|
Backstory
A backstory, background story, background, or legend is a set of events invented for a plot, preceding and leading up to that plot. In acting, it is the history of the character before the drama begins, and is created during the actor's preparation. Usage As a literary device, backstory is often employed to lend depth or believability to the main story. The usefulness of having a dramatic revelation was recognized by Aristotle, in ''Poetics''. Backstories are usually revealed, partially or in full, chronologically or otherwise, as the main narrative unfolds. However, a story creator may also create portions of a backstory or even an entire backstory that is solely for their own use. Backstory may be revealed by various means, including flashbacks, dialogue, direct narration, summary, recollection, and exposition. Recollection Recollection is the fiction-writing mode whereby a character calls something to mind, or remembers it. A character's memory plays a role fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flashback (narrative)
A flashback, more formally known as analepsis, is an interjected scene (fiction), scene that takes the narrative back in time from the current point in the Plot (narrative), story. Flashbacks are often used to recount events that happened before the story's primary sequence of events to fill in crucial backstory. In the opposite direction, a flashforward (or prolepsis) reveals events that will occur in the future. Both flashback and flashforward are used to cohere a story, develop a character, or add structure to the narrative. In literature, internal analepsis is a flashback to an earlier point in the narrative; external analepsis is a flashback to a time before the narrative started. In film, flashbacks depict the subjective experience of a character by showing a memory of a previous event and they are often used to "resolve an enigma". Flashbacks are important in film noir and melodrama films. In films and television, several camera techniques, editing approaches and special e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orson Scott Card
Orson Scott Card (born August 24, 1951) is an American writer known best for his science fiction works. , he is the only person to have won a Hugo Award for Best Novel, Hugo Award and a Nebula Award for Best Novel, Nebula Award in List of joint winners of the Hugo and Nebula awards, consecutive years, winning both awards for his novel ''Ender's Game'' (1985) and its sequel ''Speaker for the Dead'' (1986). A Ender's Game (film), feature film adaptation of ''Ender's Game'', which Card coproduced, was released in 2013. Card also wrote the Locus Award for Best Fantasy Novel, Locus Fantasy Award-winning series ''The Tales of Alvin Maker'' (1987–2003). Card's fiction often features characters with exceptional gifts who make difficult choices with high stakes. Card has also written political, religious, and social commentary in his columns and other writing; his opposition to homosexuality has provoked public criticism. Card, who is a great-great-grandson of Brigham Young, was born i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiction-writing Modes
A fiction-writing mode is a manner of writing fiction, imaginary stories with its own set of conventions regarding how, when, and where it should be used. Fiction is a form of narrative, one of the four rhetorical modes of discourse. Fiction-writing also has distinct forms of expression, or modes, each with its own purposes and conventions. Currently, there is no consensus within the writing community regarding the number and composition of fiction-writing modes and their uses. Some writing modes suggested include action, dialogue, thoughts, summary, scene, description, background, exposition and transition. Overview The concept goes back at least as far as Aristotle who, in ''Poetics'', referred to narration and action as different modes or manner of representing something. For many years, fiction writing was described as having two types: narration and dialogue. Evan Marshall, in ''The Marshall Plan for Novel Writing'' (1998) noted that writers should know what they are doing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition (literary Technique)
Narrative exposition, now often simply exposition, is the insertion of background information within a narrative, story or narrative. This information can be about the Setting (narrative), setting, characters' backstory, backstories, prior plot events, historical context, etc. In literature, exposition appears in the form of expository writing embedded within the narrative. Infodumping An ''information dump'' (more commonly now, ''Infodumping, infodump'') is a large drop of information by the author to provide background they deem necessary to continue the plot. This is ill-advised in narrative and is even worse when used in dialogue. There are cases where an information dump can work, but in many instances it slows down the plot or breaks immersion for the readers. Exposition works best when the author provides only the bare minimum of surface information and allows the readers to discover as they go. Indirect exposition/incluing ''Indirect exposition'', sometimes called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
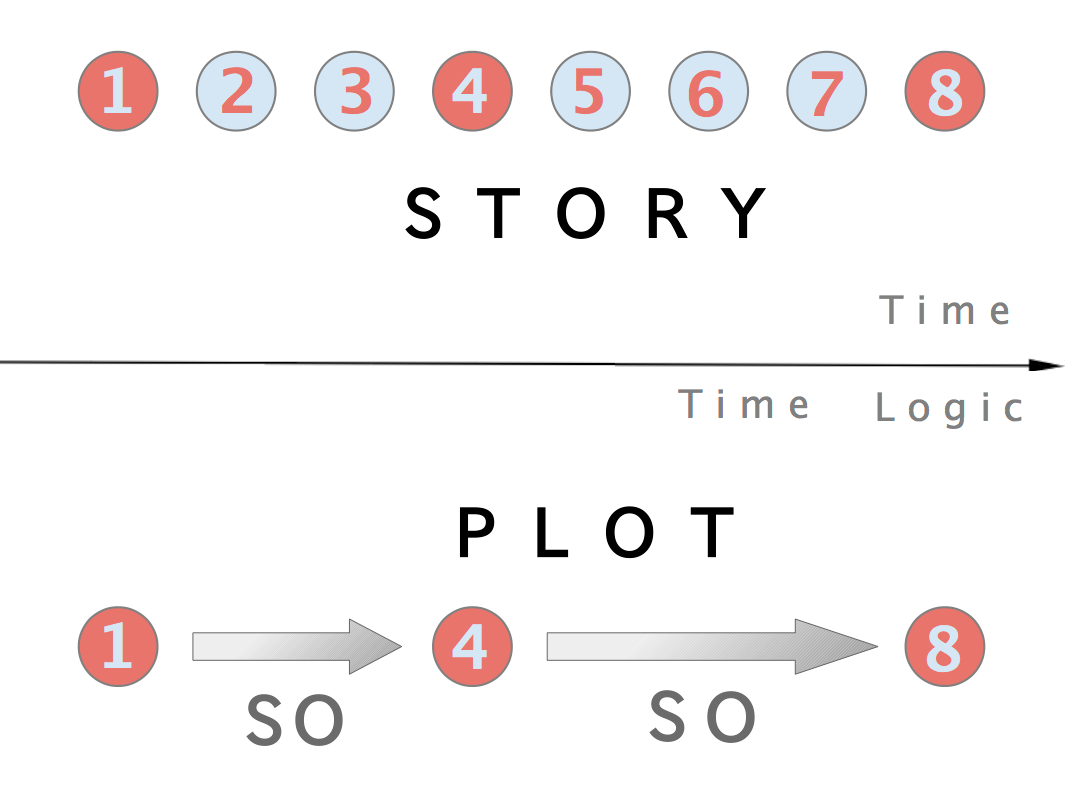
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the mapping of events in which each one (except the final) affects at least one other through the principle of Causality, cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a selective collection of events from a narrative, all linked by the connector "and so". Simple plots, such as in a traditional ballad, can be linearly sequenced, but plots can form complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The Premise (narrative), premise sets up the plot, the Character (arts), characters take part in events, while the Setting (narrative), setting is not only part of, but also influences, the final story. An can convolute the plot based on a misunderstanding. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prequel
A prequel is a literary, dramatic or cinematic work whose story precedes that of a previous work, by focusing on events that occur before the original narrative. A prequel is a work that forms part of a backstory to the preceding work. The term "prequel" is a 20th-century neologism from the prefix "pre-" (from Latin ''prae'', "before") and "sequel". Like sequels, prequels may or may not concern the same plot as the work from which they are derived. More often they explain the background that led to the events in the original, but sometimes the connections are not completely explicit. Sometimes prequels play on the audience's knowledge of what will happen next, using deliberate references to create dramatic irony. History Though the word "prequel" is of recent origin, works fitting this concept existed long before. The '' Cypria'', presupposing hearers' acquaintance with the events of the Homeric epic, confined itself to what preceded the ''Iliad'', and thus formed a kind of int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Story
In fiction, an origin story is an account or backstory revealing how a character or group of people become a protagonist or antagonist. In American comic books, it also refers to how characters gained their superpowers and/or the circumstances under which they became superheroes or supervillains. In order to keep their characters current, comic book companies, as well as cartoon companies, game companies, children's show companies, and toy companies, frequently rewrite the origins of their oldest characters. This goes from adding details that do not contradict earlier facts to a totally new origin which makes it seem that it is an altogether different character. A pourquoi story, also dubbed an "origin story", is also used in mythology, referring to narratives of how a world began, how creatures and plants came into existence, and why certain things in the cosmos have certain yet distinct qualities. Critical explorations of the origin story In ''The Superhero Reader'' (nomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative Techniques
A narrative technique (also, in fiction, a fictional device) is any of several storytelling methods the creator of a story uses, thus effectively relaying information to the audience or making the story more complete, complex, or engaging. Some scholars also call such a technique a narrative mode, though this term can also more narrowly refer to the particular technique of using a commentary to deliver a story. Other possible synonyms within written narratives are literary technique or literary device, though these can also broadly refer to non-narrative writing strategies, as might be used in academic or essay writing, as well as poetic devices such as assonance, metre, or rhyme scheme. Furthermore, narrative techniques are distinguished from narrative elements, which exist inherently in all works of narrative, rather than being merely optional strategies. Setting Plots Perspective Style Theme Character See also * Plot device * Rhetorical device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether non-fictional (memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travel literature, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller (genre), thriller, novel, etc.). Narratives can be presented through a sequence of written or spoken words, through still or moving images, or through any combination of these. The word derives from the Latin verb ''narrare'' ("to tell"), which is derived from the adjective ''gnarus'' ("knowing or skilled"). Historically preceding the noun, the adjective "narrative" means "characterized by or relating to a story or storytelling". Narrative is expressed in all mediums of human creativity, art, and entertainment, including public speaking, speech, literature, theatre, dance, music and song, comics, journalism, animation, video (including film and television), video games, radio program, radio, game, structured and play (activity), unstructu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Universe
A shared universe or shared world is a fictional universe from a set of creative works where one or more writers (or other artists) independently contribute works that can stand alone but fits into the joint development of the storyline, characters, or world of the overall project. It is common in genres like science fiction. It differs from collaborative writing in which multiple artists are working together on the same work and from crossovers where the works and characters are independent except for a single meeting. The term ''shared universe'' is also used within comics to reflect the overall milieu created by the comic book publisher in which characters, events, and premises from one product line appear in other product lines in a media franchise. A specific kind of shared universe that is published across a variety of media (such as novels and films), each of them contributing to the growth, history, and status of the setting is called an "imaginary entertainment enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuity (fiction)
In fiction, continuity is the consistency of the characteristics of people, plot, objects, and places seen by the audience over some period of time. It is relevant to many genres and forms of storytelling, especially if it is long-running. Continuity is particularly a concern in the process of film and television production due to the difficulty in rectifying errors after filming ends. Continuity can also apply to other art forms, such as novels, comics, and video games, though usually on a smaller scale; it also applies to fiction used by persons, corporations, and governments in the public eye. Most film and TV productions have a script supervisor on hand whose job is to pay attention to and attempt to maintain continuity across the chaotic and typically non-linear production schedule. It is an inconspicuous job because if done well, none may ever notice. The script supervisor gathers numerous paperwork, photographs, and other documentation which note a large quantity of detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |