|
Amelioration Act
The Amelioration Act 1798Leeward Islands Act No. 36, vol. 1., The Laws of the Island of Antigua Consisting of the Acts of the Leeward Islands, 1690–1798, and Acts of Antigua, 1668–1845 (London: Samuel Bagster, 1805–46) (sometimes referred to as the Melioration Act or the Slavery Amelioration Act) was a statute passed by the Leeward Islands to improve the conditions of slaves in the British Caribbean colonies. It introduced financial compensation for slaves, and therefore penalties for owners, for instances of cruelty or serious neglect. The Act prohibited marriages between slaves according to Christian religious ceremony. The Act was effectively repealed by the Slave Trade Act 1807, which made it illegal to trade in slaves in any British territory. The Act applied in all of the British Leeward Island colonies in the Caribbean until its implied repeal by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. The Act is most often noted for its provisions for financial penalties for inflicting cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur William Hodge
Arthur William Hodge (1763–1811) was a plantation farmer, member of the Executive Council and Legislative Assembly, and slave owner in the British Virgin Islands, who was hanged on 8 May 1811, for the murder of one of his slaves. He was the first West Indian slave owner to be executed for the murder of a slave considered his property, and perhaps the only British West Indian slave owner, or British subject, to be executed for murdering his slave. He was not however the first white person to have been lawfully executed for the killing of a slave, as some historians have claimed. Early life Arthur William Hodge was born in the British Virgin Islands, the son of Arthur Hodge of Tortola. He studied at Oriel College, Oxford, matriculating in December 1781. He briefly served in the British Army and was commissioned as a second lieutenant in the 23rd Regiment of Foot on 3 December 1782. One of his three wives, Ann Hoggins (1779–1808), was a sister-in-law of the Marquess of Exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
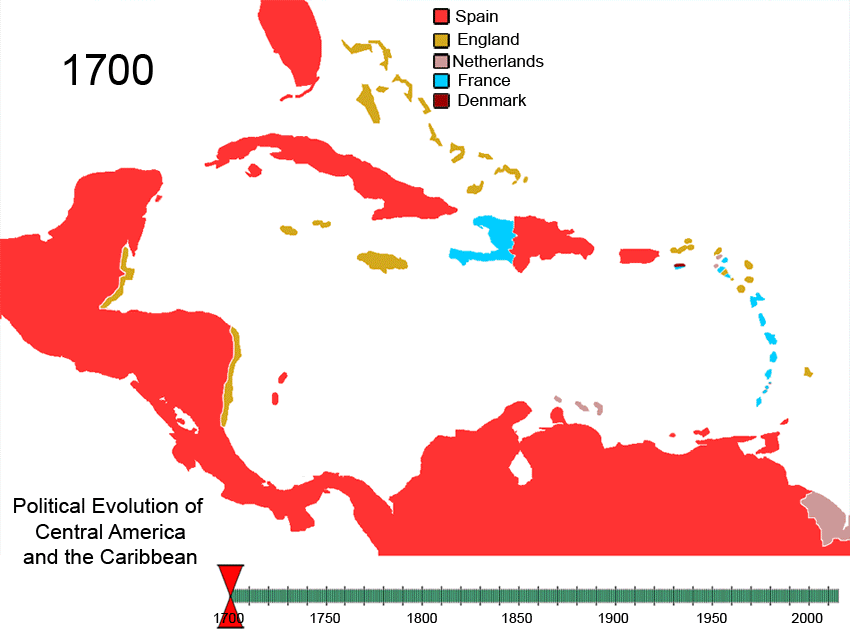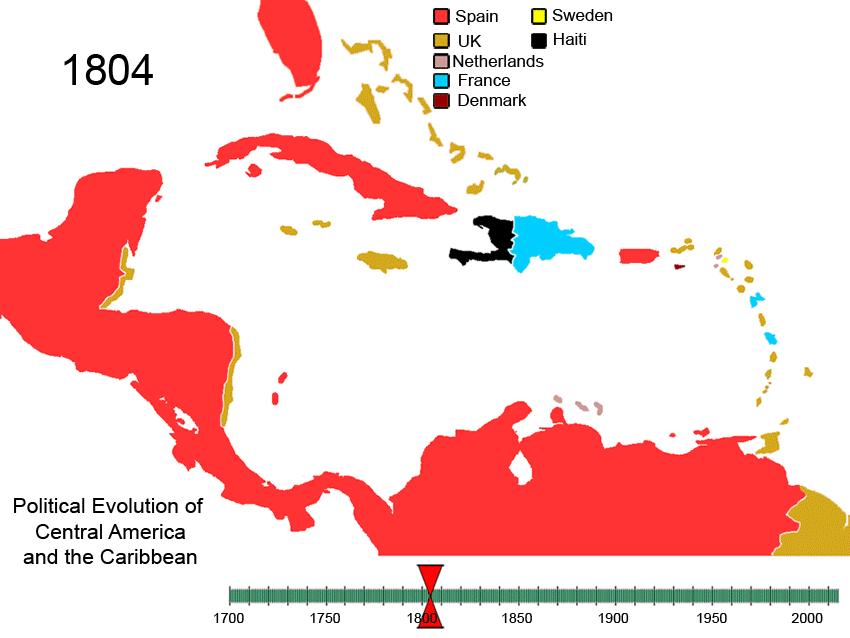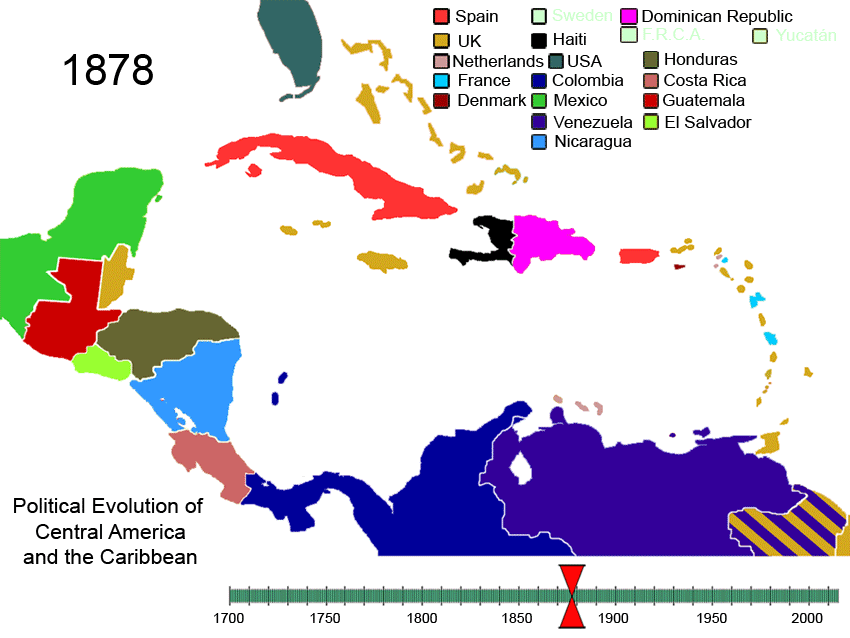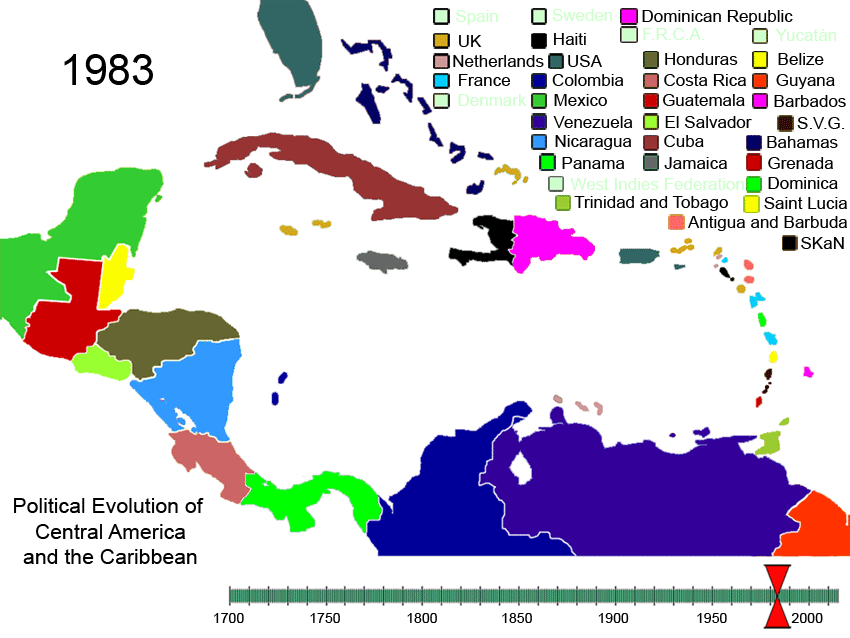
History Of The Caribbean
The history of the Caribbean reveals the significant role the region played in the colonial struggles of the European powers since the 15th century. In 1492, Christopher Columbus landed in the Caribbean and claimed the region for Spain. The following year, the first Spanish settlements were established in the Caribbean. Although the Spanish conquests of the Aztec empire and the Inca empire in the early sixteenth century made Mexico and Peru more desirable places for Spanish exploration and settlement, the Caribbean remained strategically important. From the 1620s and 1630s onwards, non-Hispanic privateers, traders, and settlers established permanent colonies and trading posts on the Caribbean islands neglected by Spain. Such colonies spread throughout the Caribbean, from the Bahamas in the North West to Tobago in the South East. Furthermore, during this period, French and English buccaneers settled on the island of Tortuga, the northern and western coasts of Hispaniola ( Haiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery Legislation
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is now outlawed in most countries of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |