|
Baldwin I RĂ¡tĂ³t
Baldwin (I) from the kindred RĂ¡tĂ³t (; died after 1255) was a Hungarian distinguished nobleman from the ''gens'' RĂ¡tĂ³t, who served as master of the cupbearers three times. His father was Rathold RĂ¡tĂ³t, ispĂ¡n (''comes'') of Somogy County in 1203. His older brother was Dominic I RĂ¡tĂ³t. He served as master of the cupbearers between 1233 and 1234.Zsoldos 2011, p. 59. After that he functioned as ispĂ¡n of Moson County in 1235.Zsoldos 2011, p. 170. He was appointed master of the cupbearers for the second time in 1235, a position which he held until 1238. He was ispĂ¡n of Vas County from 1240 to 1244.Zsoldos 2011, p. 223. After that he functioned as ispĂ¡n of Nyitra County Nyitra County (; ; ; ) was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory lay in what is now western Slovakia. Geography Nyitra County shared borders with the Austrian land Moravia and TrencsĂ©n County, TurĂ³ ... in 1244.Zsoldos 2011, p. 175. He served as master of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of The Cupbearers
The master of the cupbearers or master of the cup-bearers (, , and ) was one of the high officials of the royal household in the Kingdom of Hungary The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro .... Masters of the cupbearers were included among the "true barons"''Stephen WerbÅ‘czy: The Customary Law of the Renowned Kingdom of Hungary in Three Parts (1517)'' (ch. 1.94), p. 177. of the realm from around 1220. References Sources * * * ''Stephen WerbÅ‘czy: The Customary Law of the Renowned Kingdom of Hungary in Three Parts (1517)'' (Edited and translated by JĂ¡nos M. Bak, PĂ©ter BanyĂ³ and Martyn Rady with an introductory study by LĂ¡szlĂ³ PĂ©ter) (2005). Charles Schlacks, Jr. Publishers. . Barons of the realm (Kingdom of Hungary) {{Hungary-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyitra County
Nyitra County (; ; ; ) was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory lay in what is now western Slovakia. Geography Nyitra County shared borders with the Austrian land Moravia and TrencsĂ©n County, TurĂ³c County, Bars County, KomĂ¡rom County and Pozsony County. In its final phase, it was a strip of land between the Morava river in the north and the town of ÉrsekĂºjvĂ¡r (present-day NovĂ© ZĂ¡mky) in the south, plus an outlier around the town of Privigye (present-day Prievidza). The river VĂ¡g (present-day VĂ¡h) flowed through the county. Its area was 5519 km2 around 1910. Capitals The capital of the county was the Nitra Castle () and since the Late Middle Ages the town of Nyitra (present-day Nitra). History A predecessor to Nyitra county may have existed as early as in the 9th century at the time of Great Moravia. Around 1000, Nyitra county arose as one of the first comitatus of the Kingdom of Hungary. The southern part, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
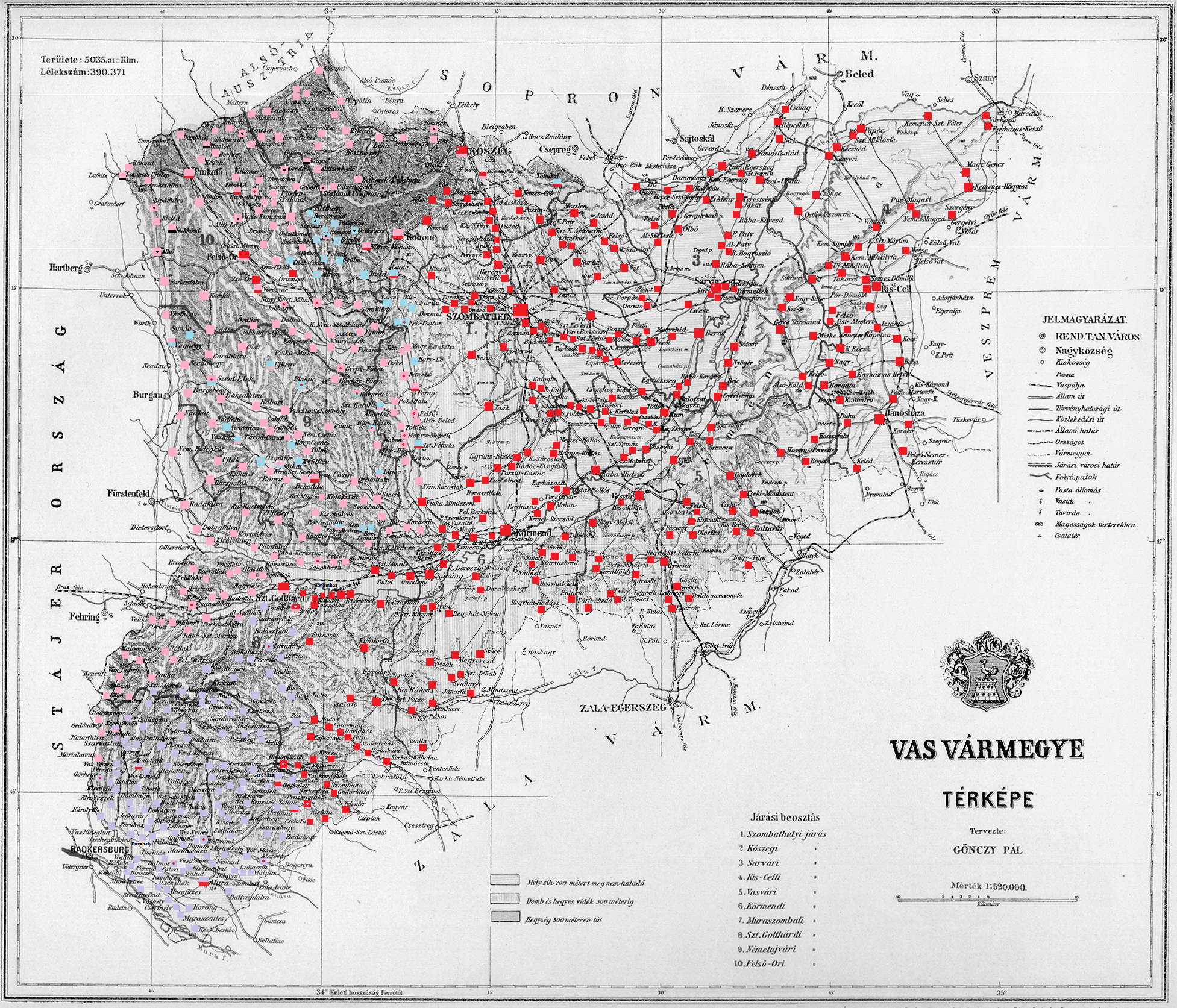
Vas County (former)
Vas (, , or ) was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Hungary, Austria and Slovenia. Geography Vas County shared borders with the Austrian lands Lower Austria and Styria (duchy), Styria and the Hungarian counties Sopron County, Sopron, VeszprĂ©m County (former), VeszprĂ©m and Zala County (former), Zala. It stretched between the river Mur River, Mura in the south, the foothills of the Alps in the west and the river Marcal in the east. The RĂ¡ba River flowed through the county. Its area was 5474 km² around 1910. History Vas County arose as one of the first ''comitatuses'' of the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon, the western part of the county became part of First Austrian Republic, Austria, and a small part in the southwest became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (from 1929 as Yugoslavia). The remainder stayed in Hungary. The fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moson County
Moson (German language, German: Wieselburg, Slovak language, Slovak: MoÅ¡on) was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary, situated mostly on the right (south) side of the Danube river. Its territory is now divided between Austria and Hungary, except a small area which is part of Slovakia. Moson is also the name of a town, nowadays part of the city MosonmagyarĂ³vĂ¡r, Hungary. Geography Moson county shared borders with the Austrian land Lower Austria and the Hungarian counties Pozsony county, Pozsony, GyÅ‘r (county), GyÅ‘r and Sopron (county), Sopron. The river Danube runs along the north of the county, and the Lake Neusiedl (Hungarian: FertÅ‘ tĂ³) lies partly in the county. Its area was 2013 km2 around 1910. Capitals The capital of the county was the town of Moson initially. The capital was moved to nearby MagyarĂ³vĂ¡r in the Middle Ages. Moson and MagyarĂ³vĂ¡r merged in 1939 to form the city of MosonmagyarĂ³vĂ¡r. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominic I RĂ¡tĂ³t
Dominic (I) from the kindred RĂ¡tĂ³t (; died 11 April 1241) was a Hungarian distinguished nobleman from the ''gens'' RĂ¡tĂ³t, who served as master of the treasury between 1238 and 1240. His father was Rathold RĂ¡tĂ³t, ispĂ¡n (''comes'') of Somogy County in 1203. His younger brother was Baldwin I RĂ¡tĂ³t. Dominic I had four sons and a daughter (spouse of Maurice II Pok). He also functioned as ispĂ¡n of Nyitra (1238) and Bihar Counties (1240).Zsoldos 2011, p. 62. He was killed in the Battle of Mohi The Battle of Mohi (11 April 1241) was a pivotal conflict between the Mongol Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary during the Mongol invasion of Europe. The battle took place at Muhi (then Mohi), a town located in present-day Hungary, southwest of ... on 11 April 1241.MarkĂ³ 2006, p. 364. References Sources * MarkĂ³, LĂ¡szlĂ³ (2006). ''A magyar Ă¡llam fÅ‘mĂ©ltĂ³sĂ¡gai Szent IstvĂ¡ntĂ³l napjainkig – Életrajzi Lexikon'' ("The High Officers of the Hungarian State from Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somogy County (former)
Somogy was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was slightly larger than that of present Somogy county, is now in south-western Hungary. The capital of the county was KaposvĂ¡r. Geography Somogy County shared borders with the Hungarian counties of Zala (former county), Zala, VeszprĂ©m County (former), VeszprĂ©m, Tolna County (former), Tolna, Baranya County (former), Baranya, Virovitica County, VerÅ‘ce and BelovĂ¡r-Körös (the latter two part of Croatia-Slavonia). It extended along the southern shore of Lake Balaton and encompassed the region south of the lake. The river Drava (Hungarian: DrĂ¡va) formed most of its southern border. Its area was 6530 km2 around 1910. History In the 10th century, the Hungarian NyĂ©k tribe occupied the region around Lake Balaton, mainly the areas which are known today as Zala County, Zala and Somogy counties. Somogy County arose as one of the first comitatuses of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IspĂ¡n
The ispĂ¡nRady 2000, p. 19.''Stephen WerbÅ‘czy: The Customary Law of the Renowned Kingdom of Hungary in Three Parts (1517)'', p. 450. or countEngel 2001, p. 40.Curta 2006, p. 355. (, , and ),Kirschbaum 2007, p. 315. deriving from title of župan, was the leader of a castle district (a fortress and the royal lands attached to it) in the Kingdom of Hungary from the early 11th century. Most of them were also heads of the basic administrative units of the kingdom, called County (Kingdom of Hungary), counties, and from the 13th century the latter function became dominant. The ''ispĂ¡ns'' were appointed and dismissed by either the king of Hungary, monarchs or a high-ranking royal official responsible for the administration of a larger territorial unit within the kingdom. They fulfilled administrative, judicial and military functions in one or more counties. Heads of counties were often represented locally by their deputies, the vice-ispĂ¡nsRady 2000, p. 41. (,Nemes 1989, p. 21. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rathold RĂ¡tĂ³t
Rathold (I) from the kindred RĂ¡tĂ³t () was a Hungarian distinguished nobleman from the ''gens'' RĂ¡tĂ³t, who served as ispĂ¡n (''comes'') of Somogy County in 1203.Zsoldos 2011, p. 192. He was the eldest son of voivode Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ... Leustach RĂ¡tĂ³t.Zsoldos 2011, p. 348. As his brother, Julius I RĂ¡tĂ³t had no successors, Rathold was the ancestor of the Gyulafi branch of the RĂ¡tĂ³t clan. References Sources * Zsoldos, Attila (2011). ''MagyarorszĂ¡g vilĂ¡gi archontolĂ³giĂ¡ja, 1000–1301'' ("Secular Archontology of Hungary, 1000–1301"). HistĂ³ria, MTA TörtĂ©nettudomĂ¡nyi IntĂ©zete. Budapest. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ratot, Rathold Rathold 13th-century Hungarian people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen CsĂ¡k, Ban Of Severin
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" (and its comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RĂ¡tĂ³t (genus)
RĂ¡tĂ³t (''RĂ¡thold'' or ''RĂ¡told'') was the name of a ''gens'' (Latin for "clan"; ''nemzetsĂ©g'' in Hungarian) in the Kingdom of Hungary. According to Simon of KĂ©za and other chroniclers, the ancestors of the clan were Italians from Caserta, Naples, by name Rathold and Oliver, who settled down in Hungary around 1097 during the reign of Coloman, King of Hungary. Vajai, Szabolcs (1968)A magyar Roland-Ă©nek nyomĂ¡ban ''IrodalomtörtĂ©neti KözlemĂ©nyek''. 334–335. They came to Hungary alongside Felicia of Sicily. The LorĂ¡ntffy, Kakas de Kaza, Feledi, Putnoki, Jolsvai, Kakas, Gyulaffy, ElefĂ¡nti, Paksi, PĂ¡sztĂ³i, Kaplai, RĂ¡day and Tari families were originate from the Genus RĂ¡tĂ³t. The ancestors of the RĂ¡told family came to Hungary from the town of Caserta in the province of Puglia, according to Simon KĂ©zai and other chronicles following him. According to another opinion, Olivier and Reithold arrived in Hungary from Naples at the end of the 11th century, around 1079, durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin II RĂ¡tĂ³t
Baldwin (II) from the kindred RĂ¡tĂ³t (; died after 1283) was a Hungarian distinguished nobleman from the ''gens'' RĂ¡tĂ³t as the son of Baldwin I RĂ¡tĂ³t, who served as ispĂ¡n (''comes'') of Zala County Zala (, ; ; ) is an administrative county (Counties of Hungary, comitatus or ''vĂ¡rmegye'') in south-western Hungary. It is named after the Zala River. It shares borders with Croatia (Koprivnica–Križevci County, Koprivnica–Križevci and MeÄ ... from 1275 to 1276 and in 1276.Zsoldos 2011, p. 233. His older brother was Julius II RĂ¡tĂ³t. Baldwin's only son, Lawrence was the ancestor of the RĂ¡tĂ³ti and Gyulaffy de RĂ¡tĂ³t noble families. References Sources * Zsoldos, Attila (2011). ''MagyarorszĂ¡g vilĂ¡gi archontolĂ³giĂ¡ja, 1000–1301'' ("Secular Archontology of Hungary, 1000–1301"). HistĂ³ria, MTA TörtĂ©nettudomĂ¡nyi IntĂ©zete. Budapest. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ratot, Baldwin 02 Baldwin 02 13th-century Hungarian people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |