|
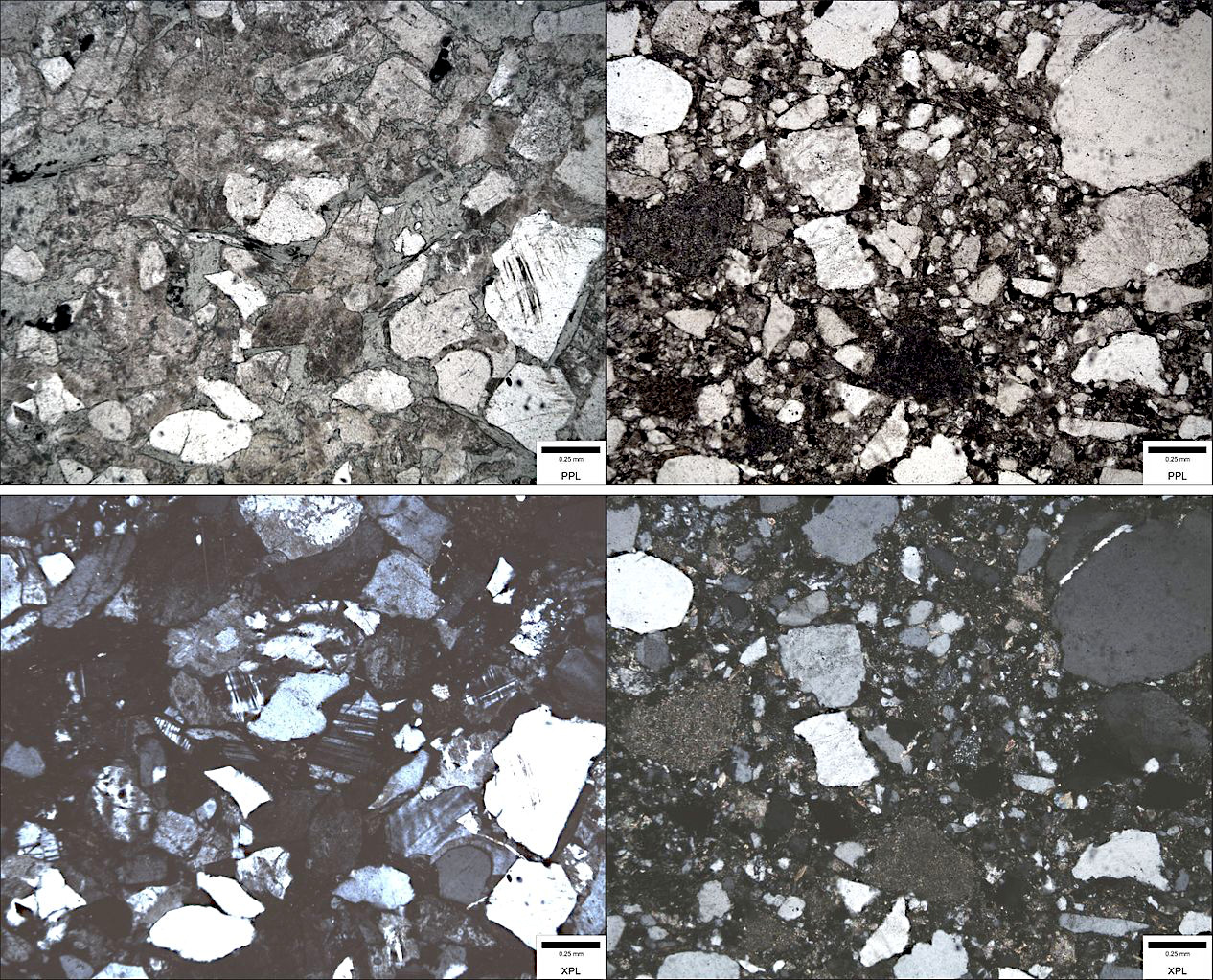
Bahía Mansa Metamorphic Complex
The Bahía Mansa Metamorphic Complex (Spanish: ''Complejo Metamórfico Bahía Mansa'', CMBM), also known as the Western Series, is a group of geologic formations in the Chilean Coast Range in southern Chile that have been transformed by heat and pressure (a process called metamorphism). It includes pelitic schists (layered rocks from mud or clay), metagreywackes (hardened sandy sediments altered by metamorphism), and mafic A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ... metavolcanics (dark-colored rocks from ancient ocean floors). The complex is named after Bahía Mansa, a nearby coastal bay. References Lithodemic units of Chile Geology of Araucanía Region Geology of Biobío Region Geology of Los Ríos Region Geology of Los Lagos Region Metamorphic complexes Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Geological Society
The ''Journal of the Geological Society '' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Geological Society of London. It covers research in all aspects of the Earth sciences. References External links * Proceedings of the Geological Society of London Vol 1 (1826–1833) to Vol 4 (1843–1845) available online at the Biodiversity Heritage Library The Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) is the world’s largest open-access digital library for biodiversity literature and archives. BHL operates as a worldwide consortium of natural history, botanical, research, and national libraries working ...The Quarterly journal of the Geological Society of London Vol 1 (1845) to Vol 72 (1923) available online at the Biodiversity Heritage Library Publications established in 1826 Geology journals Bimonthly journals Geological Society of London academic journals English-language journals Academic journals published by learned and professional societies 1826 establishments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Chilean Coast Range
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Complexes
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Los Lagos Region
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their Geochronology, absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metavolcanic
Metavolcanic rock is volcanic rock that shows signs of having experienced metamorphism. In other words, the rock was originally produced by a volcano, either as lava or tephra. The rock was then subjected to high pressure, high temperature or both, for example by burial under younger rocks, causing the original volcanic rock to recrystallize. Metavolcanic rocks are sometimes described informally as ''metavolcanics''. When it is possible to determine the original volcanic rock type from the properties of the metavolcanic rock (particularly if the degree of metamorphism is slight), the rock is more precisely named by appylying the prefix ''meta-'' to the original rock type. For example, a weakly metamorphosed basalt would be described as a '' metabasalt'', or a weakly metamorphosed tuff as a ''metatuff''. Metavolcanic rock is commonly found in greenstone belt Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Mafic rocks often also contain calcium-rich varieties of plagioclase feldspar. Mafic materials can also be described as ferromagnesian. History The term ''mafic'' is a portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric" and was coined by Charles Whitman Cross, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis V. Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington in 1912. Cross' group had previously divided the major rock-forming minerals found in igneous rocks into ''salic'' minerals, such as quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids, and ''femic'' minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. However, micas and aluminium-rich amphiboles were excluded, while some calcium minerals containing little iron or magnesium, such as wollastonite or apatite, were included in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke ( ) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness (6–7 on Mohs scale), dark color, and Sorting (sediment), poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or sand-size Lithic fragment (geology), lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic Stratum, strata. The larger Particle size (grain size), grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and Matrix (geology), matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume. Formation The origin of greywacke was unknown until turbidity currents and turbidites were understood, since, according to the normal laws of sedimentation, gravel, sand and mud should not be laid down together. Geologists now attribute its formation to submarine avalanches or strong turbidity currents. These actions churn sediment and cause mixed-sediment slurries, in which the resulting deposits may ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |