|
BLCAP
Bladder cancer-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BLCAP'' gene. Function BLCAP was identified using a differential display procedure with tumor biopsies obtained from a noninvasive and an invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Although database searches revealed no homology to any human gene at the time of identification, mouse, rat and zebrafish orthologs have since been identified. The protein appears to be down-regulated during bladder cancer progression. The protein also known as BC10 is an 87-amino-acid-long protein, but its biological functions are largely unknown. However it is a widely believed that the protein is involved in tumour suppression by decreasing cell growth through initiating apoptosis. It is widely expressed protein but expression is particularly high in brain and B lymphocytes. Alternative promoters and alternative splicing allow the protein to exist as several different transcript variants. This number is further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hydroxyl group can change the activity of the targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
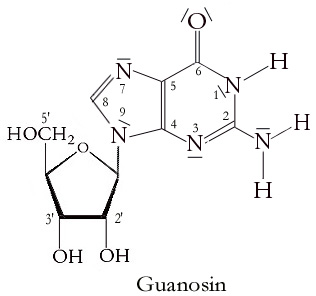
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ( ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inosine
Inosine is a nucleoside that is formed when hypoxanthine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. It was discovered in 1965 in analysis of RNA transferase. Inosine is commonly found in tRNAs and is essential for proper translation of the genetic code in wobble base pairs. Knowledge of inosine metabolism has led to advances in immunotherapy in recent decades. Inosine monophosphate is oxidised by the enzyme inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, yielding xanthosine monophosphate, a key precursor in purine metabolism. Mycophenolate mofetil is an anti-metabolite, anti-proliferative drug that acts as an inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. It is used in the treatment of a variety of autoimmune diseases including granulomatosis with polyangiitis because the uptake of purine by actively dividing B cells can exceed 8 times that of normal body cells, and, therefore, this set of white cells (which cannot operate purine salvage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Deaminase
Adenosine deaminase (also known as adenosine aminohydrolase, or ADA) is an enzyme () involved in purine metabolism. It is needed for the breakdown of adenosine from food and for the turnover of nucleic acids in tissues. Its primary function in humans is the development and maintenance of the immune system. However, the full physiological role of ADA is not yet completely understood. Structure ADA exists in both small form (as a monomer) and large form (as a dimer-complex). In the monomer form, the enzyme is a polypeptide chain, folded into eight strands of parallel α/β barrels, which surround a central deep pocket that is the active site. In addition to the eight central β-barrels and eight peripheral α-helices, ADA also contains five additional helices: residues 19-76 fold into three helices, located between β1 and α1 folds; and two antiparallel carboxy-terminal helices are located across the amino-terminal of the β-barrel. The ADA active site contains a zinc ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Untranslated Region
In molecular genetics, an untranslated region (or UTR) refers to either of two sections, one on each side of a coding sequence on a strand of mRNA. If it is found on the 5' side, it is called the 5' UTR (or leader sequence), or if it is found on the 3' side, it is called the 3' UTR (or trailer sequence). mRNA is RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosome, the site of protein synthesis (translation) within a cell. The mRNA is initially transcribed from the corresponding DNA sequence and then translated into protein. However, several regions of the mRNA are usually not translated into protein, including the 5' and 3' UTRs. Although they are called untranslated regions, and do not form the protein-coding region of the gene, uORFs located within the 5' UTR can be translated into peptides. The 5' UTR is upstream from the coding sequence. Within the 5' UTR is a sequence that is recognized by the ribosome which allows the ribosome to bind and initiate translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' derives from the expressed region and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron… must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before being translated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Editing
RNA editing (also RNA modification) is a molecular process through which some cells can make discrete changes to specific nucleotide sequences within an RNA molecule after it has been generated by RNA polymerase. It occurs in all living organisms and is one of the most evolutionarily conserved properties of RNAs. RNA editing may include the insertion, deletion, and base substitution of nucleotides within the RNA molecule. RNA editing is relatively rare, with common forms of RNA processing (e.g. splicing, 5'-capping, and 3'-polyadenylation) not usually considered as editing. It can affect the activity, localization as well as stability of RNAs, and has been linked with human diseases. RNA editing has been observed in some tRNA, rRNA, mRNA, or miRNA molecules of eukaryotes and their viruses, archaea, and prokaryotes. RNA editing occurs in the cell nucleus, as well as within mitochondria and plastids. In vertebrates, editing is rare and usually consists of a small number of chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor MRNA
Precursor or Precursors may refer to: *Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor ** The Precursor, John the Baptist Science and technology * Precursor (bird), a hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of unrelated animals * Precursor (chemistry), a compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound * Precursor (physics), a phenomenon of wave propagation in dispersive media * Precursor in the course of a disease, a state preceding a particular stage in that course * Precursor cell (biology), a unipotent stem cell * Earthquake precursor, a diagnostic phenomenon that can occur before an earthquake * Gehrlein Precursor, a glider * LNWR Precursor Class (other), classes of passenger locomotives developed for the London and North Western Railway Fiction *Precursors Halo (series), an extremely advanced race that preceded and were destroyed by The Forerunners * ''Precursor'' (novel), a 1999 novel set in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |