|
Armanum
Armanum, was a city-state in the ancient Near East whose location is still unknown. It lies in the same general area as Mari and Ebla. It is known from texts of the Akkadian period, during the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad. The proposed site of Armanum is Tall Bazi. Armanum is mentioned in three sources: *Year Name of Naram-Sin - Rulers of that period named the years of their reign after major events that occurred in them, in this case "The year in which Naram-Sin conquered Armanum and tore d wn itswalls". *Royal Tutelary - Afterwards, Naram-Sin added "conqueror of Armanum and Ebla" to his tutelary. *Statue Inscription - A Old Babylonian table fragment (UET 1 275) was found in Ur which was a copy of an inscription on a statue of Naram-Sin which at that time stood in the Temple of Sin next to a statue of Sin-Eribam, a ruler of Larsa. It described the military campaign during which Armanum was defeated. The text begins "As to the fact that from immemorial time, since the creation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Sin Of Akkad
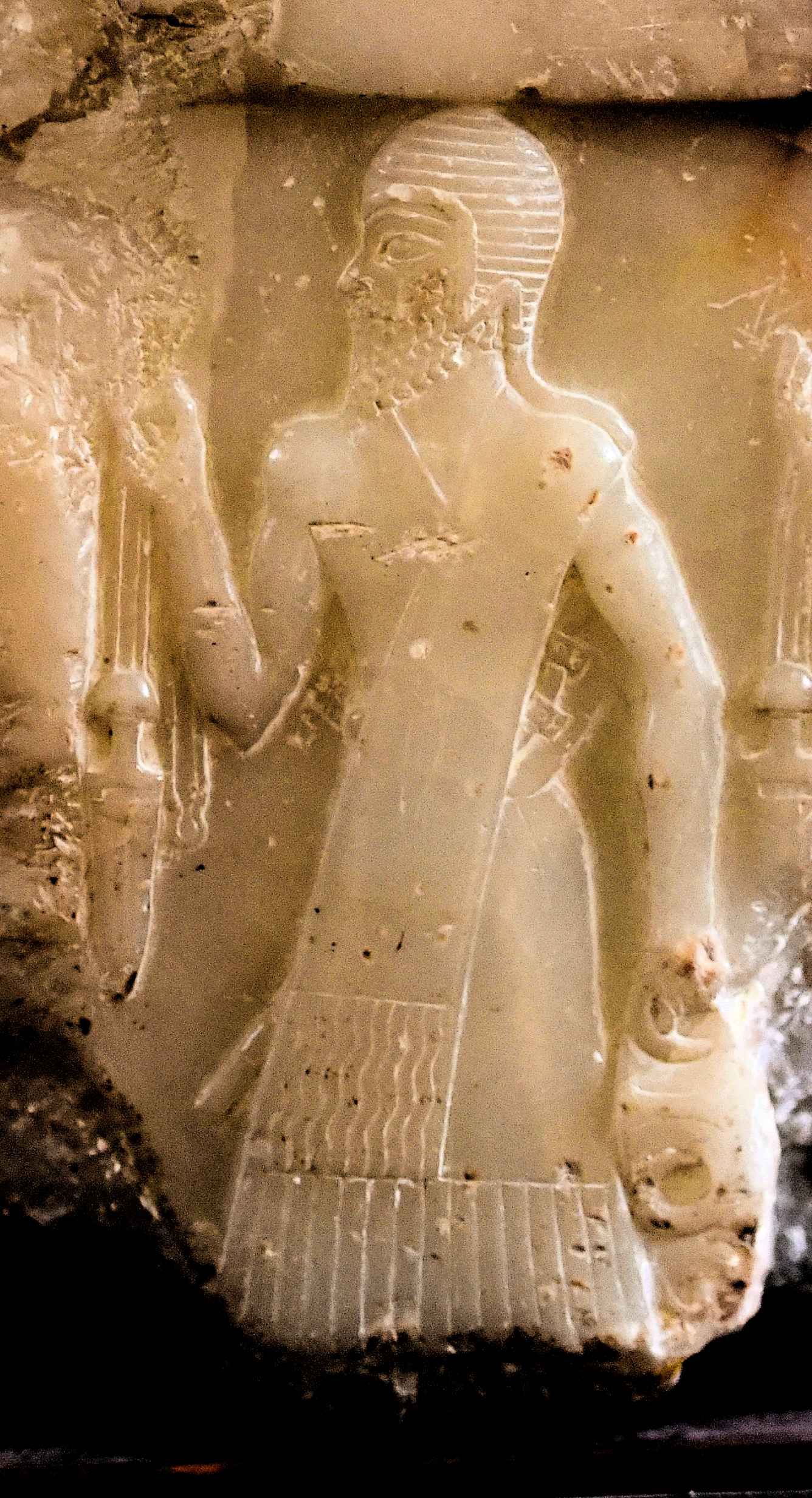
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen ( akk, : '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine"), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC ( middle chronology), and was the third successor and grandson of King Sargon of Akkad. Under Naram-Sin the empire reached its maximum strength. He was the first Mesopotamian king known to have claimed divinity for himself, taking the title "God of Akkad", and the first to claim the title " King of the Four Quarters, King of the Universe". As part of that he became city god of Akkade in the same way Enlil was city god of Nippur. Biography Naram-Sin was born as a son of Manishtushu. He was thus a nephew of King Rimush and grandson of Sargon and Tashlultum. Naram-Sin's aunt was the High Priestess En-hedu-ana. To be fully correct, rather than Naram-Sin or Naram-Suen "in Old Akkadian, the name in question should rather be reconstructed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (modern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Akkad" ''Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. ninth ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster 1985. ). The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad. Under Sargon and his successors, the Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam and Gutium. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though the meaning of this term is not p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
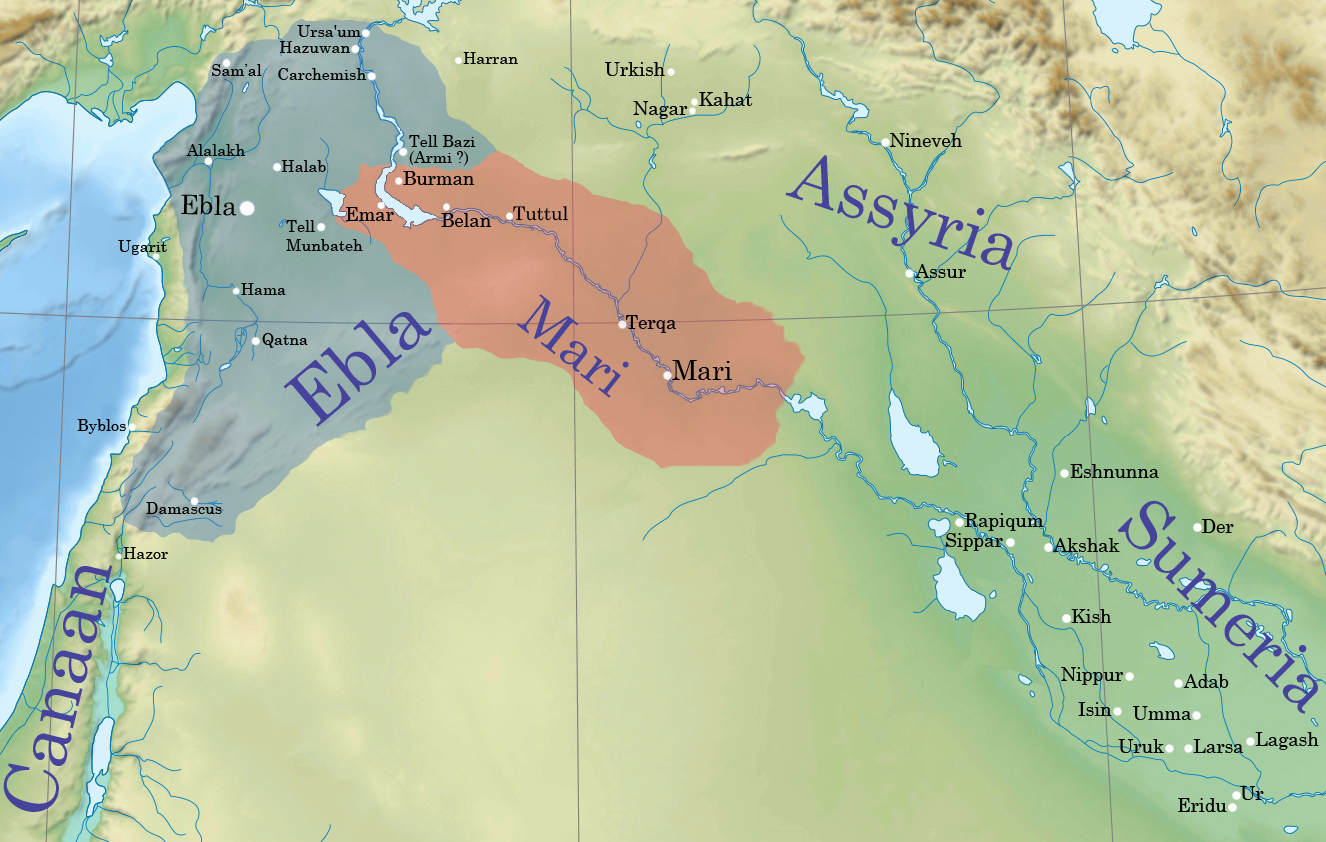
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armani (kingdom)
Armani was an ancient kingdom mentioned by Sargon of Akkad. Location Syria: ''Armani'' was mentioned alongside ''Ibla'' in the geographical treaties of Sargon. This led some historians to identify ''Ibla'' with Syrian Ebla and ''Armani'' with Syrian Armi. Mesopotamia: Michael C. Astour refused to identify ''Armani'' with Armi, as Naram-Sin makes it clear that the ''Ibla'' he sacked (in c. 2240 BC) was a border town of the land of ''Armani'', while the Armi in the Eblaite tablets is a vassal to Ebla. ''Armani'' was attested in the treaties of Sargon in a section that mentions regions located in Assyria and Babylonia or territories adjacent to the east, in contrast to the Syrian Ebla, located in the west. The later King Adad-Nirari I of Assyria also mentions ''Armani'' as being located east of the Tigris and on the border between Assyria and Babylon. Historians who disagree with the identification of Akkadian ''Armani'' with Syrian Armi place it (along with Akkadian ''Ibla'') north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Bazi
Tall Bazi, is an ancient Near East archaeological site in Raqqa Governorate of Syria in the same general area as Mari and Ebla. It is located on the Euphrates river in upper Syria, about 60 kilometers south of Turkey near the abandoned town of Tall Banat. Tall Bazi has been proposed as the location of Armanum, known from texts of the Akkadian period, during the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad. It was occupied into the Mitanni period at which time it was destroyed. In the late Roman Empire a large building was constructed at the top of the main mound. Archaeology The main mound rises 60 meters above the plain with the lower town portion being only 7 meters high. It was excavated by German archaeologists in 1993–1997, in 1999, in 2001–2005, and then in 2007–2009. At this point local conditions became too difficult to continue work. The excavations were under the auspices of the German Research Foundation and later the Institute of Near Eastern Archaeology. Due to the Tishrin Dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulul Al-Baqarat
Tulul al-Baqarat or Tulūl al-Baqarāt, is an ancient Near East archaeological site in Wasit Governorate of Iraq. It is located seven kilometers to the northeast of Tell al-Wilayah (with which it was connected by an ancient canal) and 20 kilometers south of the city of Kut. The site was occupied from the 4th millennium BC to the Islamic period. It is thought to be the site of the ancient Early Dynastic city of Kesh. History Various portions of Tulul al-Baqarat were occupied from the 4th millennium BC all the way up to the 1st millennium AD. *The main mound, TB1, was occupied in the Uruk, Jemdet Nasr, Early Dynastic, Akkadian, Ur III period, Neo-Babylonian, Parthian and Islamic periods. Occupation in the 2nd millennium BC was sparse. This mound, the largest mound, measures 330 meters by 260 meters with an area of about 10 hectares and rises to about 12 meters in height. *Mound TB2 dates to the Late Islamic period. Stone inscriptions and tablets found by the Italian excavators c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of The Ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. The largest cities of the Bronze Age Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (around 700 BC). In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin-Eribam
Sin-Eribam ruled the ancient Near East Amorite city-state of Larsa for only two years, from c. 1778 BC to 1776 BC (short chronology). Chronology of the Larsa Dynasty, E.M. Grice , C.E. Keiser, M. Jastrow, AMS Press, 1979, See also *Chronology of the ancient Near East The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ... Notes External linksSin-Eribam Year Names at CDLI Amorite kings 18th-century BC Sumerian kings Kings of Larsa 18th-century BC people {{AncientNearEast-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilaba
Ilaba was a Mesopotamian god. He is best attested as the tutelary deity of the kings of the Akkadian Empire, and functioned both as their personal god and as the city god of Akkad. Textual sources indicate he was a warlike deity, frequently described as armed with a mace. Whether he was understood as a fully independent deity or as a deified ancestor, as well as his proposed connection to the similarly named Ugaritic ancestral deity Ilib, remain a matter of dispute among researchers. He is not mentioned in any sources predating the reign of Sargon of Akkad. After the end of the Akkadian Empire, he continued to be worshiped in various cities in Mesopotamia, for example Mari, and in the Old Babylonian period he became the tutelary deity of the rulers of the Kingdom of Khana. He also continued to appear in literary texts describing the feats of Akkadian rulers and in god lists. Name and character Ilaba's name was written in cuneiform as ''Ìl-a-ba4'', DINGIR.A.MAL. It is underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Cities Of The Middle East
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)