|
Aminoacyl TRNA Synthetases, Class I
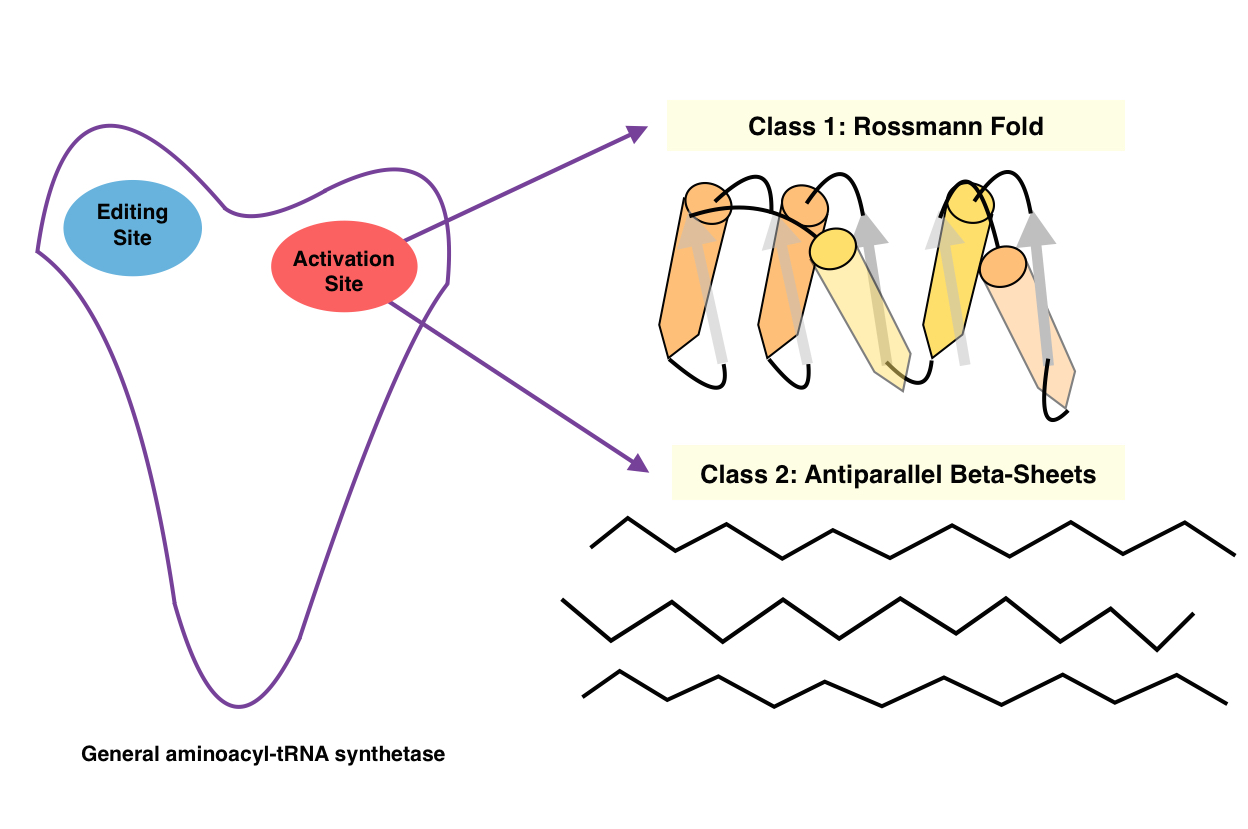
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyse the attachment of an amino acid to its cognate transfer RNA molecule in a highly specific two-step reaction. These proteins differ widely in size and oligomeric state, and have limited sequence homology. The 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are divided into two classes, I and II. Class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases contain a characteristic Rossmann fold catalytic domain and are mostly monomeric. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, class II, Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases share an anti-parallel beta-sheet fold flanked by alpha-helices, and are mostly dimeric or multimeric, containing at least three conserved regions. However, tRNA binding involves an alpha-helical structure that is conserved between class I and class II synthetases. In reactions catalysed by the class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, the aminoacyl group is coupled to the 2'-hydroxyl of the tRNA, while, in class II reactions, the 3'-hydroxyl site is preferred. The synthetases specific for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The adenylate-aaRS complex th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |