|
Ansbach
Ansbach (; ; East Franconian: ''Anschba'') is a city in the German state of Bavaria. It is the capital of the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Ansbach is southwest of Nuremberg and north of Munich, on the river Fränkische Rezat, a tributary of the river Main. In 2020, its population was 41,681. Developed in the 8th century as a Benedictine monastery, it became the seat of the Hohenzollern family in 1331. In 1460, the Margraves of Brandenburg-Ansbach lived here. The city has a castle known as Margrafen–Schloss, built between 1704 and 1738. It was not badly damaged during the World Wars and hence retains its original historical baroque sheen. Ansbach is now home to a US military base and to the Ansbach University of Applied Sciences. The city has connections via autobahn A6 and highways B13 and B14. Ansbach station is on the Nürnberg–Crailsheim and Treuchtlingen–Würzburg railways and is the terminus of line S4 of the Nuremberg S-Bahn. Name orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansbach University Of Applied Sciences
Ansbach (; ; East Franconian: ''Anschba'') is a city in the German state of Bavaria. It is the capital of the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Ansbach is southwest of Nuremberg and north of Munich, on the river Fränkische Rezat, a tributary of the river Main. In 2020, its population was 41,681. Developed in the 8th century as a Benedictine monastery, it became the seat of the Hohenzollern family in 1331. In 1460, the Margraves of Brandenburg-Ansbach lived here. The city has a castle known as Margrafen–Schloss, built between 1704 and 1738. It was not badly damaged during the World Wars and hence retains its original historical baroque sheen. Ansbach is now home to a US military base and to the Ansbach University of Applied Sciences. The city has connections via autobahn A6 and highways B13 and B14. Ansbach station is on the Nürnberg–Crailsheim and Treuchtlingen–Würzburg railways and is the terminus of line S4 of the Nuremberg S-Bahn. Name origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Hohenzollern
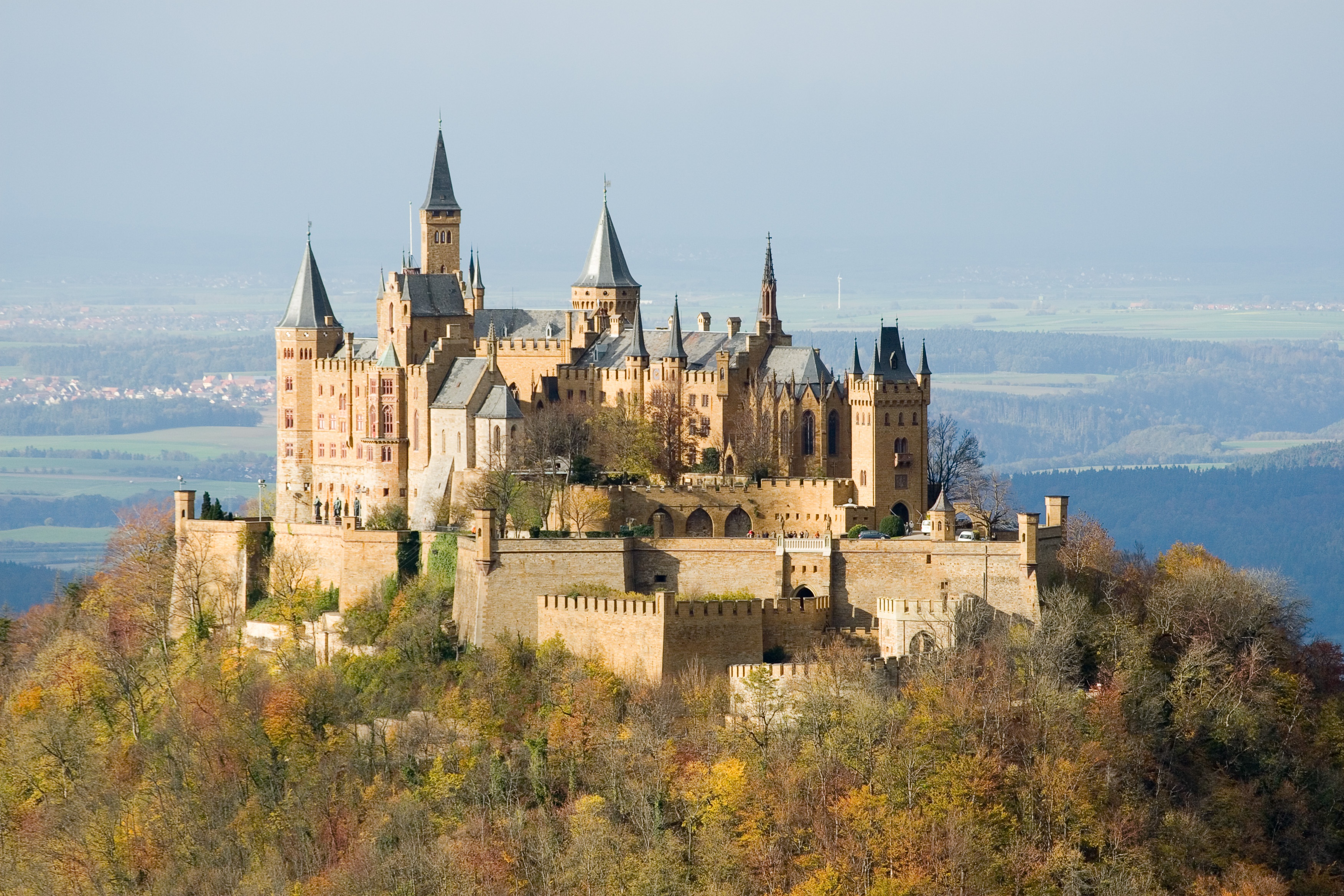
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. The family came from the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the late 11th century and took their name from Hohenzollern Castle. The first ancestors of the Hohenzollerns were mentioned in 1061. The Hohenzollern family split into two branches, the Catholic Swabian branch and the Protestant Franconian branch,''Genealogisches Handbuch des Adels, Fürstliche Häuser'' XIX. "Haus Hohenzollern". C.A. Starke Verlag, 2011, pp. 30–33. . which ruled the Burgraviate of Nuremberg and later became the Brandenburg-Prussian branch. The Swabian branch ruled the principalities of Hohenzollern-Hechingen and Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen until 1849, and also ruled Romania from 1866 to 1947. Members o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markgrafenschloß
Residenz Ansbach (Ansbach Residence), also known as Markgrafenschloß (Margrave's Palace), is a palace in Ansbach, Germany. It was the government seat of the Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach. Today it is the administrative seat of the government of Middle Franconia. The Great Hall and the Orangerie in its garden serve as venues for the biennial music festival Bachwoche Ansbach. History The palace was developed from a medieval building. From 1398 to 1400 Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg, expanded a ''Stiftshof'' outside the city walls to a water castle. Structural remains are preserved in the northwest wing of the present building. George Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach, ordered the Swabian architect Blasius Berwart (his chief architect from 1563 to 1580) to build a palace. It was erected in Renaissance style from 1565 to 1575. A large hall was built from 1565 to 1575, now called the "Gothische Halle" (Gothic Hall) because of its rib vault. It now houses the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fürst Und Markgraf Von Ansbach
The Principality or Margraviate of (Brandenburg-)Ansbach (german: Fürstentum Ansbach or ) was a principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Franconian city of Ansbach. The ruling Hohenzollern princes of the land were known as margraves, as their ancestors were margraves (so the principality was a margraviate but not a march). History The principality was established at the death of Frederick V, Burgrave of Nuremberg, on 21 January 1398, when his lands were partitioned between his two sons. The younger son, Frederick VI, received Ansbach and the elder, John III, received Bayreuth. After John III's death on 11 June 1420, the two principalities were reunited under Frederick VI, who had become Elector Frederick I of Brandenburg in 1415. Upon Frederick I's death on 21 September 1440, his territories were divided between his sons; John received the principality of Bayreuth (Brandenburg-Kulmbach), Frederick received Brandenburg, and Albert received Ansbach. Thereaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg–Crailsheim Railway
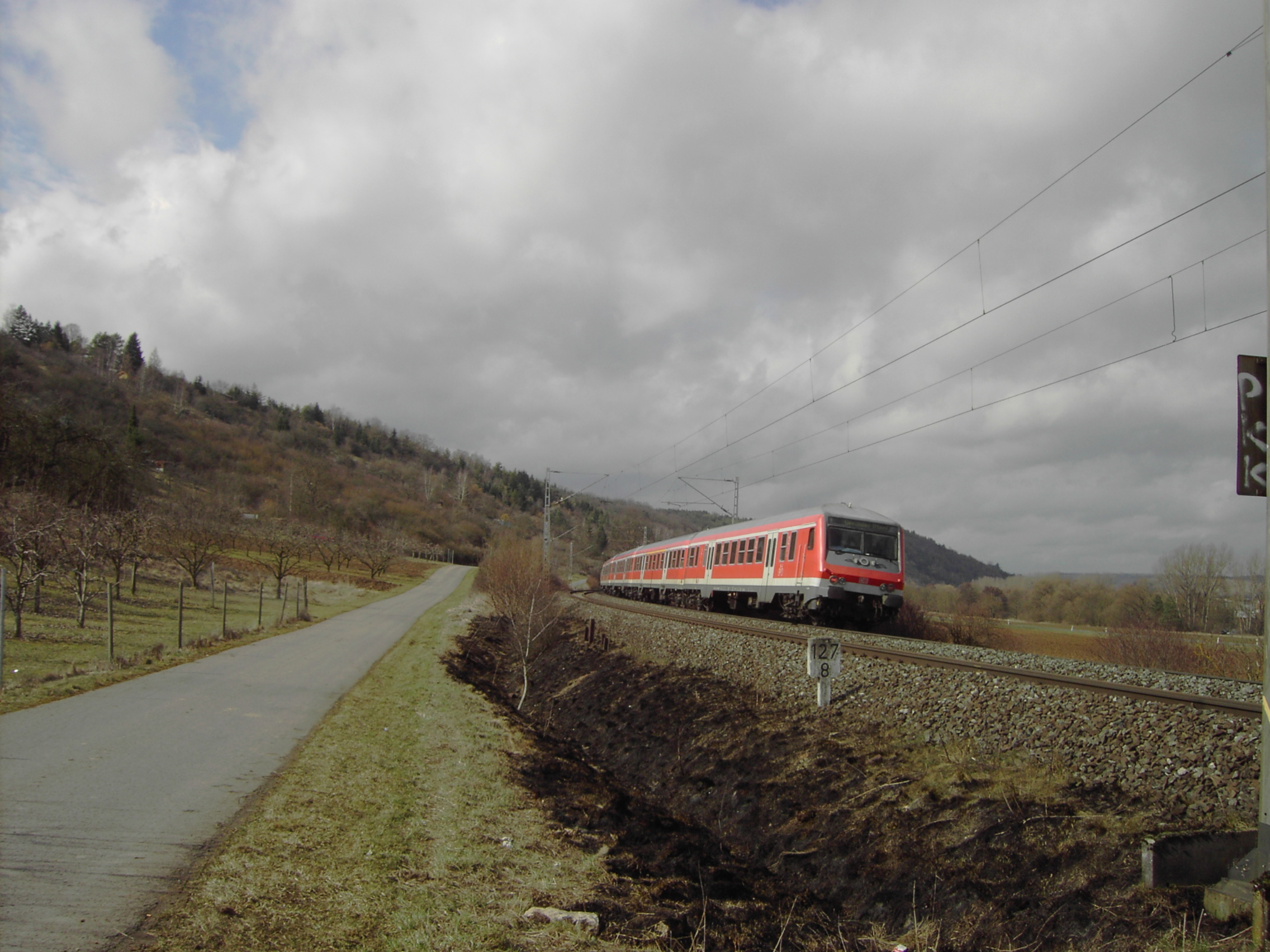
The Nuremberg–Crailsheim railway is a major railway in the north of the German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg, which links Nuremberg, Ansbach and Crailsheim. The line has the current timetable number of 891.7 and is an important German railway line. The Nuremberg–Ansbach section is used as an alternative route when problems occur for long-distance services between Nuremberg and Würzburg (via Uffenheim) and Nuremberg and Treuchtlingen (via Gunzenhausen) and to relieve the Nuremberg–Würzburg railway of some of its freight traffic. History A Bavarian politician, Gustav von Schlör advocated the planning of the line in 1862 during a tour of the route via Fürth and Zirndorf to Crailsheim. On 15 May 1875, the Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königlich Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen'') opened the Nuremberg–Ansbach section on a direct route, as the industrialist Lothar von Faber had succeeded in having the route of the line moved closer to his factories in Stein. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansbach Station
Ansbach station is the central transportation hub in the town of Ansbach in southern Germany. It is here that two main lines cross: the Nürnberg–Crailsheim and Treuchtlingen–Würzburg railways. History Ansbach was first connected to the railway network by a leased railway, that linked the town to the Ludwig South-North Railway at Gunzenhausen 28 kilometres away and which was opened on 1 July 1859. In 1869, the railway was open all the way from Würzburg to Treuchtlingen and, in 1875, it was joined by the line from Nuremberg, which was extended over the state border to Crailsheim in 1876. In 1903, the Leutershausen-Wiedersbach–Bechhofen railway was opened, whose trains were nicknamed ''Boggala'' in the Bechhofen dialect, and usually ran through to Ansbach. However it was closed as early as 28 November 1966. With the establishment of the Nuremberg Regional Transport Union (''Verkehrsverbund Großraum Nürnberg'' or ''VGN'') the line to Nuremberg was integrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treuchtlingen–Würzburg Railway
The Treuchtlingen–Würzburg railway is a 140 km long main line in the northwest of the German state of Bavaria. It runs from Treuchtlingen in southern Middle Franconia through Gunzenhausen, Ansbach, Steinach (b Rothenb), Marktbreit and Ochsenfurt to the capital of Lower Franconia, Würzburg. It was opened in three separate sections and is one of the oldest lines in Germany. History The line was built in three sections: # the line from Ansbach to Gunzenhausen was opened on 1 July 1859, # the line from Würzburg to Ansbach was opened on 1 July 1864 and # the line from Gunzenhausen to Treuchtlingen was opened on 2 October 1869. Ansbach initially had no connection with the Ludwig South-North Railway, completed between Nuremberg and Augsburg in 1849. It decided to finance a railway to Gunzenhausen. This was the third railway in Bavaria operated under lease by the Royal Bavarian State Railways after the Neuenmarkt–Bayreuth (1853) and Pasing–Starnberg (1854) rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Franconian German
East Franconian (german: Ostfränkisch) or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian (') in German, is a dialect which is spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg. East Franconian is one of the German dialects with the highest number of speakers. The scope of East Franconian is disputed, because it overlaps with neighbouring dialects like Bavarian and Swabian in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
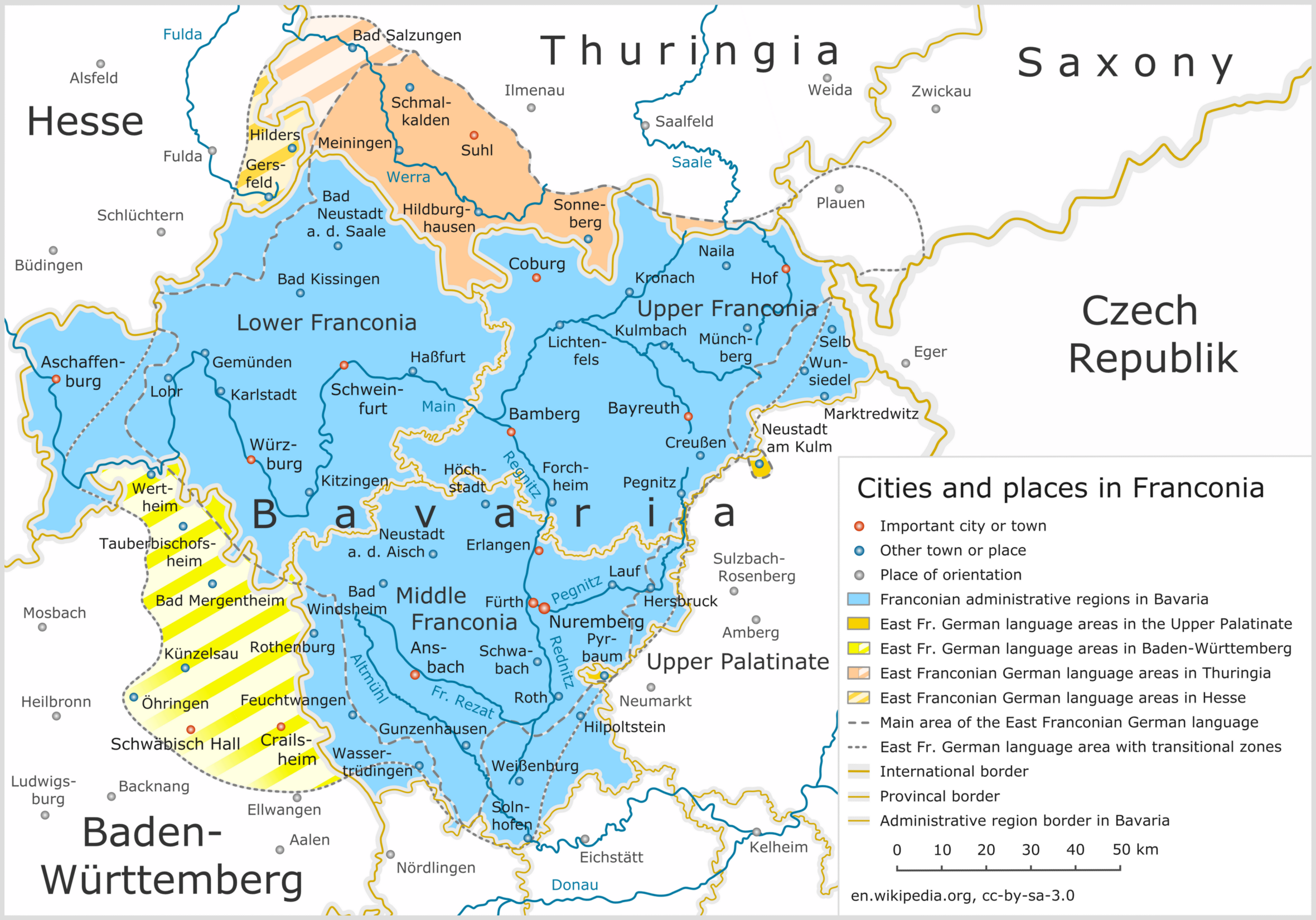
Mittelfranken
Middle Franconia (german: Mittelfranken, ) is one of the three administrative regions of Franconia in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the west of Bavaria and borders the state of Baden-Württemberg. The administrative seat is Ansbach; however, the most populous city is Nuremberg. Subdivisions The region is divided into seven districts ('Landkreise') and five independent cities ('Kreisfreie Städte'). Independent cities * Ansbach * Erlangen * Fürth * Nuremberg * Schwabach Districts * Ansbach * Erlangen-Höchstadt * Fürth * Neustadt (Aisch)-Bad Windsheim * Nürnberger Land * Roth * Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen History After the founding of the Kingdom of Bavaria the state was totally reorganised and, in 1808, divided into 15 administrative government regions (German: Regierungsbezirke (singular Regierungsbezirk)), in Bavaria called Kreise (singular: Kreis). They were created in the fashion of the French departements, quite even in size and population, and named after their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg S-Bahn
The Nuremberg S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn Nürnberg) is an S-Bahn network covering the region of Nuremberg, Fürth and Erlangen which started operations in 1987 and is now integrated into the Greater Nuremberg Transport Association (Verkehrsverbund Großraum Nürnberg). The full length of the five current lines is about 277.6 kilometres. The S-Bahn trains are operated by DB Regio Mittelfranken, a subsidiary of DB Regio Bayern. From December 2018 the service was due to be taken over by National Express Germany, however it withdrew from the bidding process on 25 October 2016, so the lines will continue to be operated by DB Regio Mittelfranken for the foreseeable future. The service between Fürth and Erlangen-Bruck has been marred by frequent delays and service restrictions due to the slow construction for four-track expansion. No completion date is given. The original plans for the upgrade of the Nuremberg Bamberg line to four tracks called for a new alignment of S-Bahn tracks east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fränkische Rezat
The Franconian Rezat (german: Fränkische Rezat) is a river in southern Germany. It is the western, left source river of the Rednitz. It rises in the Franconian Heights near Oberdachstetten. It flows generally east through the towns Lehrberg, Ansbach, Windsbach and Spalt. Together with the Swabian Rezat (), it forms the Rednitz in Georgensgmünd. See also *List of rivers of Bavaria A list of rivers of Bavaria, Germany: A * Aalbach * Abens * Ach * Afferbach *Affinger Bach *Ailsbach * Aisch * Aiterach *Alpbach * Alster * Altmühl * Alz *Amper * Anlauter * Arbach *Arbachgraben *Aschaff * Aschbach *Attel * Aubach, tributary of ... References Rivers of Bavaria Ansbach (district) Roth (district) Rivers of Germany {{Bavaria-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |