|
BNIP3
BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 is a protein found in humans that is encoded by the ''BNIP3'' gene. BNIP3 is a member of the apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family. It can induce cell death while also assisting with cell survival. Like many of the Bcl-2 family proteins, BNIP3 modulates the permeability state of the outer mitochondrial membrane by forming homo- and hetero-oligomers inside the membrane. Upregulation results in a decrease in mitochondrial potential, an increase in reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial swelling and fission, and an increase in mitochondrial turnover via autophagy. Sequence similarity with Bcl-2 family members was not detected. Humans and other animals (''Drosophila, Caenorhabditis''), as well as lower eukaryotes (''Dictyostelium, Trypanosoma, Cryptosporidium, Paramecium'') encode several BNIP3 paralogues including the human NIP3L, which induces apoptosis by interacting with viral and cellular anti-apoptosis proteins. Structure T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCL2-like 1 (gene)
Bcl-2-like protein 1 is a protein encoded in humans by the ''BCL2L1'' gene. Through alternative splicing, the gene encodes both of the human proteins Bcl-xL and Bcl-xS. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro- apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. The proteins encoded by this gene are located at the outer mitochondrial membrane, and have been shown to regulate outer mitochondrial membrane channel ( voltage-dependent anion channels (VDACs) opening. VDACs regulate mitochondrial membrane potential, and thus controls the production of reactive oxygen species and release of cytochrome C by mitochondria, both of which are the potent inducers of cell apoptosis. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode distinct isoforms, have been reported. The longer isoform ( Bcl-xL) acts as an apoptotic inhibitor and the sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bcl-2
Bcl-2, encoded in humans by the ''BCL2'' gene, is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of regulator proteins. BCL2 blocks programmed cell death (apoptosis) while other BCL2 family members can either inhibit or induce it. It was the first apoptosis regulator identified in any organism. Bcl-2 derives its name from ''B-cell lymphoma 2'', as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in follicular lymphomas. Orthologs (such as ''Bcl2'' in mice) have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Like BCL3, BCL5, BCL6, BCL7A, BCL9, and BCL10, it has clinical significance in lymphoma. Isoforms The two isoforms of Bcl-2, Isoform 1, and Isoform 2, exhibit a similar fold. However, results in the ability of these isoforms to bind to the BAD and BAK proteins, as well as in the structural topology and electrostatic potential of the binding groove, sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
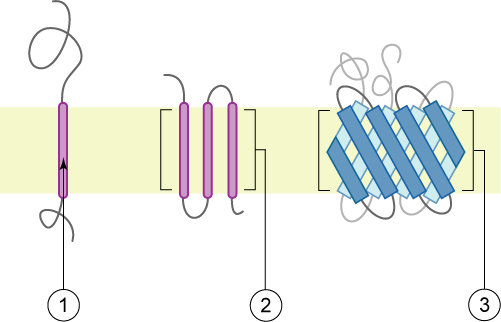
Transmembrane Domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD, TM domain) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs may consist of one or several alpha-helices or a transmembrane beta barrel. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in size and hydrophobicity; they may adopt organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracellular signals. TMDs then propagate those signals across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Transporters
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-pass membrane proteins, or as multipass membrane proteins. Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Proteins
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them ( beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-pass membrane proteins, or as multipass membrane proteins. Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. Sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence) is one of the most common indicators of homology, or common evolutionary ancestry. Some frameworks for evaluating the significance of similarity between sequences use sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families. Families are sometimes grouped together into larger clades called superfamilies based on stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD47
CD47 (Cluster of Differentiation 47) also known as integrin associated protein (IAP) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the CD47 gene. CD47 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and partners with membrane integrins and also binds the ligands thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) and signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). CD-47 acts as a ''Eat-me signals, don't eat me'' signal to macrophages of the immune system which has made it a potential therapeutic target in some cancers, and more recently, for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. CD47 is involved in a range of cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell growth, proliferation, cell adhesion, adhesion, and cell migration, migration. Furthermore, it plays a role in insulin secretion, as well as immune response, immune and angiogenic responses. CD47 is ubiquitously expressed in human cells and has been found to be overexpressed in many different tumor cells. Expression in equine cutaneous tumors has been repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Transporter
In biology, an ion transporter is a transmembrane protein that moves ions (or other small molecules) across a biological membrane to accomplish many different biological functions, including cellular communication, maintaining homeostasis, energy production, etc. There are different types of transporters including pumps, uniporters, antiporters, and symporters. Active transporters or ion pumps are transporters that convert energy from various sources—including adenosine triphosphate (ATP), sunlight, and other redox reactions—to potential energy by pumping an ion up its concentration gradient. This potential energy could then be used by secondary transporters, including ion carriers and ion channels, to drive vital cellular processes, such as ATP synthesis. This article is focused mainly on ion transporters acting as pumps, but transporters can also function to move molecules through facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion does not require ATP and allows molecules that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |