|
Baháʼí Faith In Jamaica
The Baháʼí Faith in Jamaica begins with a mention by ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, then head of the religion, in 1916 as Latin America being among the places Baháʼís should take the religion to. The community of the Baháʼís begins in 1942 with the arrival of Dr. Malcolm King. The first Baháʼí Local Spiritual Assembly of Jamaica, in Kingston, was elected in 1943. By 1957 the Baháʼís of Jamaica were organized under the regional National Spiritual Assembly of the Greater Antilles, and on the eve of national independence in 1962, the Jamaica Baháʼís elected their own National Spiritual Assembly in 1961. By 1981 hundreds of Baháʼís and hundreds more non-Baháʼís turned out for weekend meetings when Rúhíyyih Khánum spent six days in Jamaica. Public recognition of the religion came in the form of the Governor General of Jamaica, Sir Howard Cooke, proclaiming a National Baháʼí Day first on July 25 in 2003 and it has been an annual event since. While there is evidence of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the Middle East, where it has faced Persecution of Baháʼís, ongoing persecution since its inception. The religion has 5-8 million adherents (known as Baháʼís) spread throughout most of the world's countries and territories. The Baháʼí Faith has three central figures: the Báb (1819–1850), executed for heresy, who taught that a prophet similar to Jesus and Muhammad would soon appear; Baháʼu'lláh (1817–1892), who claimed to be said prophet in 1863 and who had to endure both exile and imprisonment; and his son, ʻAbdu'l-Bahá (1844–1921), who made teaching trips to Europe and the United States after his release from confinement in 1908. After ʻAbdu'l-Bahá's death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirza Ahmad Sohrab
Mírzá Aḥmad Sohráb (March 21, 1890 – April 20, 1958) was a Persian- American author and Baháʼí who served as 'Abdu'l-Bahá's secretary and interpreter from 1912 to 1919. He co-founded the New History Society and the Caravan of East and West in New York and was excommunicated from the Baháʼí Faith in 1939 by Shoghi Effendi. Biography Early life Born a Baháʼí in Sedeh, Isfahan Province, Persia (now Iran), Sohrab's father 'Abdu'l-Baghi was a descendant of Muhammad. 'Abdu'l-Baghi was the chief dyer of the town. Both sides of Sohrab's family, his mother and his father, claimed descent from Imam Husayn, grandson of Muhammad. His mother died when Sohrab was a few months old, while she herself was still a teenager, and he was taken to live with his maternal grandmother in Isfahan. New History Society By 1911, he had founded an organization called the Persian-American Educational Society. Later that year he sailed to Europe "in the interests of his work". Sohrab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Spiritual Assembly
Spiritual Assembly is a term given by ʻAbdu'l-Bahá to refer to elected councils that govern the Baháʼí Faith. Because the Baháʼí Faith has no clergy, they carry out the affairs of the community. In addition to existing at the local level, there are national Spiritual Assemblies (although "national" in some cases refers to a portion of a country or to a group of countries). Spiritual Assemblies form part of the elected branch of the Baháʼí administration. Nature and purpose Baháʼu'lláh, ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, and Shoghi Effendi stated how Spiritual Assemblies should be elected by the Baháʼís, defined their nature and purposes, and described in considerable detail how they should function. Since these institutions are grounded in the Baháʼí authoritative texts, Baháʼís regard them as divine in nature, and contrast the wealth of scriptural guidance with the paucity of scriptural texts on which Jewish, Christian, and Islamic religious institutions are based. The U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneering (Baháʼí)
Pioneer commonly refers to a person who is among the first at something that is new to a community. A pioneer as a settler is among the first settling at a place that is new to the settler community. A historic example are American pioneers, persons in American history who migrated westward to settle in what is now the Western and Midwestern United States. Pioneer, The Pioneer, or pioneering may also refer to: Companies and organizations *Pioneer Aerospace Corporation * Pioneer Chicken, an American fast-food restaurant chain * Pioneer Club Las Vegas, a casino in Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Corporation, a Japanese electronics manufacturer * Pioneer Energy, a Canadian gas station chain * Pioneer Entertainment, a Japanese anime company *Pioneer Fund, racist foundation, 1937 *Pioneer Hi-Bred, a U.S.-based agriculture company * Pioneer Hotel & Gambling Hall, Laughlin, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Instrument Company, an American aeronautical instrument manufacturer *Pioneer movement, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baháʼí Administration
The Baháʼí administration is a system of elected and appointed institutions to govern the affairs of the Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community. Its supreme body is the Universal House of Justice, elected every five years. Some features set apart the Baháʼí administration from similar systems of governance: elected representatives should follow their conscience, rather than being responsible to the views of electors; political campaigning, nominations and parties are prohibited; and structure and authority of institutions to lead Baháʼís flowed directly from the religion's founder, Baháʼu'lláh. The Baháʼí administration has four charter documents, the Kitáb-i-Aqdas, the Tablets of the Divine Plan, the Tablets of Baháʼu'lláh#Lawh-i-Karmil (Tablet of Carmel), Tablet of Carmel and the Will and Testament of ʻAbdu'l-Bahá. Character Consultation A central and distinct aspect of the administration of the Baháʼí Faith is the approach to decision-making through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
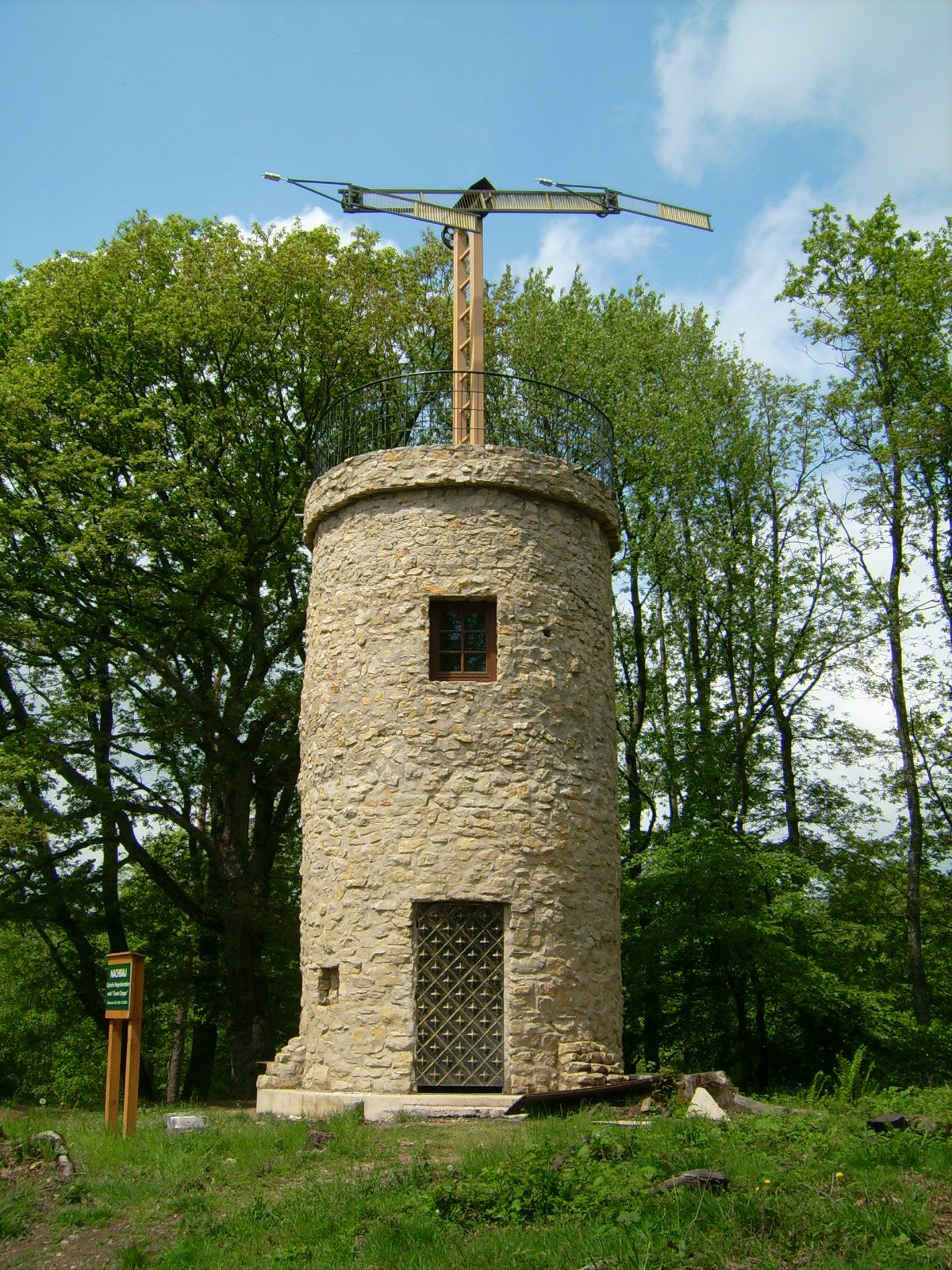
Telegraphy
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined, so such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the Chappe telegraph, an optical telegraph invented by Claude Chappe in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoghi Effendi
Shoghí Effendi (; ;1896 or 1897 – 4 November 1957) was Guardian of the Baháʼí Faith from 1922 until his death in 1957. As the grandson and successor of ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, he was charged with guiding the development of the Baháʼí Faith, including the creation of its global administrative structure and the prosecution of Baháʼí teaching plans, a series of teaching plans that oversaw the expansion of the religion to a number of new countries. As the authorized interpreter of the Baháʼí writings, Baháʼí Writings his translations of the primary written works of the Faith's central figures, provided unity of understanding about essential teachings of the Faith and safeguarded its followers from division. Upon his death in 1957, leadership passed to the Hands of the Cause, and in 1963 the Baháʼís of the world elected the Universal House of Justice, an institution which had been described and planned by Baháʼu’llah. Effendi, an Afnán, was born Shoghí Rabbání i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watling Island
San Salvador Island, previously Watling's Island, is an island and district of The Bahamas, famed for being the probable location of Christopher Columbus's first landing of the Americas on 12 October 1492 during his first voyage. This historical importance, the island's tropical beaches, and its proximity to the United States have made tourism central to the local economy. The island has a population of 824 (2022) and is under the administration of Gilbert C. Kemp. Its largest settlement and seat of local government is Cockburn Town. Names ''Watling's Island'' was named for George or John Watling, an Englishman who settled it in the 17th century. The name was used officially from the 1680s until 1926. It is still used unofficially in discussions of the actual location of Columbus's first landfall. ''San Salvador'' derives from the Spanish ("Island of the Holy Savior"), bestowed by Christopher Columbus in honor of Jesus Christ in thanks for his fleet's safe arrival. in what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahama Islands
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. It comprises more than 3,000 islands, cays and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and north-west of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida and east of the Florida Keys. The capital and largest city is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes the Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama islands were inhabited by the Arawak and Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the "New World" in 1492 when he landed on the island of San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles is a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea, forming part of the West Indies in Caribbean, Caribbean region of the Americas. They are distinguished from the larger islands of the Greater Antilles to the west. They form an arc which begins east of Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico at the Virgin Islands, archipelago of the Virgin Islands, swings southeast through the Leeward Islands, Leeward and Windward Islands towards South America, and turns westward through the Leeward Antilles along the Geography of Venezuela, Venezuelan coast. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic arc, volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States under the designation of Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth. Located about southeast of Miami, Miami, Florida between the Dominican Republic in the Greater Antilles and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands in the Lesser Antilles, it consists of the eponymous main island and numerous smaller islands, including Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Isla de Mona, Mona. With approximately 3.2 million Puerto Ricans, residents, it is divided into Municipalities of Puerto Rico, 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the Capital city, capital municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan, followed by those within the San Juan–Bayamón–Caguas metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean, and with an estimated population of 11.4 million, is the most populous Caribbean country. The capital and largest city is Port-au-Prince. Haiti was originally inhabited by the Taíno people. In 1492, Christopher Columbus established the first European settlement in the Americas, La Navidad, on its northeastern coast. The island was part of the Spanish Empire until 1697, when the western portion was Peace of Ryswick, ceded to France and became Saint-Domingue, dominated by sugarcane sugar plantations in the Caribbean, plantations worked by enslaved Africans. The 1791–1804 Haitian Revolution made Haiti the first sovereign state in the Caribbean, the second republic in the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |