|
Air Shower (physics)
An air shower is an extensive (many kilometres wide) cascade of ionized particles and electromagnetic radiation produced in the atmosphere when a ''primary'' cosmic ray (i.e. one of extraterrestrial origin) enters the atmosphere. When a particle, which could be a proton, a nucleus, an electron, a photon, or (rarely) a positron, strikes an atom's nucleus in the air it produces many energetic hadrons. The unstable hadrons decay in the air speedily into other particles and electromagnetic radiation, which are part of the particle shower components. The secondary radiation rains down, including x-rays, muons, protons, antiprotons, alpha particles, pions, electrons, positrons, and neutrons. The dose from cosmic radiation is largely from muons, neutrons, and electrons, with a dose rate that varies in different parts of the world and based largely on the geomagnetic field, altitude, and solar cycle. Airline crews receive more cosmic rays if they routinely work flight routes that ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, which is also often called the weak force or weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interaction, and gravitation. It is the mechanism of interaction between subatomic particles that is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms: The weak interaction participates in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. The theory describing its behaviour and effects is sometimes called quantum flavourdynamics (QFD); however, the term QFD is rarely used, because the weak force is better understood by electroweak theory (EWT). The effective range of the weak force is limited to subatomic distances and is less than the diameter of a proton. Background The Standard Model of particle physics provides a uniform framework for understanding electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions. An interaction occurs when two particles (typically, but not nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrinos
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muons
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the non-elementary neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pair Production
Pair production is the creation of a subatomic particle and its antiparticle from a neutral boson. Examples include creating an electron and a positron, a muon and an antimuon, or a proton and an antiproton. Pair production often refers specifically to a photon creating an electron–positron pair near a nucleus. As energy must be conserved, for pair production to occur, the incoming energy of the photon must be above a threshold of at least the total rest mass energy of the two particles created. (As the electron is the lightest, hence, lowest mass/energy, elementary particle, it requires the least energetic photons of all possible pair-production processes.) Conservation of energy and momentum are the principal constraints on the process. All other conserved quantum numbers (angular momentum, electric charge, lepton number) of the produced particles must sum to zero thus the created particles shall have opposite values of each other. For instance, if one particle has electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroweak Interaction
In particle physics, the electroweak interaction or electroweak force is the unified description of two of the four known fundamental interactions of nature: electromagnetism and the weak interaction. Although these two forces appear very different at everyday low energies, the theory models them as two different aspects of the same force. Above the unification energy, on the order of 246 GeV,The particular number 246 GeV is taken to be the vacuum expectation value v = (G_\text \sqrt)^ of the Higgs field (where G_\text is the Fermi coupling constant). they would merge into a single force. Thus, if the temperature is high enough – approximately 1015 K – then the electromagnetic force and weak force merge into a combined electroweak force. During the quark epoch (shortly after the Big Bang), the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak force. It is thought that the required temperature of 1015 K has not been seen widely throughout the uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
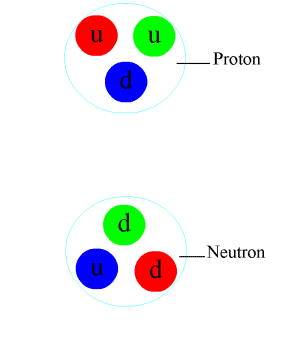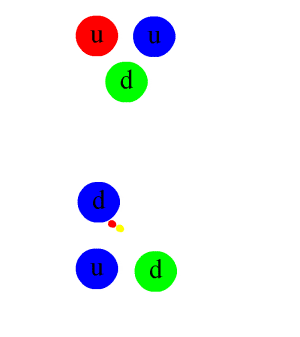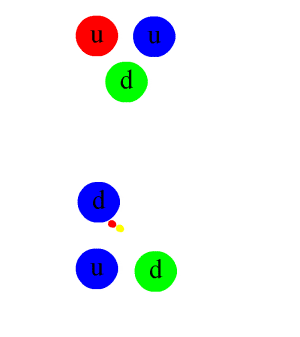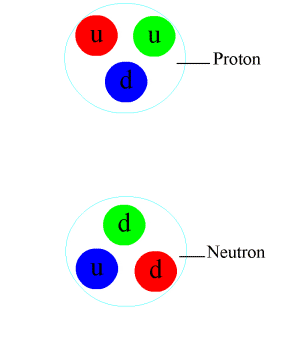
Baryon
In particle physics, a baryon is a type of composite subatomic particle which contains an odd number of valence quarks (at least 3). Baryons belong to the hadron family of particles; hadrons are composed of quarks. Baryons are also classified as fermions because they have half-integer spin. The name "baryon", introduced by Abraham Pais, comes from the Greek word for "heavy" (βαρύς, ''barýs''), because, at the time of their naming, most known elementary particles had lower masses than the baryons. Each baryon has a corresponding antiparticle (antibaryon) where their corresponding antiquarks replace quarks. For example, a proton is made of two up quarks and one down quark; and its corresponding antiparticle, the antiproton, is made of two up antiquarks and one down antiquark. Because they are composed of quarks, baryons participate in the strong interaction, which is mediated by particles known as gluons. The most familiar baryons are protons and neutrons, both of wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON. There are ontology learning companion tools which take non-annotated natural language text as input: TextToOnto (KAON-based) and Text2Onto (KAON2-based). Text2Onto is based on the Probabilistic Ontology Model (POM). In 2005, the first version of KAON2 was released, offering fast reasoning support for OWL ontologies. KAON2 is not backward-compatible with KAON. KAON2 is developed as a joint effort of the Information Process Engineering (IPE) at the Research Center for Information Technologies (FZI), the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods (AIFB) at the University of Karlsruhe, and the Information M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is an academic publisher of scientific, technical, and medical books and journals headquartered in Singapore. The company was founded in 1981. It publishes about 600 books annually, along with 135 journals in various fields. In 1995, World Scientific co-founded the London-based Imperial College Press together with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Company structure The company head office is in Singapore. The Chairman and Editor-in-Chief is Dr Phua Kok Khoo, while the Managing Director is Doreen Liu. The company was co-founded by them in 1981. Imperial College Press In 1995 the company co-founded Imperial College Press, specializing in engineering, medicine and information technology, with Imperial College London. In 2006, World Scientific assumed full ownership of Imperial College Press, under a license granted by the university. Finally, in August 2016, ICP was fully incorporated into World Scientific under the new impr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Victor Auger
Pierre Victor Auger (; 14 May 1899 – 24 December 1993) was a French physicist, born in Paris. He worked in the fields of atomic physics, nuclear physics, and cosmic ray physics. He is famous for being one of the discoverers of the Auger effect, named after him. Early life Pierre's father was chemistry professor Victor Auger. Pierre Auger was a student at the École normale supérieure in Paris from 1919 to 1922, the year when he passed the agrégation of physics. He then joined the physical chemistry laboratory of the faculté des sciences of the University of Paris under the direction of Jean Perrin to work there on the photoelectric effect. Career In 1926 he obtained his doctorate in physics from the University of Paris. In 1927, he was named assistant to the faculté des sciences of Paris and, at the same time, adjoint chief of service to l'Institut de biologie physico-chimique. Chief of work to faculty in 1934 and general secretary of the annual tables of the constants in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |