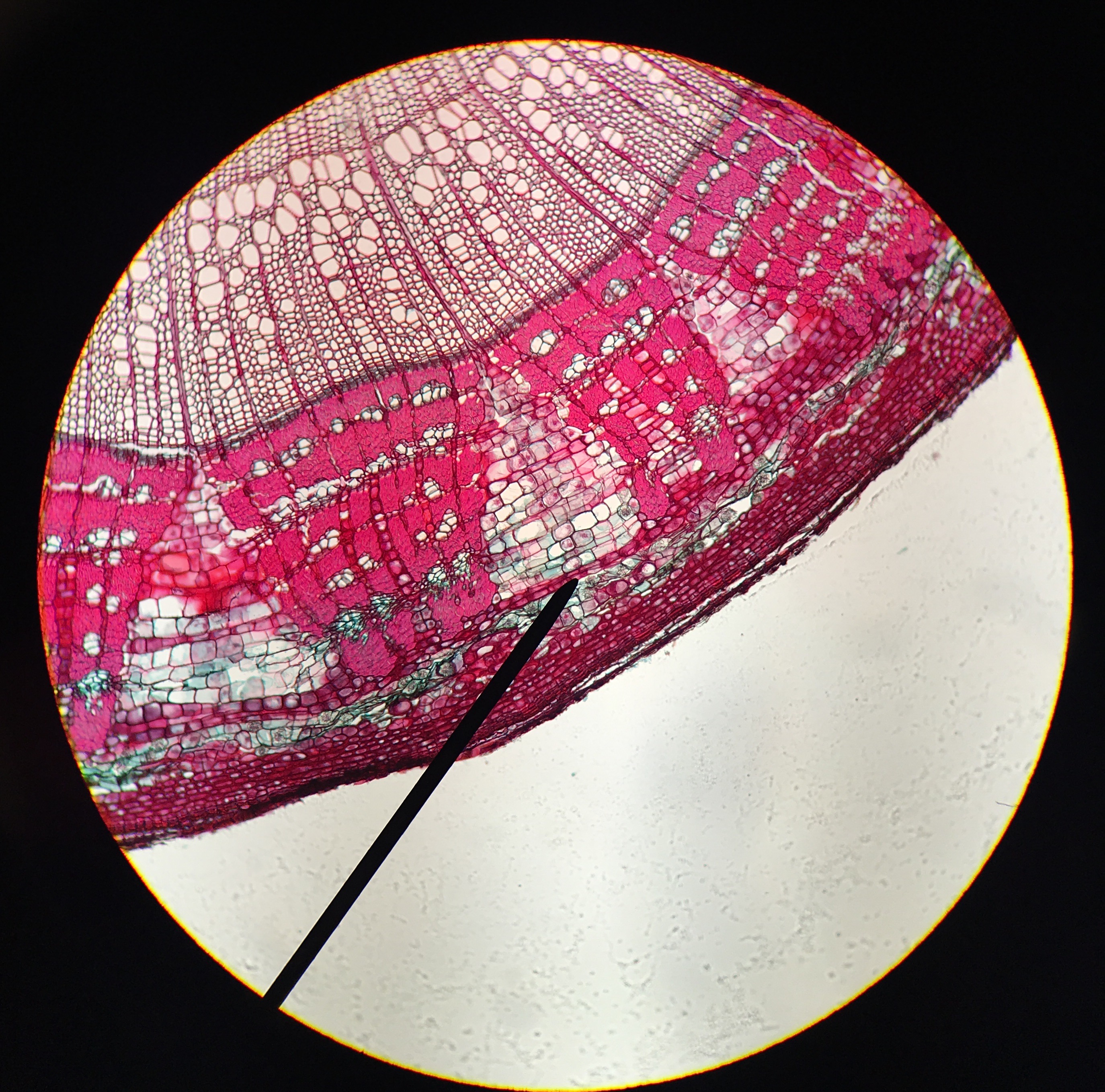
Cambium
A cambium (: cambiums or cambia), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internode (botany)
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaf, leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, engages in photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue. The stem can also be called the culm, halm, haulm, stalk, or thyrsus. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes: * The nodes are the points of attachment for leaves and can hold one or more leaves. There are sometimes axillary buds between the stem and leaf which can grow into branches (with leaf, leaves, conifer cones, or inflorescence, flowers). Adventitious roots (e.g. brace roots) may also be produced from the nodes. Vines may produce tendrils from nodes. * The internodes distance one node from another. The term "Shoot (botany), shoots" is often confused with "stems"; "shoots" generally refers to new fresh plant growth, including both stems and other str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |