|
B-cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, referred to as B-PLL, is a rare blood cancer. It is a more aggressive, but still treatable, form of leukemia. Specifically, B-PLL is a prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL) that affects prolymphocytes – immature forms of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes – in the peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleen. It is an aggressive cancer that presents poor response to treatment. Mature lymphocytes are infection-fighting immune system cells. B-lymphocytes have two responsibilities: # Production of antibodies – In response to antigens, B-lymphocytes produce and release antibodies specific to foreign substances in order to aid in their identification and elimination phagocytes # Generation of memory cells – Interactions between antibodies and antigens allow B-lymphocytes to establish cellular memories, otherwise known as immunities that allow the body to respond more rapidly and efficiently to previously encountered species Classification It is categor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolymphocyte
A prolymphocyte is a white blood cell with a certain state of cellular differentiation in lymphocytopoiesis. In the 20th century it was believed that a sequence of general cell growth, maturation changed cells from lymphoblasts to prolymphocytes and then to lymphocytes (the lymphocytic series), with each being a precursor of the last. Today it is believed that the differentiation of cells in the lymphocyte line is not always simply chronologic but rather depends on antigen exposure, such that, for example, lymphocytes can become lymphoblasts. The size is between 10 and 18 μm. See also * Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell * Prolymphocytic leukemia References External links Histology at hematologyatlas.com (found in sixth row) Lymphocytes {{Developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
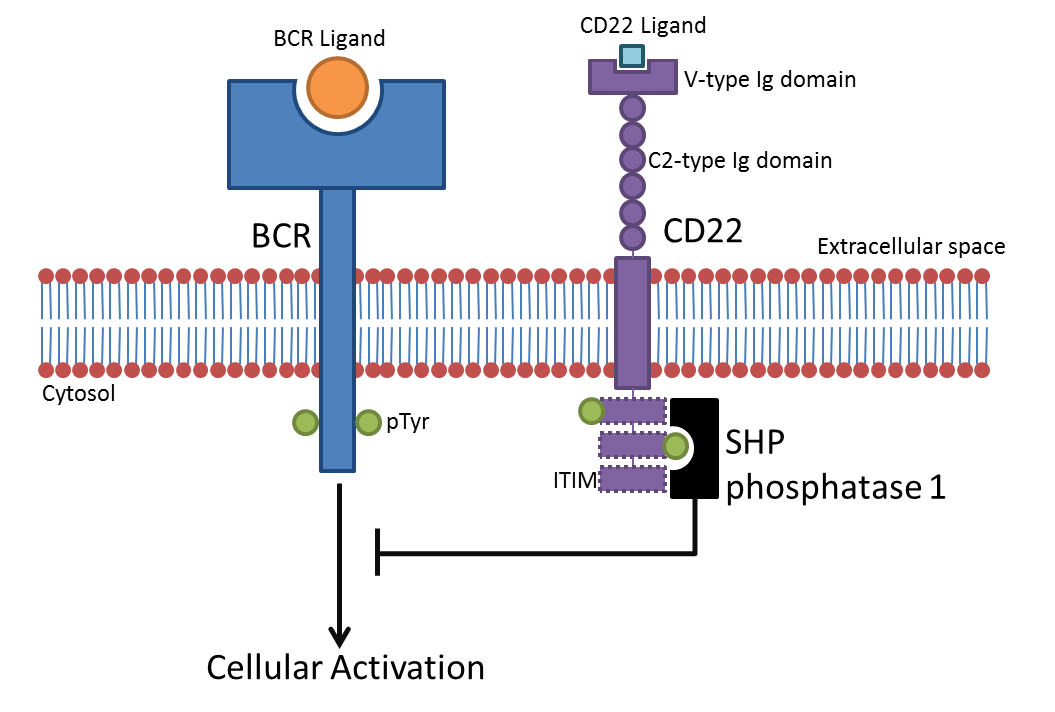
CD22
CD22, or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that prevents the overactivation of the immune system and the development of autoimmune diseases. CD22 is a sugar binding transmembrane protein, which specifically binds sialic acid with an immunoglobulin (Ig) domain located at its N-terminus. The presence of Ig domains makes CD22 a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD22 functions as an inhibitory receptor for B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. It is also involved in the B cell trafficking to Peyer's patches in mice. In mice, it has been shown that CD22 blockade restores homeostatic microglial phagocytosis in aging brains. Structure CD22 is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 140 kDa. The extracellular part of CD22 consists of seven immunoglobulin domains and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD20
B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is B lymphocyte cell-surface molecule. It is a 33-37 kDa non-glycosylated protein. CD20 is expressed on the surface of B-cells from the pre-B phase, the expression is lost in terminally differentiated plasma cells. CD20 is used as a therapeutical target of B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. Gene In humans CD20 is encoded by the ''MS4A1'' gene localized to 11q12. The gene is 16 kbp long and consists of 8 exons. There are at least 3 mRNA transcripts (resulting from alternative splicing), that are all translated into an identical full-length CD20 protein product. Variants 1 and 2 are poorly translated due to inhibitory upstream open reading frames and stem-loop structures within their 5' untranslated regions. The relative abundance of translation-competent variant 3, as opposed to the poorly translated variants 1 and 2, may be a key determinant of CD20 levels in normal and malignant human B cells and their responses to CD20-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD19
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule ( Cluster of Differentiation 19), B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene ''CD19''. In humans, CD19 is expressed in all B lineage cells. Contrary to some early doubts, human plasma cells do express CD19. CD19 plays two major roles in human B cells: on the one hand, it acts as an adaptor protein to recruit cytoplasmic signaling proteins to the membrane; on the other, it works within the CD19/ CD21 complex to decrease the threshold for B cell receptor signaling pathways. Due to its presence on all B cells, it is a biomarker for B lymphocyte development, lymphoma diagnosis and can be utilized as a target for leukemia immunotherapies. Structure In humans, CD19 is encoded by the 7.41 kilobase ''CD19'' gene located on the short arm of chromosome 16. It contains at least fifteen exons, four that encode extracellular domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NC Ratio
NC may refer to: People * Naga Chaitanya, an Indian Telugu film actor; sometimes nicknamed by the initials of his first and middle name, NC * Nathan Connolly, lead guitarist for Snow Patrol * Nostalgia Critic, the alter ego of Internet comedian Doug Walker from ''That Guy with the Glasses'' Places * New Caledonia, special collectivity of France (ISO 3166-1 country code NC) * New Canaan, a town in Connecticut, U.S. * North Carolina, a U.S. state by postal abbreviation * Northern Cyprus, a self-declared state on the island of Cyprus Science, technology, and mathematics Biology and medicine * Nasal cannula, a device used to deliver supplemental oxygen * Nasal chondrocytes, the cell type within the hyaline cartilage of the nasal septum * Neural crest, a transient component of the ectoderm * Effective number of codons, a measure to study the state of codon usage biases in genes Chemistry * (-NC) Isocyanide, an organic functional group. Computing and internet *NC (complexity) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30 nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (; : nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the cell nucleus, nucleus of eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of the nucleolus is the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Theodor Schwann in his 1839 treatise described that Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden had identified small corpuscles in nuclei, and named the structures "Kernkörperchen". In a 1947 translation of the work to English, the structure was named "nucleolus". Little was known about the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have Multinucleate, many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are Nuclear organization, structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. In addition, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells, APCs) and secrete cytokines. In mammals B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the ''B'' stands for ''bursa'' and not ''bone marrow'', as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and natural killer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include Karyotype, karyotyping, analysis of G banding, G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as Fluorescence in situ hybridization, fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunophenotyping
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspension, etc. An example is the detection of tumor markers, such as in the diagnosis of leukemia. It involves the labelling of white blood cells with antibodies directed against surface proteins on their membrane. By choosing appropriate antibodies, the differentiation of leukemic cells can be accurately determined. The labelled cells are processed in a flow cytometer, a laser-based instrument capable of analyzing thousands of cells per second. The whole procedure can be performed on cells from the blood, bone marrow Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |