|
Ali Farka Touré
Ali Ibrahim "Ali Farka" Touré (31 October 1939 – 6 March 2006) was a Malian singer and multi-instrumentalist, and one of the African continent's most internationally renowned musicians. His music blends traditional Music of Mali, Malian music and its derivative, African American blues and is considered a pioneer of African desert blues. Touré was ranked number 76 on ''Rolling Stone''s list of "The 100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time" and number 37 on Spin (magazine), ''Spin'' magazine's "100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time". Some years after his death, a group of musicians playing in his style performed as the Ali Farka Touré Allstars (2012), and later the Ali Farka Touré Band (formed 2014). Early life Touré was born in 1939 in the village of Kanau, on the banks of the Niger River in Gourma-Rharous Cercle in the northwestern Malian region of Tombouctou Region, Tombouctou. His family belonged to the Arma people, Arma community and moved to the nearby village of Niafunké ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou; Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali and one town of Songhai people. It had a population of 54,453 in the 2009 census. Timbuktu began as a seasonal settlement and became a permanent settlement early in the 12th century. After a shift in trading routes, particularly after the visit by Mansa Musa around 1325, Timbuktu flourished from the trade in salt, gold, ivory and slaves. It gradually expanded as an important Islamic city on the Saharan trade route and attracted many scholars and traders. It became part of the Mali Empire early in the 14th century. In the first half of the 15th century, the Tuareg people took control of the city for a short period until the expanding Songhai Empire absorbed the city in 1468. A Moroccan army defeated the Songhai in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Blues
Tishoumaren (ⵜⵉⵛⵓⵎⴰⵔⴻⵏ in Neo-Tifinagh script) or assouf, internationally known as desert blues, is a style of music from the Sahara region of northern and west Africa. Critics describe the music as a fusion of blues and rock music with Tuareg, Malian or North African music. Various other terms are used to describe it including desert rock, Saharan rock, Takamba, Mali blues, Tuareg rock or simply "guitar music". The style has been pioneered by Tuareg musicians in the Sahara region, particularly in Mali, Niger, Libya, Western Sahara, Algeria, Burkina Faso and others. The musical style took shape as an expression of the culture of the traditionally nomadic Tuareg people, amid their difficult sociopolitical situation, including rebellions, widespread displacement and exile in post-colonial Africa. The word ''Tishoumaren'' is derived from the French word '' chômeur'', meaning "the unemployed". The genre was first pioneered by and popularized outside of Africa by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Cote d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sierra Leone and Liberia to the south. It is sometimes referred to as Guinea-Conakry after its capital Conakry, to distinguish it from other territories in the eponymous region such as Guinea-Bissau and Equatorial Guinea. It has a population of million and an area of . Formerly French Guinea, it achieved independence in 1958. It has a history of military coups d'état.Nicholas Bariyo & Benoit FauconMilitary Faction Stages Coup in Mineral-Rich Guinea ''Wall Street Journal'' (September 5, 2021).Krista LarsonEXPLAINER: Why is history repeating itself in Guinea's coup? Associated Press (September 7, 2021).Danielle PaquettHe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochord
A monochord, also known as sonometer (see below), is an ancient musical and scientific laboratory instrument, involving one (mono-) string ( chord). The term ''monochord'' is sometimes used as the class-name for any musical stringed instrument having only one string and a stick shaped body, also known as musical bows. According to the Hornbostel–Sachs system, string bows are bar zithers (311.1) while monochords are traditionally board zithers (314). The "harmonical canon", or monochord is, at its least, "merely a string having a board under it of exactly the same length, upon which may be delineated the points at which the string must be stopped to give certain notes," allowing comparison. A string is fixed at both ends and stretched over a sound box. One or more movable bridges are then manipulated to demonstrate mathematical relationships among the frequencies produced. "With its single string, movable bridge and graduated rule, the monochord (''kanōn'' reek: law stradd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. The griot is a repository of oral tradition and is often seen as a leader due to their position as an advisor to royal personages. As a result of the former of these two functions, they are sometimes called bards. They also act as mediators in disputes. Occurrence and naming Many griots today live in many parts of West Africa and are present among the Mande peoples (Mandinka or Malinké, Bambara, Soninke etc.), Fulɓe ( Fula), Hausa, Songhai, Tukulóor, Wolof, Serer,Unesco. Regional Office for Education in Africa, ''Educafrica, Numéro 11'', (ed. Unesco, Regional Office for Education in Africa, 1984), p. 110Hale, Thomas Albert, ''Griots and Griottes: Masters of Words and Music'', Indiana University Press (1998), p. 176, Mossi, Dagomba, Maurita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 12 to 13 million – are pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai People
The Songhai people (also Ayneha, Songhay or Sonrai)'' are an ethnolinguistic group in West Africa who speak the various Songhai languages. Their history and ''lingua franca'' is linked to the Songhai Empire which dominated the western Sahel in the 15th and 16th century. Predominantly a Muslim community, the Songhai are found primarily throughout Niger and Mali in the Sahel and Sahara. The name Songhai was historically neither an ethnic nor linguistic designation, but a name for the ruling caste of the Songhai Empire which are the Songhai proper of ''sunni'' and ''Askya'' dynasty found predominantly in present-day Niger. These people call themselves ''Ayneha''. Although some Speakers in Mali have also adopted the name ''Songhay'' as an ethnic designation, other Songhay-speaking groups identify themselves by other ethnic terms such as Zarma (or Djerma, the largest subgroup) or Isawaghen. The dialect of Koyraboro Senni spoken in Gao is unintelligible to speakers of the Zarma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkey
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domesticated in Africa some years ago, and has been used mainly as a working animal since that time. There are more than 40 million donkeys in the world, mostly in underdeveloped countries, where they are used principally as draught or pack animals. While working donkeys are often associated with those living at or below subsistence, small numbers of donkeys or asses are kept for breeding or as pets in developed countries. A male donkey is known as a ''jack'' or ''jackass'', a female is a ''jenny'' or ''jennet'', and an immature donkey of either sex is a ''foal''. Jacks are often mated with female horses (mares) to produce '' mules''; the less common hybrid of a male horse (stallion) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Forces. The current Chief of Staff of the French Army (CEMAT) is General , a direct subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA). General Schill is also responsible to the Ministry of the Armed Forces for organization, preparation, use of forces, as well as planning and programming, equipment and Army future acquisitions. For active service, Army units are placed under the authority of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), who is responsible to the President of France for planning for, and use of forces. All French soldiers are considered professionals, following the suspension of French military conscription, voted in parliament in 1997 and made effective in 2001. , the French Army employed 118,600 personnel (including the Foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arma People
The Arma people are an ethnic group of the middle Niger River valley, descended from Moroccan invaders of the 16th century . The name, applied by other groups, derives from the word ''ar-rumah'' ( ar, الرماة) "fusiliers". N. Levtzion, "North-West Africa: from the Maghrib to the fringes of the forest" inThe Cambridge history of Africa, Volume 4 : c.1600-c.1790 Ed. Cambridge University Press (1975), pp.154-155 The Arma ethnicity is distinct from (but sometimes confused with) the 3.6 million Zarma people of western Niger, who predate the Moroccan invasion and speak the Zarma language, also a member of the Songhay languages. As of 1986, there were some 20,000 self-identified Arma in Mali, mostly around Timbuktu, the middle Niger bend and the Inner Niger Delta. The Songhai expedition and aftermath The 1590 expedition sent to conquer the Songhai Empire trade routes by the Saadi dynasty of Morocco was made up of four thousand Moroccan, Morisco refugees and European reneg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombouctou Region
Tombouctou Region ( Bambara: ߕߎߡߎߕߎ ߘߌߣߋߖߊ tr. Tumutu Dineja) is one of the administrative regions of Mali. For administrative purposes, the region is subdivided into five cercles. The region is part of northern Mali that was separated and declared independent by the National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA) during the Tuareg rebellion of 2012. In the course of the conflict, the MNLA lost control of the territory to Islamist militias. Tombouctou Region is world-famous for its capital, the ancient city Timbuktu (french: Tombouctou), synonymous to 19th-century Europeans with an elusive, hard-to-reach destination. The city gained fame in 1390 when its ruler, Mansa Musa, went on a pilgrimage to Mecca, stopping with his entourage in Egypt and dispensing enough gold to devalue the Egyptian currency. This started the legend of a city in the interior of Africa, where roads were said to be paved with gold and buildings topped with roofs of gold. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
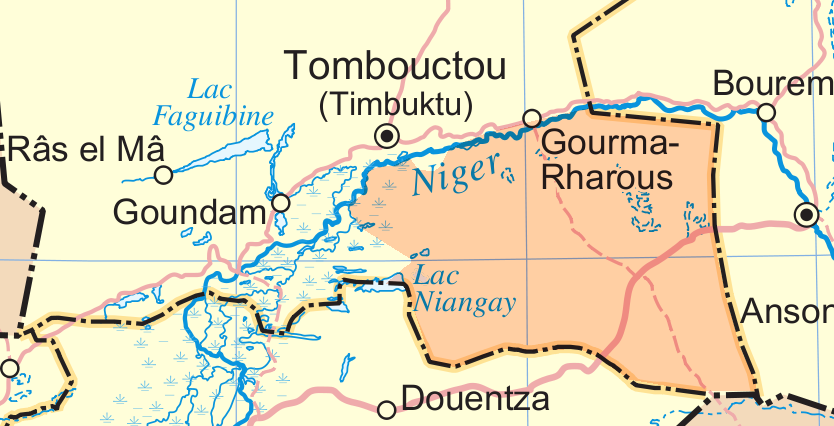
Gourma-Rharous Cercle
Gourma-Rharous Cercle is an administrative subdivision of the Tombouctou Region of Mali. The administrative center is the town of Gourma-Rharous. The route of the annual circular migration of the Gourma elephants crosses a number of communes in the cercles of Gourma-Rharous and Douentza ( Mopti Region). Lake Banzena () in the commune of Bambara Maoudé serves as an important source of water for the elephants at the end of the dry season (April to June). The cercle is divided into nine communes:. * Bambara Maoudé * Banikane *Gossi Gossi is a town and rural commune in the Cercle of Gourma-Rharous of the Tombouctou Region of Mali, lying northeast of Hombori and southwest of Gao. The town is just to the west of the main RN15 highway that links Mopti with Gao. It is on a se ... * Hamzakoma * Haribomo * Inadiatafane * Ouinerden * Rharous * Séréré References Cercles of Mali Tombouctou Region {{Tombouctou-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |