|
Baillon's Shearwater
The tropical shearwater (''Puffinus bailloni'') is a seabird in the family Procellariidae formerly considered conspecific with Audubon's shearwater (''Puffinus lherminieri''). Subspecies There are five listed subspecies of the tropical shearwater: * ''Puffinus bailloni nicolae'' – ( Jouanin, 1971): breeds on islands in the northwest Indian Ocean. * ''Puffinus bailloni colstoni'' – ( Shirihai & Christie, 1996): breeds in the Aldabra Islands in the Seychelles. * ''Puffinus bailloni bailloni'' – ( Bonaparte, 1857): Mauritius, Réunion & Europa Island. * ''Puffinus bailloni dichrous'' – ( Finsch & Hartlaub, 1867): Central Pacific islands. * ''Puffinus bailloni gunax'' – ( Mathews, 1930): Vanuatu. Range The tropical shearwater is found in the tropical parts of the western Indian Ocean from East Africa to southern India and in similar regions of the Pacific from just to the southeast of Japan to French Polynesia. Population The total population has not been definitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the island of Madagascar and southwest of the island of Mauritius. , it had a population of 896,175. Its capital and largest city is Saint-Denis, La Réunion, Saint-Denis. Réunion was uninhabited until French immigrants and colonial subjects settled the island in the 17th century. Its tropical climate led to the development of a plantation economy focused primarily on sugar; slaves from East Africa were imported as fieldworkers, followed by Malays, Annamite, Vietnamese, Chinese, and Indians as indentured laborers. Today, the greatest proportion of the population is of mixed descent, while the predominant language is Réunion Creole, though French remains the sole official language. Since 1946, Réunion has been governed as a regions of France, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Mathews
Gregory Macalister Mathews CBE FRSE FZS FLS (10 September 1876 – 27 March 1949) was an Australian-born amateur ornithologist who spent most of his later life in England. Life He was born in Biamble in New South Wales the son of Robert H. Mathews. He was educated at The King's School, Parramatta. Mathews made his fortune in mining shares and moved to England in 1902. In 1910, he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were William Eagle Clarke, Ramsay Heatley Traquair, John Alexander Harvie-Brown and William Evans. Ornithology Mathews was a controversial figure in Australian ornithology. He was responsible for bringing trinomial nomenclature into local taxonomy, however he was regarded as an extreme splitter. He recognised large numbers of subspecies on scant evidence and few notes. The extinct Lord Howe Pigeon was described by Mathews in 1915, using a painting as a guide. At the time, he named it ''Raperia godmanae'' after Alice Mary God ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of The Pacific Ocean
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of The Indian Ocean
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shearwaters
Shearwaters are medium-sized long-winged seabirds in the petrel family Procellariidae. They have a global marine distribution, but are most common in temperate and cold waters, and are pelagic outside the breeding season. Description These Procellariiformes, tubenose birds fly with stiff wings and use a "shearing" flight technique (flying very close to the water and seemingly cutting or "shearing" the tips of waves) to move across wave fronts with the minimum of active flight. This technique gives the group its English name. Some small species like the Manx shearwater are cruciform in flight, with their long wings held directly out from their bodies. Behaviour Movements Many shearwaters are long-distance migrants, perhaps most spectacularly sooty shearwaters, which cover distances in excess of from their breeding colonies on the Falkland Islands (52°S 60°W) to as far as 70° north latitude in the North Atlantic Ocean off northern Norway, and around New Zealand to as far as 60� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puffinus
''Puffinus'' is a genus of seabirds in the order Procellariiformes that contains about 20 small to medium-sized shearwaters. Two other shearwater genera are named: '' Calonectris'', which comprises three or four large shearwaters, and '' Ardenna'' with another seven species (formerly often included within ''Puffinus''). The taxonomy of this group is the cause of much debate, and the number of recognised species varies with the source. The species in this group are long-winged birds, dark brown or black above, and white to dark brown below. They are pelagic outside the breeding season. They are most common in temperate and cold waters. These tubenose birds fly with stiff wings, and use a shearing flight technique to move across wave fronts with the minimum of active flight. Some small species, such as the Manx shearwater, are cruciform in flight, with their long wings held directly out from their bodies. Many are long-distance migrants, perhaps most spectacularly the sooty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
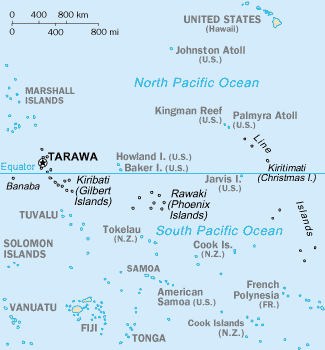
Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic of Kiribati. Their combined land area is . The only island of any commercial importance is Canton Island (also called Abariringa). The other islands are Enderbury, Rawaki (formerly Phoenix), Manra (formerly Sydney), Birnie, McKean, Nikumaroro (formerly Gardner), and Orona (formerly Hull). The Phoenix Islands Protected Area, established in 2008, is one of the world's largest protected areas and is home to about 120 species of coral and more than 500 species of fish. The Phoenix Islands are uninhabited, except for a few families who live on Canton Island. Historically, the Phoenix Islands have been considered part of the Gilberts Island group (sometimes known as the ''Kingsmill'' island group). Geographically, Baker Island and Howland Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands () are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons, except Vostok and Jarvis) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. Eight of the atolls are parts of Kiribati. The remaining three— Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef, and Palmyra Atoll—are territories of the United States grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The Line Islands, all of which were formed by volcanic activity, are one of the longest island chains in the world, stretching from northwest to southeast. One of them, Starbuck Island, is near the geographic center of the Pacific Ocean (). Another, Kiritimati, has the largest land area of any atoll in the world. Only Kiritimati, Tabuaeran, and Teraina have a permanent population. Besides the 11 confirmed atolls and islands, Filippo Reef is shown on some maps, but its existence is doubted. The International Date L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aride Island
Aride Island is the northernmost Granite, granitic island in the Seychelles (Bird Island, Seychelles, Bird Island is the northernmost Seychelles island overall). A nature reserve, it is leased and managed by the Island Conservation Society of Seychelles. History The name ‘Aride’ first appears on nautical charts after French voyages of exploration in 1770 and 1771. The first written account was in 1787 by Jean-Baptiste Malavois, French commandant of Seychelles, who described it as being “…no more than a pile of rocks covered with a few bushes.” Between 1817 and 1829 Aride was possibly an unofficial leper colony. In 1868, the Irishman Perceval Wright, who gave his name to Aride's unique gardenia and one of its endemic lizards, visited Aride. In 1883, the British artist Marianne North painted a scene on the island, reporting just one large tree, beneath which the island staff sheltered from the sun. Coconut palms were planted over much of Aride and copra production became i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The total land area of French Polynesia is , with a population of 278,786 (Aug. 2022 census) of which at least 205,000 live in the Society Islands and the remaining population lives in the rest of the archipelago. French Polynesia is divided into five island groups: the Austral Islands; the Gambier Islands; the Marquesas Islands; the Society Islands (comprising the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward and Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward Islands); and the Tuamotus. Among its 121 islands and atolls, 75 were inhabited at the 2017 census. Tahiti, which is in the Society Islands group, is the most populous island, being home to nearly 69% of the population of French Polynesia . Papeete, located on Tahiti, is the capital of French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |