|
Astana Cemetery
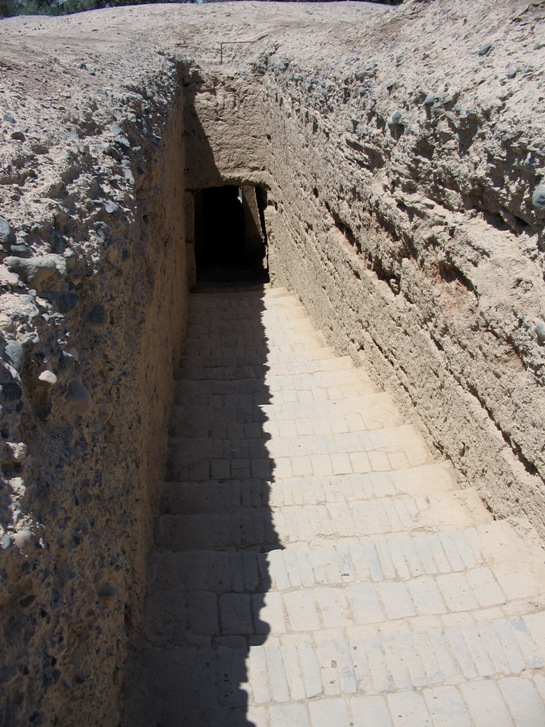
The Astana Cemetery () is an ancient cemetery southeast of Turpan, in Xinjiang, China, from the ancient city of Gaochang. It served mainly as the cemetery for the descendants of Chinese settlers in Gaochang from the 4th century to the first half of the 8th century. The complex covers and contains over 1,000 tombs. Due to the arid environment many important artifacts have been well preserved at the tombs, including natural mummies. Description of the tombs The tombs consist of sloping passageways leading downwards for 4 or 5m to a rockcut entrance, about a meter wide and over a meter high. A step then leads into a brick-lined chamber, square or oblong and measuring between two and four meters wide, three to four meters long and up to two meters high. Some tombs contain one or two narrow antechambers in which there are niches on either side for guardian beasts in effigy. These figures show a variety of animal features and some have human faces. In their exuberance they resem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the largest province-level division of China by area and the 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang borders the countries of Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both administered by China, are claimed by India. Xinjiang also borders the Tibet Autonomous Region and the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. The most well-known route of the historic Silk Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus''''.'' Dried plums are called prunes. History Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found in the wild, only around human settlements: '' Prunus domestica'' has been traced to East European and Caucasian mountains, while '' Prunus salicina'' and '' Prunus simonii'' originated in China. Plum remains have been found in Neolithic age archaeological sites along with olives, grapes and figs. According to Ken Albala, plums originated in Iran. They were brought to Britain from Asia. An article on plum tree cultivation in Andalusia (southern Spain) appears in Ibn al-'Awwam's 12th-century agricultural work, ''Book on Agriculture''. Etymology and names The name plum derived from Old English ''plume'' "plum, plum tree", borrowed from Germanic or Middle Dutch, derived from Latin ' and ultimately from Ancient Greek ''proumnon'', itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘, , also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the ''Mountains of Heaven'' or the ''Heavenly Mountain'', is a large system of mountain ranges located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Jengish Chokusu, at high. Its lowest point is the Turpan Depression, which is below sea level. One of the earliest historical references to these mountains may be related to the Xiongnu word ''Qilian'' ( zh, s=祁连, t=祁連, first=t, p=Qílián) – according to Tang commentator Yan Shigu, ''Qilian'' is the Xiongnu word for sky or heaven. Sima Qian in the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' mentioned ''Qilian'' in relation to the homeland of the Yuezhi and the term is believed to refer to the Tian Shan rather than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanshu
The ''Book of Han'' or ''History of the Former Han'' (Qián Hàn Shū,《前汉书》) is a history of China finished in 111AD, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. It is also called the ''Book of Former Han''. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modeled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. A second work, the ''Book of the Later Han'' covers the Eastern Han period from 25 to 220, and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiji
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gushi Culture
The Jushi (), or Gushi (), were a people who established a kingdom during the 1st millennium BC in the Turpan basin (modern Xinjiang, China). The kingdom included the area of Ayding Lake, in the eastern Tian Shan range. During the late 2nd and early 1st century BC, the area was increasingly dominated by the Han Dynasty and the northern neighbours of the Jushi, the Xiongnu, and became one of the many minor states of the Western Regions of Han dynasty China. The Jushi capital (Jiaohe, later known as Yarkhoto, and Yarghul) was destroyed in a Mongol attack in the 13th century. They may have been one of the Tocharian peoples and spoken one of the associated languages. Historical accounts According to J. P. Mallory and Victor H. Mair, the earliest accounts of the Jushi report them to have "lived in tents, followed the grasses and waters, and had considerable knowledge of agriculture. They owned cattle, horses, camels, sheep and goats. They were proficient with bows and arrows". Jushi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynasty' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nüwa
Nüwa, also read Nügua, is the mother goddess of Chinese mythology. She is credited with creating humanity and repairing the Pillar of Heaven. As creator of mankind, she molded humans individually by hand with yellow clay. In the Huainanzi, there is described a great battle between deities that broke the pillars supporting Heaven and caused great devastation. There was great flooding, and Heaven had collapsed. Nüwa was the one who patched the holes in Heaven with five colored stones, and she used the legs of a tortoise to mend the pillars. There are many instances of her in literature across China which detail her in creation stories, and today remains a figure important to Chinese culture. Name The character ''nü'' ( zh, t=女, l=female) is a common prefix on the names of goddesses. The proper name is ''wa'', also read as ''gua'' ( zh, t=媧). The Chinese character is unique to this name. Birrell translates it as 'lovely', but notes that it "could be construed as 'fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuxi
Fuxi or Fu Hsi (伏羲 ~ 伏犧 ~ 伏戲) is a culture hero in Chinese legend and mythology, credited along with his sister and wife Nüwa with creating humanity and the invention of music, hunting, fishing, domestication, and cooking as well as the Cangjie system of writing Chinese characters around 2,000BC. Fuxi was counted as the first of the Three Sovereigns at the beginning of the Chinese dynastic period. Origin Pangu was said to be the creation god in Chinese mythology. He was a giant sleeping within an egg of chaos. As he awoke, he stood up and divided the sky and the earth. Pangu then died after standing up, and his body turned into rivers, mountains, plants, animals, and everything else in the world, among which is a powerful being known as Huaxu (華胥). Huaxu gave birth to a twin brother and sister, Fuxi and Nüwa. Fuxi and Nüwa are said to be creatures that have faces of human and bodies of snakes. Fuxi was known as the "original god", and he was said to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
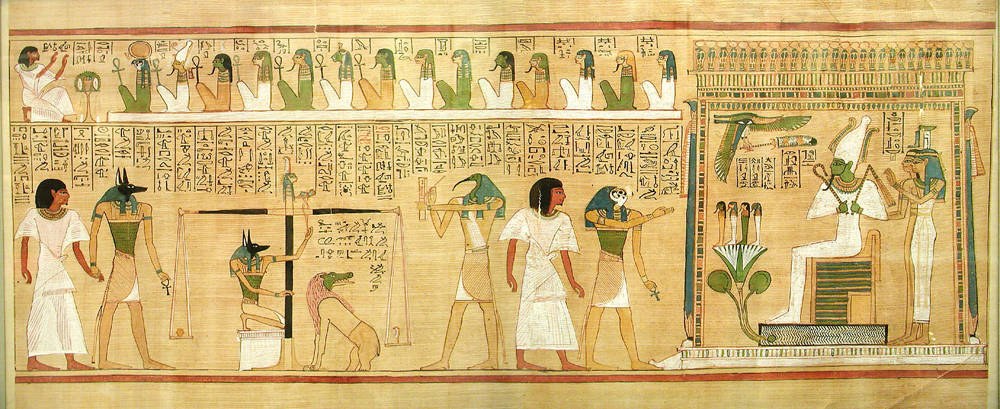
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jam Tart
A tart is a baked dish consisting of a filling over a pastry base with an open top not covered with pastry. The pastry is usually shortcrust pastry; the filling may be sweet or savoury, though modern tarts are usually fruit-based, sometimes with custard. Tartlet refers to a miniature tart; an example would be egg tarts. The categories of "tart", " flan", " quiche", and " pie" overlap, with no sharp distinctions. History The French word ''tarte'' can be translated to mean either pie or tart, as both are mainly the same with the exception of a pie usually covering the filling in pastry, while flans and tarts leave it open. Tarts are thought to have either come from a tradition of layering food, or to be a product of Medieval pie making. Enriched dough (i.e. short crust) is thought to have been first commonly used in 1550, approximately 200 years after pies. In this period, they were viewed as high-cuisine, popular with nobility, in contrast to the view of a commoners pie. Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastry
Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening (solid fats, including butter or lard) that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as '' bakers' confectionery''. The word "pastries" suggests many kinds of baked products made from ingredients such as flour, sugar, milk, butter, shortening, baking powder, and eggs. Small tarts and other sweet baked products are called pastries as a synecdoche. Common pastry dishes include pies, tarts, quiches, croissants, and pasties. The French word pâtisserie is also used in English (with or without the accent) for the same foods. Originally, the French word referred to anything, such as a meat pie, made in dough (''paste'', later ''pâte'') and not typically a luxurious or sweet product. This meaning still persisted in the nineteenth century, though by then the term more often referred to the sweet and often ornate confections implied today. Pastry can also refer to the pastry d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |