|
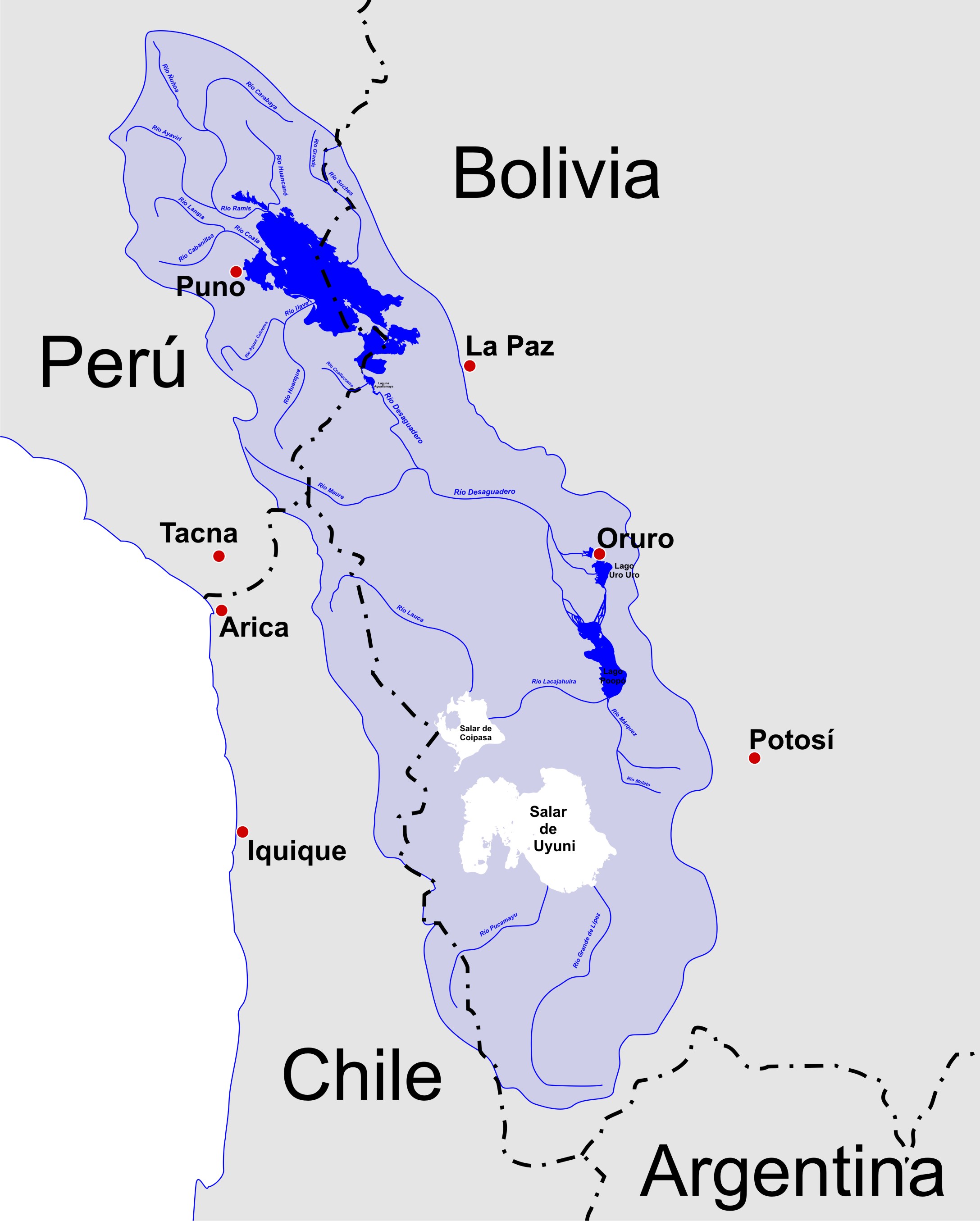
Andean Plateau
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in Bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapa Cuencas Endorréicas Meseta Del Collao
Mapa or MAPA may refer to: People * Alec Mapa (born 1965), American actor, comedian and writer * Dennis Mapa (born 1969), Filipino economist and statistician * Jao Mapa (born 1976), Filipino actor * Placido Mapa Jr. (born 1932), Filipino businessman, economist, and government official * Suraj Mapa (born 1980), Sri Lankan actor * Victorino Mapa (1855–1927), Filipino chief justice and government official Other uses * "Mapa" (song), a 2021 song by SB19 * Mexican American Political Association * Mapa (publisher), an Israeli subsidiary of Ituran * Mapa Group, a Turkish conglomerate * Mapa, a company producing latex gloves that merged with Hutchinson SA in 1973 * Most Affected People and Areas, a climate justice concept See also * * Mappa (other) * Mapah (other) Mapah may refer to: * ''Ha-Mapah'' (Hebrew: "the tablecloth"), a commentary on the Shulchan Aruch by Moses Isserles * The Mapah, title of the French mystic Simon Ganneau Simon Ganneau (born circa 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Poopó
__NOTOC__ Lake Poopó ( es, Lago Poopó ) was a large saline lake in a shallow depression in the Altiplano Mountains in Oruro Department, Bolivia, at an altitude of approximately . Because the lake was long and wide (), it made up the eastern half of the department, known as a mining region in southwest Bolivia. The permanent part of the lake body covered approximately and it was the second-largest lake in the country. The lake received most of its water from the Desaguadero River, which flows from Lake Titicaca at the north end of the Altiplano. Since the lake lacked any major outlet and had a mean depth of less than , the surface area differed greatly seasonally. In 2002 the lake was designated as a site for conservation under the Ramsar Convention. By December 2015, the lake had completely dried up, leaving only a few marshy areas. Although the lake has dried up completely twice in the past, it does not appear that it will recover this time. Suggested causes of the declin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parinacota (volcano)
Parinacota (in Hispanicized spelling), Parina Quta or Parinaquta is a dormant stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. Together with Pomerape it forms the Nevados de payachata, Nevados de Payachata volcanic chain. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit reaches an elevation of above sea level. The symmetrical cone is capped by a summit crater with widths of or . Farther down on the southern slopes lie three Parasitic vents, parasitic centres known as the Ajata cones. These cones have generated lava flows. The volcano overlies a platform formed by lava domes and Andesite, andesitic lava flows. The volcano started growing during the Pleistocene and formed a large cone. At some point between the Pleistocene and the Holocene, the western flank of the volcano collapsed, generating a giant landslide that spread west and formed a large, hummocky landslide deposit. The avalanche crossed and dammed a previously existing drainage, impounding or enlarging Chun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutupaca
Tutupaca is a volcano in the region of Tacna in Peru. It is part of the Peruvian segment of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of several volcanic belts in the Andes. Tutupaca consists of three overlapping volcanoes formed by lava flows and lava domes made out of andesite and dacite, which grew on top of older volcanic rocks. The highest of these is usually reported to be tall and was glaciated in the past. Several volcanoes in Peru have been active in recent times, including Tutupaca. Their volcanism is caused by the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South America Plate. One of these volcanoes collapsed in historical time, probably in 1802, generating a large debris avalanche with a volume likely exceeding and a pyroclastic flow. The associated eruption was among the largest in Peru for which there are historical records. The volcano became active about 700,000 years ago, and activity continued into the Holocene, but whether there were historical eruptions was initially un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


