|
Aichi M6A
The is a submarine-launched attack floatplane designed for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. It was intended to operate from I-400 class submarines whose original mission was to conduct aerial attacks against the United States. Design and development From the late 1920s, the Imperial Japanese Navy had developed a doctrine of operating floatplanes from submarines to search for targets.Layman and McLaughlin 1991, p. 176. In December 1941, Commander-in-Chief of the Japanese Combined Fleet, Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, proposed constructing a large fleet of submarine aircraft carriers (also designated STo or ''sen-toku'' — special submarine) whose purpose was to mount aerial attacks against American coastal cities. The submarines would surface to launch their aircraft by catapult, submerge to avoid detection, then surface again to retrieve the aircrews who would ditch their planes nearby. By June 1942, the plan was to build a fleet of eighteen such submarines. This wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dive Bomber
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact throughout the bomb run. This allows attacks on point targets and ships, which were difficult to attack with conventional level bombers, even ''en masse''. After World War II, the rise of precision-guided munitions and improved anti-aircraft defences—both fixed gunnery positions and fighter interception—led to a fundamental change in dive bombing. New weapons, such as rockets, allowed for better accuracy from smaller dive angles and from greater distances. They could be fitted to almost any aircraft, including fighters, improving their effectiveness without the inherent vulnerabilities of dive bombers, which needed air superiority to operate effectively. Method A dive bomber dives at a steep angle, normally between 45 and 60 degrees or ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V12 Engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines. The first V12 engine was built in 1904 for use in racing boats. Due to the balanced nature of the engine and the smooth delivery of power, V12 engines were found in early luxury automobiles, boats, aircraft, and tanks. Aircraft V12 engines reached their apogee during World War II, following which they were mostly replaced by jet engines. In Formula One racing, V12 engines were common during the late 1960s and early 1990s. Applications of V12 engines in the 21st century have been as marine engines, in railway locomotives, as large stationary power as well as in some European sports and luxury cars. Design Balance and smoothness Each bank of a V12 engine essentially functions as a straight-six engine, which by itself has perfect primary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama Canal Locks
The Panama Canal locks ( es, Esclusas del Canal de Panamá) are a lock system that lifts ships up to the main elevation of the Panama Canal and down again. The original canal had a total of six steps (three up, three down) for a ship's passage. The total length of the lock structures, including the approach walls, is over . The locks were one of the greatest engineering works ever to be undertaken when they opened in 1914. No other concrete construction of comparable size was undertaken until the Hoover Dam, in the 1930s. There are two independent transit lanes, since each lock is built double. The size of the original locks limits the maximum size of ships that can transit the canal; this size is known as Panamax. Construction on the Panama Canal expansion project, which included a third set of locks, began in September 2007, finished by May 2016 and began commercial operation on 26 June 2016. The new locks allow transit of larger, New Panamax ships, which have a greater cargo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Submarine I-14
''I-14'' was an Imperial Japanese Navy Type AM submarine that served during World War II. Designed as a submarine aircraft carrier, she was commissioned in March 1945. She surrendered in August 1945 and was sunk as a target in 1946. Design and description Previous Type A submarines — both Type A1 and Type A2 — were submarine aircraft carriers capable of carrying a single reconnaissance floatplane and fitted with command facilities so that they could serve as flagships for embarked admirals and their staffs. The Type AM submarines were versions of the preceding Type A2, but with the command facilities replaced by an enlarged aircraft hangar fitted for a pair of Aichi M6A1 ''Seiran'' ("Clear Sky Storm") floatplane bombers.Layman & McLaughlin, p. 176 They displaced surfaced and submerged. The submarines were long overall and had a beam of and a draft of . They had a diving depth of .Bagnasco, p. 189 For surface running, the submarines were powered by two diesel engines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Submarine I-13
''I-13'' was an Imperial Japanese Navy Type AM submarine that served during World War II. Designed as a submarine aircraft carrier, she was commissioned in December 1944 and sunk in July 1945. Design and description Previous Type A submarines — both Type A1 and Type A2 — were submarine aircraft carriers capable of carrying a single reconnaissance floatplane and fitted with command facilities so that they could serve as flagships for embarked admirals and their staffs. The Type AM submarines were versions of the preceding Type A2, but with the command facilities replaced by an enlarged aircraft hangar fitted for a pair of Aichi M6A1 ''Seiran'' ("Clear Sky Storm") floatplane bombers.Layman & McLaughlin, p. 176 They displaced surfaced and submerged. The submarines were long overall and had a beam of and a draft of . They had a diving depth of .Bagnasco, p. 189 For surface running, the submarines were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Submarine I-401
was an Imperial Japanese Navy ''Sentoku''-type (or ''I-400''-class) submarine commissioned in 1945 for service in World War II. Capable of carrying three two-seat Aichi M6A1 "Seiran" (Mountain Haze) float-equipped torpedo bombers, the ''Sentoku''-class submarines were built to launch a surprise air strike against the Panama Canal. Until 1965, the ''Sentaku''-type submarines — ''I-401'' and her sister ships and — were the largest submarines ever commissioned. Design and description The ''I-400''-class submarines had four diesel engines and carried enough fuel to circumnavigate the world one-and-a-half times. Measuring long overall, they displaced , more than double their typical American contemporaries. Until the commissioning of the United States Navy ballistic missile submarine in 1965, the ''I-400''-class were the largest submarines ever commissioned. The cross-section of the pressure hull had a unique figure-of-eight shape which afforded the strength and stability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IJN 6th Fleet
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) that during World War II, had primary responsibility for the command of submarine operations. History The 6th Fleet was formed on 15 November 1940, and was assigned general control of all IJN submarine operations. Its initial mission was reconnaissance off the west coast of the United States, east coast of Australia, and the sea lanes of the Indian Ocean. Background Japan had prior to the attack on Pearl Harbor a diverse submarine fleet, some of which had unique distinctions: the only submarines in existence of over 5,000 tons submerged displacement, submarines over 400 feet in length (until the advent of nuclear power), the 41 submarines in its retinue (and of the world) that could carry specially designed aircraft, and submarines with the longest ranges and highest speeds of any nation. With the development of the Type 95 submarine-launched variant of the Long Lance oxygen-propelled torpedo, Japan not only had the world's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type AM Submarine
The , also called was a pair of large, aircraft-carrying cruiser submarines built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. Design and description The Type AM submarines were versions of the preceding A2 class with the command facilities replaced by an enlarged aircraft hangar, which was fitted for a pair of Aichi M6A1 floatplane bombers.Layman & McLaughlin, p. 176 They displaced surfaced and submerged. The submarines were long, had a beam of and a draft of . They had a diving depth of .Bagnasco, p. 189 The machinery was reduced in power from the A2-class boats. For surface running, the boats were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater.Chesneau, p. 200 On the surface, the ''AM''s had a range of at ; submerged, they had a range of at . The boats were armed with six internal bow torpedo tubes and carried a total o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
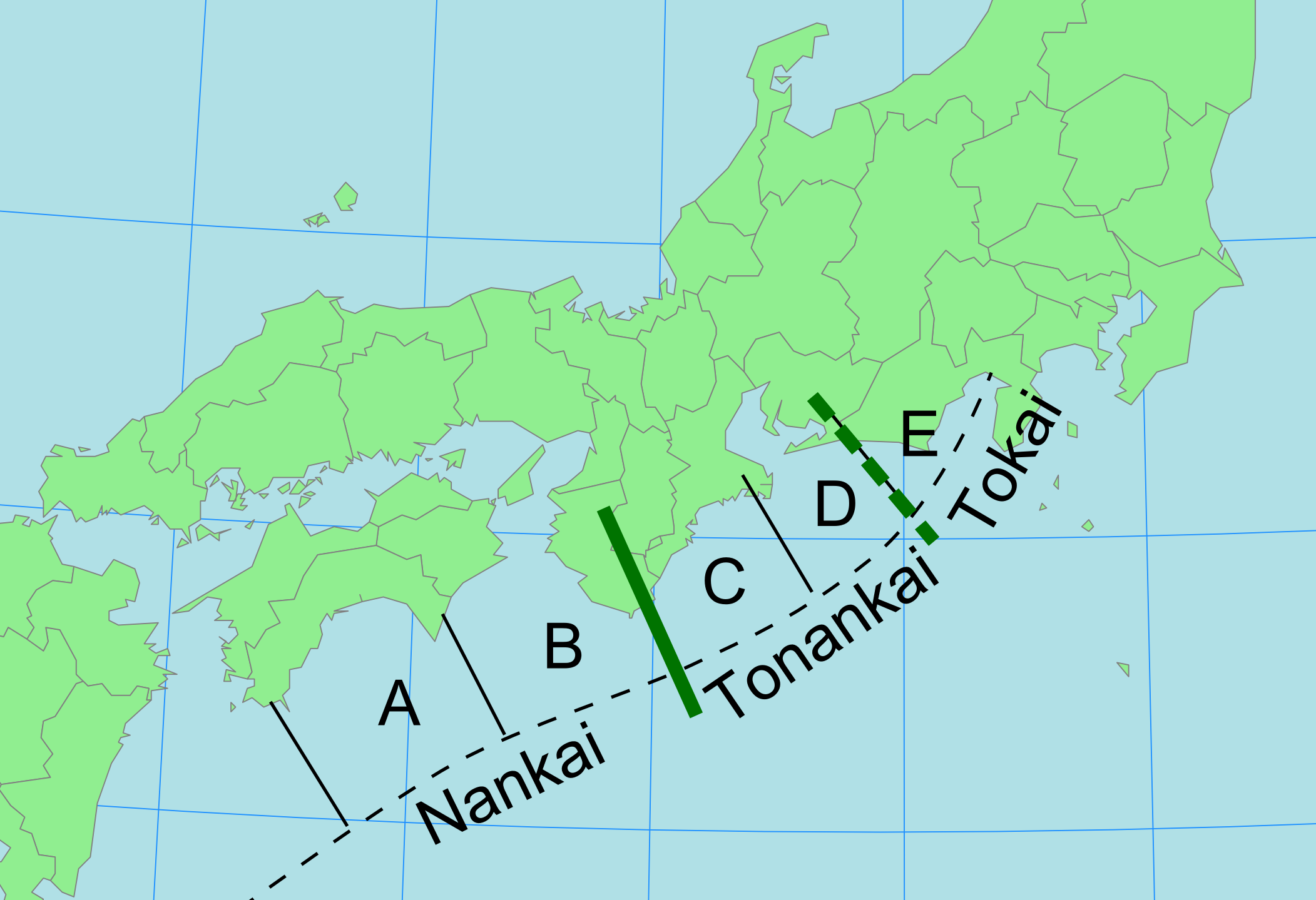
1944 Tōnankai Earthquake
The 1944 Tōnankai earthquake occurred at 13:35 local time (04:35 UTC) on 7 December. It had an estimated magnitude of 8.1 on the moment magnitude scale (making it the strongest known earthquake of 1944) and a maximum felt intensity of greater than 5 Shindo (about VIII (''Severe'') on the Mercalli intensity scale). It triggered a large tsunami that caused serious damage along the coast of Wakayama Prefecture and the Tōkai region. Together, the earthquake and tsunami caused 3,358 casualties. Tectonic setting The southern coast of Honshū runs parallel to the Nankai Trough, which marks the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate. Movement on this convergent plate boundary leads to many earthquakes, some of them of megathrust type. The Nankai megathrust has five distinct segments (A–E) that can rupture independently, the segments have ruptured either singly or together repeatedly over the last 1300 years. Megathrust earthquakes on this structure tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Stabilizer
A vertical stabilizer or tail fin is the static part of the vertical tail of an aircraft. The term is commonly applied to the assembly of both this fixed surface and one or more movable rudders hinged to it. Their role is to provide control, stability and trim in yaw (also known as directional or weathercock stability). It is part of the aircraft empennage, specifically of its stabilizers. The vertical tail is typically mounted on top of the rear fuselage, with the horizontal stabilizers mounted on the side of the fuselage (a configuration termed "conventional tail"). Other configurations, such as T-tail or twin tail, are sometimes used instead. Vertical stabilizers have occasionally been used in motor sports, with for example in Le Mans Prototype racing. Function Principle The vertical tail of an aircraft typically consists of a fixed vertical stabilizer or fin on which a movable rudder is mounted. A trim tab may similarly be mounted on the rudder. Together, their role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Landing Gear
Conventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 133. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. From the Ground Up, 27th edition, page 11 The term taildragger is also used, although some argue it should apply only to those aircraft with a tailskid rather than a wheel. The term "conventional" persists for historical reasons, but all modern jet aircraft and most modern propeller aircraft use tricycle gear. History In early aircraft, a tailskid made of metal or wood was used to support the tail on the ground. In most modern aircraft with conventional landing gear, a small articulated wheel assembly is attached to the rearmost part of the airframe in place of the skid. This wheel may be steered by the pilot through a connection to the rudder pedals, allowing the rudd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trainer (aircraft)
A trainer is a class of aircraft designed specifically to facilitate flight training of pilots and aircrews. The use of a dedicated trainer aircraft with additional safety features—such as tandem flight controls, forgiving flight characteristics and a simplified cockpit arrangement—allows pilots-in-training to safely advance their skills in a more forgiving aircraft. Civilian pilots are normally trained in a light aircraft, with two or more seats to allow for a student and instructor. Tandem and side by side The two seating configurations for trainer aircraft are: pilot and instructor side by side, or in tandem, usually with the pilot in front and the instructor behind. The side-by-side seating configuration has the advantage that pilot and instructor can see each other's actions, allowing the pilot to learn from the instructor and the instructor to correct the student pilot. The tandem configuration has the advantage of being closer to the normal working environment that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |