|
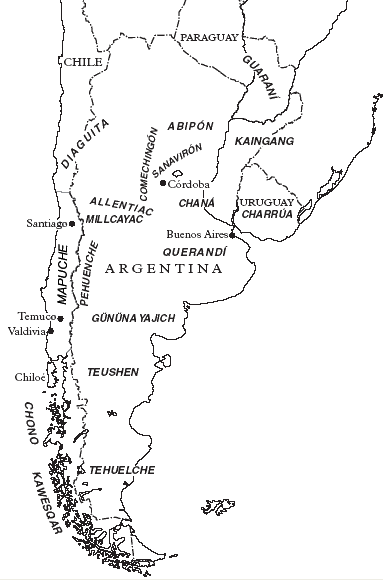
Araucanians
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arauco War
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities and force Mapuches into servitude. It subsequently evolved over time into phases comprising drawn-out sieges, slave-hunting expeditions, pillaging raids, punitive expeditions, and renewed Spanish attempts to secure lost territories. Abduction of women and war rape was common on both sides. After many initial Spanish successes in penetrating Mapuche territory, the Battle of Curalaba in 1598 and the following destruction of the Seven Cities marked a turning point in the war leading to the establishment of a clear frontier between the Spanish domains and the land of the independent Mapuche. From the 17th to the late 18th century a series of parliaments were held between royal governors and Mapuche lonkos and the war devolved to sporadic pillaging car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunco People
Cuncos or Juncos is a poorly known subgroup of Huilliche people native to coastal areas of southern Chile and the nearby inland. Mostly a historic term, Cuncos are chiefly known for their long-running conflict with the Spanish during the colonial era of Chilean history. Cuncos cultivated maize, potatoes and quinoa and raised chilihueques.Urbina 2009, p. 44. Their economy was complemented by travels during spring and summer to the coast where they gathered shellfish and hunted sea lions. They were said to live in large rukas.Alcamán 1997, p. 32. Cuncos were organized in small local chiefdoms forming a complex system intermarried families or clans with local allegiance.Alcamán 1997, p. 47. Ethnicity and identity The details of the identity of the Cuncos is not fully clear. José Bengoa defines "Cunco" as a category of indigenous Mapuche-Huilliche people in southern Chile used by the Spanish in colonial times.Bengoa 2000, p. 122. The Spanish referred to them as ''indios c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picunche
The Picunche (a Mapudungun word meaning "North People"), also referred to as ''picones'' by the Spanish, were a Mapudungun-speaking people living to the north of the Mapuches or Araucanians (a name given to those Mapuche living between the Itata and Toltén rivers) and south of the Choapa River and the Diaguitas. Until the Conquest of Chile the Itata was the natural limit between the Mapuche, located to the south, and Picunche, to the north. During the Inca attempt to conquer Chile the southern Picunche peoples that successfully resisted them were later known as the Promaucaes. The Picunche living north of the Promaucaes were called ''Quillotanes'' (those living in the Aconcagua River valley north to the Choapa) and ''Mapochoes'' (those living in the Maipo River basin) by the Spanish, and were part of the Inca Empire at the time when the first Spaniards arrived in Chile. Among the peoples the Spanish called the Promaucaes, the people of the Rapel River valley were particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moluche
The Moluche ("people from where the sun sets" or "people from the west") or Nguluche are an indigenous people of Chile. Their language was a dialect of Mapudungun, a Mapuche language. At the beginning of the Conquest of Chile by the Spanish Empire the Moluche lived in what came to be known as Araucanía. The Moluche were called ''Araucanos'' ("Araucanians") by the Spanish. Descendants of the Moluche and the Pehuenche and Huilliche later migrated into Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ... in later centuries mixing with the local tribes. This Araucanization made their language the common spoken language in the region. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter Berto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, Realm, kingdoms, republics, Confederation, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lautaro
Lautaro (Anglicized as 'Levtaru') ( arn, Lef-Traru " swift hawk") (; 1534? – April 29, 1557) was a young Mapuche toqui known for leading the indigenous resistance against Spanish conquest in Chile and developing the tactics that would continue to be employed by the Mapuche during the long-running Arauco War. Levtaru was captured by Spanish forces in his early youth, and he spent his teenage years as a personal servant of chief conquistador Pedro de Valdivia, but escaped in 1551. Back among his people he was declared toqui and led Mapuche warriors into a series of victories against the Spanish, culminating in the Battle of Tucapel in December 1553, where Pedro of Valdivia was killed. The outbreak of a typhus plague, a drought and a famine prevented the Mapuche from taking further actions to expel the Spanish in 1554 and 1555. Between 1556 and 1557, a small group of Mapuche commanded by Levtaru attempted to reach Santiago to liberate the whole of Central Chile from Spanish rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehuelche People
The Tehuelche people, also called the Aónikenk, are an indigenous people from eastern Patagonia in South America. In the 18th and 19th centuries the Tehuelche were influenced by Mapuche people, and many adopted a horseriding lifestyle. Once a nomadic people the lands of the Tehuelche were colonized in the 19th century by Argentina and Chile gradually disrupting their traditional economies. The establishment of large sheep farming estates in Patagonia was particularly detrimental to the Tehuelche. Contact with outsiders also brought in infectious diseases ushering deadly epidemics among Tehuelche tribes. Most existing members of the group currently reside the in cities and towns of Argentine Patagonia. The name "Tehuelche complex" has been used by researchers in a broad sense to group together indigenous peoples from Patagonia and the Pampas. Several specialists, missionaries and travelers have proposed grouping them together on account of the similarities in their cultural tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconcagua River
The Aconcagua River is a river in Chile that rises from the conflux of two minor tributary rivers at above sea level in the Andes, Juncal River from the east (which rise in the Nevado Juncal) and Blanco River from the south east. The Aconcagua river flows westward through the broad Aconcagua valley and enters the Pacific Ocean near the city of Concon, north of Valparaíso. The river has a course of about , and its waters irrigate the most populous sections of the Chilean provinces of San Felipe de Aconcagua and Los Andes, being the most important economic resource of those regions. During the course of the Aconcagua river, it receives contributions from many others rivers and swamps, reaching a mean flow of . The Aconcagua River valley was used as the route of the Transandine Railway on the Chilean side. The river flows alongside Chile Route 5 from Llaillay to La Calera. For much of their lengths, the two separate stretches of Chile Route 60 follow the course of the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and the Gulf of Corcovado in the southeast. All islands except the Desertores Islands form Chiloé Province. The main island is Chiloé Island. Of roughly rectangular shape, the southwestern half of this island is a wilderness of contiguous forests, wetlands and, in some places, mountains. The landscape of the northeastern sectors of Chiloé Island and the islands to the east is dominated by rolling hills, with a mosaic of pastures, forests and cultivated fields. The archipelago is known within Chile for its distinctive folklore, mythology, potatoes, cuisine and unique architecture. The culture of Chiloé is the result of mixing of Huilliche, Spanish and Chono influences in centuries of isolation without much contact with the rest of Chile o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_2007.jpg)