|
Alauddin Al-Kahar
Sultan Alauddin Ri'ayat Syah al-Kahar (died 29 September 1571) was the third sultan of Aceh, and was one of the strongest warrior rulers in the history of the sultanate. In his time the power structures that his father had begun were greatly strengthened. His age was marked by warfare with his Portuguese and Malay rivals, with varying degrees of success. Taking power Alauddin was the son of Sultan Ali Mughayat Syah who founded the state in the early 16th century. After Sultan Ali's death in 1530, his eldest son Salahuddin ruled for a while but was inept in governing the sultanate. The queen mother had great influence in the state and appointed a regent called ''Raja Bungsu'' who had a green ''payung'' (parasol), a symbol of authority, and a house opposite the royal abode. Meanwhile, Alauddin governed Samudra Pasai which had been conquered by Aceh in 1524. Being dissatisfied with conditions in the capital, he staged a royal coup in c. 1537 or 1539, killed ''Raja Bungsu'', and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
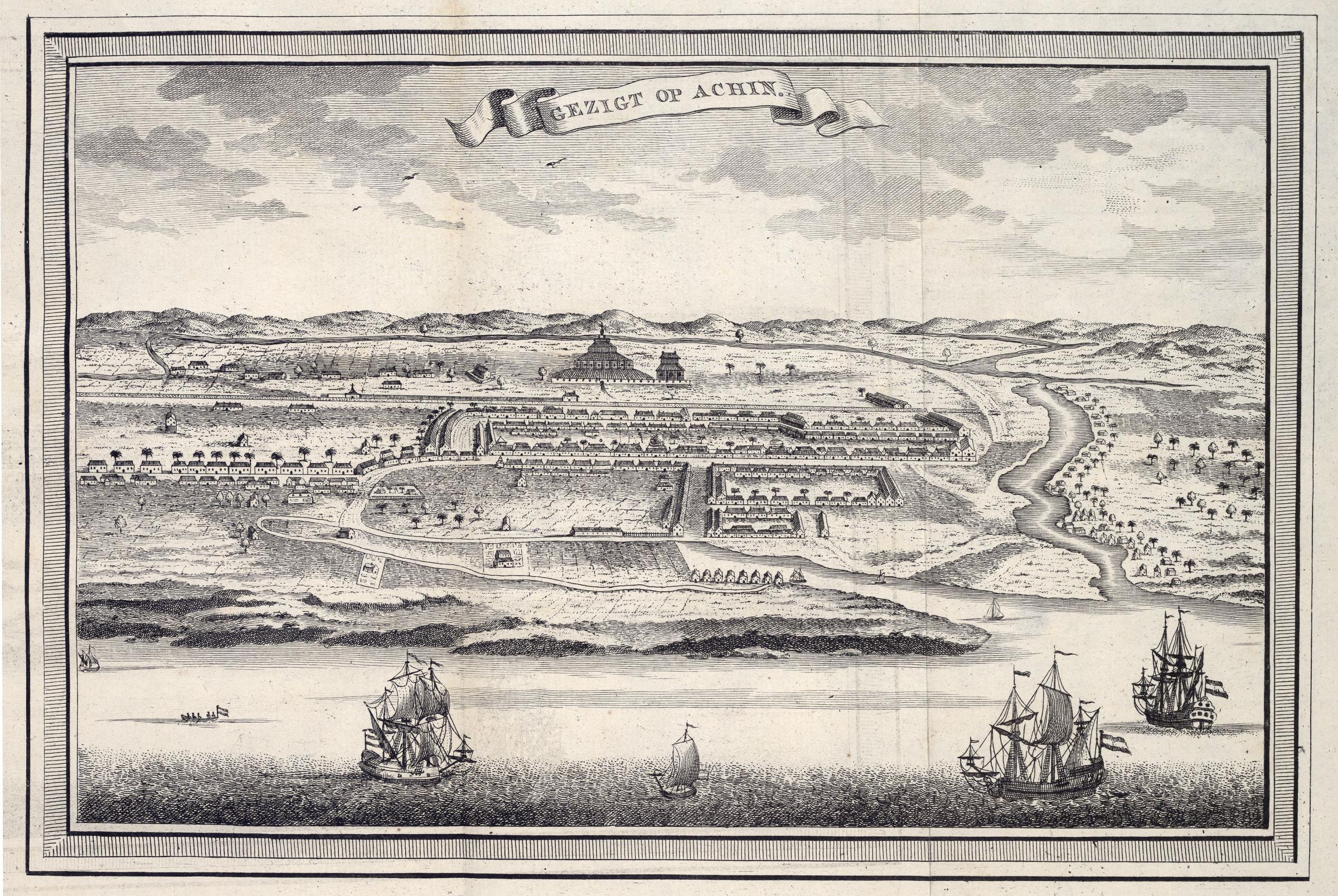
Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh ( Acehnese: ''Banda Acèh'', Jawoë: كوتا بند اچيه) is the capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra and has an elevation of . The city covers an area of and had a population of 223,446 people at the 2010 Census,Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. rising to 252,899 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 255,029.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2022. Banda Aceh is located on the northwestern tip of Indonesia at the mouth of the Aceh River. Banda Aceh itself is a semi-enclave within Aceh Besar Regency, as Banda Aceh is surrounded by Aceh Besar to the south, east, and west, while it borders with the Strait of Malacca to the north. The city was originally established as Bandar Aceh Darussalam Kandang and served as a capital and hub for the Sultanate of Aceh upon its foundation in the late 15th century. Later its name was changed to ''Bandar Aceh Darussalam'', and then it bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabar Region
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain slopes. The term is used to refer to the entire Indian coast from the western coast of Konkan to the tip of India at Kanyakumari. The peak of Anamudi, which is also the point of highest altitude in India outside the Himalayas, and Kuttanad, which is the point of least elevation in India, lie on the Malabar Coast. Kuttanad, also known as ''The Rice Bowl of Kerala'', has the lowest altitude in India, and is also one of the few places in the world where cultivation takes place below sea level. The region parallel to the Malabar Coast gently slopes from the eastern highland of Western Ghats ranges to the western coastal lowland. The moisture-laden winds of the Southwest monsoon, on reaching the southernmost point of the Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' ( Atlantic) before the Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Chinese explorers in the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman The Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳānūnī Sulṭān Süleymān) in his realm, was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1520 until his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people. Suleiman succeeded his father, Selim I, as sultan on 30 September 1520 and began his reign with campaigns against the Christian powers in central Europe and the Mediterranean. Belgrade fell to him in 1521 and the island of Rhodes in 1522–23. At Mohács, in August 1526, Suleiman broke the military strength of Hungary. Suleiman became a prominent monarch of 16th-century Europe, presiding over the apex of the Ottoman Empire's economic, military and political power. Suleiman personally led Ottoman armies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedah Sultanate
The Kedah Sultanate (كسلطانن قدح) is a Muslim dynasty located in the Malay Peninsula. It was originally an independent state, but became a British protectorate in 1909. Its monarchy was abolished after it was added to the Malayan Union but was restored and added to the Malayan Union's successor, the Federation of Malaya. The information regarding the formation of this sultanate and the history before and after its creation comes from the " Kedah Annals". The annals were written in the 18th century, over a millennium after the formation of the supposed Kedah Kingdom. It describes the first king of Kedah as arriving on the shores of Kedah as a result of an attack by a mythical gigantic beast. It states that the nation was founded by the offspring of Alexander the Great. However, Thai chronicles mention that Kedah was a Thai city like Nakhon Si Thammarat and was a part of the Siamese kingdom but later was changed into a Malay state after invasion by Muslim kingdoms until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzaffar II Of Johor
Sultan Muzaffar Shah II (1546–1570) was the second Sultan of Johor. He was known as ''Raja Muda Perdana'' before he succeeded the throne. He was installed to the throne of Johor in 1564 by the Acehnese upon the death of his father, Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah II, who died shortly after he was captured and brought back to Aceh after the Acehnese invasion of Johor. Muzaffar II moved his capital to Seluyut in 1565 from Johor Lama to assert his independence from the Acehnese. He died in 1570 of poison and was succeeded by Sultan Abdul Jalil Shah I. Personal life He had three wives. His first wife was Tun Mas Jiwa, daughter of the temenggung, Tun Hassan. His second wife was Tun Trang, daughter of Tun Ali, Seri Nara Diraja of Pahang, and Tun Fatimah. Tun Trang bore him two sons, Abdul Jalil I and Raja Radin. His third wife was the former wife of Sultan Ali Jalla Abdul Jalil Shah II and daughter of Sultan Husain Ali Riayat Shah of Aceh Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alauddin Riayat Shah II Of Johor
Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah II ibni Almarhum Sultan Mahmud Shah (died 1564) was the first sultan of Johor. He ruled Johor from 1528 to 1564. He founded the Johor Sultanate following the fall of Malacca to the Portuguese in 1511. He was the second son of Mahmud Shah of Malacca. Thus, Johor was a successor state of Malacca and Johor's sultans follow the numbering system of Malacca. Throughout his reign, he faced constant threats from the Portuguese as well as the emerging Aceh Sultanate. Founding of Johor and Portuguese threats In 1529, Alauddin Riayat founded his first capital in Hujung Tanah, known as Pekan Tua, 11 km upriver from Kota Tinggi, following the death of his father. A river fort, Kota Kara was also founded down the river. In 1535, about 400 Portuguese troops led by Estêvão da Gama invaded Johor. Kota Kara was bombarded but the Malays withstood the attack. After a few days, Portuguese troops landed and bombarded the fort but they also had to retreat. Their mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melaka Sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Melaka; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswara, also known as Iskandar Shah, although earlier dates for its founding have been proposed. At the height of the sultanate's power in the 15th century, its capital grew into one of the most important transshipment ports of its time, with territory covering much of the Malay Peninsula, the Riau Islands and a significant portion of the northern coast of Sumatra in present-day Indonesia. As a bustling international trading port, Malacca emerged as a centre for Islamic learning and dissemination, and encouraged the development of the Malay language, literature and arts. It heralded the golden age of Malay sultanates in the archipelago, in which Classical Malay became the ''lingua franca'' of Maritime Southeast Asia and Jawi script became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattani Kingdom
Patani, or the Sultanate of Patani ( Jawi: كسلطانن ڤطاني) was a Malay sultanate in the historical Pattani Region. It covered approximately the area of the modern Thai provinces of Pattani, Yala, Narathiwat and part of the northern modern-day Malaysia it is Kelantan. The 2nd–15th century state of Langkasuka and 6–7th century state of Pan Pan may or may not have been related. The golden age of Patani started during the reign of the first of its four successive queens, Raja Hijau (The Green Queen), who came to the throne in 1584 and was followed by Raja Biru (The Blue Queen), Raja Ungu (The Purple Queen) and Raja Kuning (The Yellow Queen). During this period the kingdom's economic and military strength was greatly increased to the point that it was able to fight off four major Siamese invasions. It had declined by the late 17th century and it was invaded by Siam in 1786, which eventually absorbed the state after its last raja was deposed in 1902. Predecess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perlis River
The Perlis River ( ms, Sungai Perlis) is a river in Perlis, Malaysia. Geography The river spans over 11.8 km in length, making it the fourth-longest river in Perlis. History Under the 11th Malaysia Plan, 11 km of the river will be developed and beautified, on the section from Kuala Perlis to Kangar. See also * Geography of Malaysia The geography of Malaysia includes both the physical and the human geography of Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country made up of two major landmasses separated by water—Peninsular Malaysia to the west and East Malaysia to the east—and numero ... References Rivers of Perlis Rivers of Malaysia {{Malaysia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melaka Straits
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, 500 mi (800 km) long and from 40 to 155 mi (65–250 km) wide, between the Malay Peninsula (Peninsular Malaysia) to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean). As the main shipping channel between the Indian and Pacific oceans, it is one of the most important shipping lanes in the world. It is named after the Malacca Sultanate that ruled over the strait between 1400 and 1511, the center of administration of which was located in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization define the limits of the Strait of Malacca as follows: History Early traders from Arabia, Africa, Persia, and Southern India reached Kedah before arriving at Guangzhou. Kedah served as a western port on the Malay Peninsula. They traded glassware, camphor, cotton goods, brocades, ivory, sandalwoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |