|
BRI1
Brassinosteroid insensitive 1 (BRI1) is the major Receptor (biochemistry), receptor of the plant hormone brassinosteroid. It plays very important roles in plant development, especially in the control of Plant cell, cell elongation and for the tolerance of Abiotic stress, environmental stresses. BRI1 enhances cell elongation, promotes pollen development, controls Plant vasculature, vasculature development and promotes chilling and freezing tolerance. BRI1 is one of the most well studied hormone receptors and it acts a model for the study of membrane-bound receptors in plants. Structure BRI1 is an integral membrane protein. On the extracellular side of the Cell membrane, membrane lies a series of 25 leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). The LRR Protein domain, domain forms a horseshoe shape. An atypical LRR within this domain acts as the brassinosteroid binding site. Next to the LRR domain there is a single-pass Transmembrane protein, transmembrane section. The intracellular domain of BRI1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRI1-associated Receptor Kinase 1
BRI1-associated receptor kinase 1 (BAK1- also known as somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 3 or SERK3) is an important plant protein that has diverse functions in plant development. Structure BAK1 belongs to a large group of plant proteins known as the Leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases (LRR-RKs). In the model plant species ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', BAK1 and 4 other closely related proteins form a sub-group within the LRR-RK family, known as the somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases (SERKs). All 5 SERKs are transmembrane proteins. They consist of an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane pass and an intracellular domain. The extracellular domain is composed of several leucine rich repeats, and the intracellular domain functions as a protein kinase. BAK1 is thought to interact with many other LRR-RKs and the signalling output of BAK1 is dependent on its binding partner Roles in plant development Brassinosteroid signalling BAK1 was initially identified for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brassinosteroid Signalling Kinase
Brassinosteroids (BRs or less commonly BS) are a class of polyhydroxysteroids that have been recognized as a sixth class of plant hormones and may have utility as anticancer drugs for treating endocrine-responsive cancers by inducing apoptosis of cancer cells and inhibiting cancerous growth. These brassinosteroids were first explored during the 1970s when Mitchell et al. reported promotion in stem elongation and cell division by the treatment of organic extracts of rapeseed (''Brassica napus'') pollen. Brassinolide was the first brassinosteroid to be isolated in 1979, when pollen from ''Brassica napus'' was shown to promote stem elongation and cell divisions, and the biologically active molecule was isolated. The yield of brassinosteroids from 230 kg of ''Brassica napus'' pollen was only 10 mg. Since their discovery, over 70 BR compounds have been isolated from plants. Biosynthesis The BR is biosynthesised from campesterol. The biosynthetic pathway was elucidated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anatomy), organ size, pathogen defense, Stress (biology), stress tolerance and Reproduction, reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Frits Warmolt Went, Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plant, vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungus, fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLS2
''FLS'' genes have been discovered to be involved in flagellin reception of bacteria. FLS1 was the original gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ... discovered shown to correspond with a specific ecotype within '' Arabidopsis thaliana''. Even so, further studies have shown a second FLS gene known as ''FLS2'' that is also associated with flagellin reception. ''FLS2'' and FLS1 are different genes with different responsibilities, but are related genetically. ''FLS2'' has a specific focus in plant defense and is involved in promoting the MAP kinase cascade. Mutations in the ''FLS2'' gene can cause bacterial infection by lack of response to flg22. Therefore, ''FLS2''’s primary focus is association with flg22 while its secondary focus is the involvement of promoting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellin
Flagellins are a family of proteins present in flagellated bacteria which arrange themselves in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. Flagellin has a mass on average of about 40,000 daltons. Flagellins are the principal component of bacterial flagella that have a crucial role in bacterial motility. The gene that encodes for flagellin has a different name in different bacterial species such as ''flaA'' ('' Helicobacter pylori'' for example), ''fliC'', ''fljB''. Structure The structure of flagellin is responsible for the helical shape of the flagellar filament, which is important for its proper function. It is transported through the center of the filament to the tip where it polymerases spontaneously into a part of the filament. In '' E. coli'' it is unfolded by the flagellar secretion chaperone FliS () during transport. The filament is made up of eleven smaller "protofilaments", nine of which contains flagellin in the L-type shape and the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
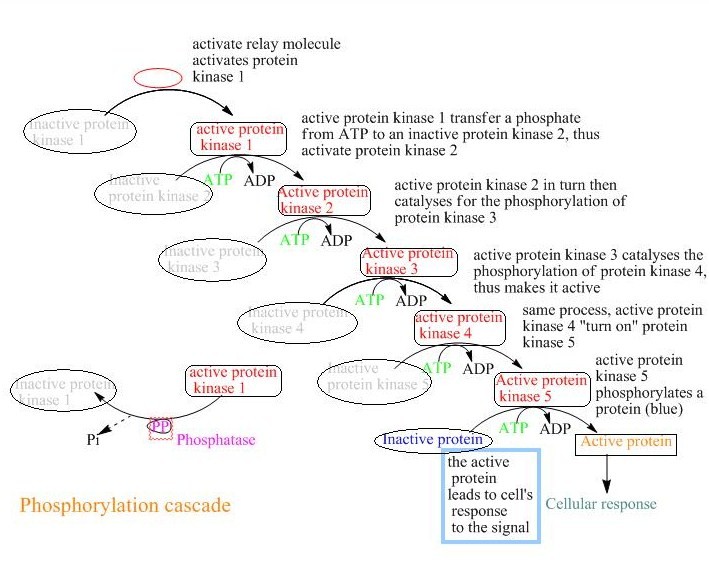
Phosphorylation Cascade
A phosphorylation cascade is a sequence of signaling pathway events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the phosphorylation of thousands of proteins. This can be seen in signal transduction of hormone messages. A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the extracellular matrix. The interactions between the molecule and receptor cause a conformational change at the receptor, which activates multiple enzymes or proteins. These enzymes activate secondary messengers, which leads to the phosphorylation of thousands of proteins. The end product of a phosphorylation cascade is the changes occurring inside the cell. These cascades work to amplify the signal where binding of one extracellular ligand can activate thousands of proteins downstream since these are allosterically regulated enzymes that make many products, amplifying the signal. MAP/ERK Phosphorylation Cascade An example of a signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally considered a weed. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome of around 135 Base pair#Length measurements, megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is an important tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and phototropism, light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual plant, annual (rarely biennial plant, biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaf, leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering Plant ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |