|
Adenosine Receptor Antagonists
Adenosine (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine triphosphate, adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supravent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA. List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases The reason for 2 symbols, shorter and longer, is that the shorter ones are better for contexts where explicit disambiguation is superfluous (because context disambiguates) and the longer ones are for contexts where explicit disambiguation is judged to be needed or wise. For example, when discussing long nucleobase sequences in genomes, the CATG symbol system is much preferable to the Cyt-Ade-Thy-Gua symbol system (see '' N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers ( atria) of the heart, rather than from the sinoatrial node, the normal origin of the heart's electrical activity. As with any other form of tachycardia (rapid heart beat), the underlying mechanism can be either the rapid discharge of an abnormal focus, the presence of a ring of cardiac tissue that gives rise to a circle movement (reentry), or a triggered rapid rhythm due to other pathological circumstances (as would be the case with some drug toxicities, such as digoxin toxicity). Classification Forms of atrial tachycardia (ATach) include multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT), focal atrial tachycardia and atrial flutter. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) is an episode of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antecubital Fossa
The cubital fossa, chelidon, or elbow pit, is the triangular area on the anterior side of the upper limb between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin ) when in standard anatomical position. Boundaries * superior (proximal) boundary – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus * medial (ulnar) boundary – lateral border of pronator teres muscle originating from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. * lateral (radial) boundary – medial border of brachioradialis muscle originating from the lateral supraepicondylar ridge of the humerus. * apex – it is directed inferiorly, and is formed by the meeting point of the lateral and medial boundaries * superficial boundary (roof) – skin, superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein, the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm and the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm, deep fascia reinforced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Of Administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body. Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral administration, oral and intravenous therapy, intravenous administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical medication, topical (local), enteral administration, enteral (system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract), or #Parenteral, parenteral (systemic action, but delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form are aspects of drug delivery. Classification Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning (also referred to as MPI or MPS) is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium). It evaluates many heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart wall motion abnormalities. It can also detect regions of myocardial infarction by showing areas of decreased resting perfusion. The function of the myocardium is also evaluated by calculating the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of the heart. This scan is done in conjunction with a cardiac stress test. The diagnostic information is generated by provoking controlled regional ischemia in the heart with variable perfusion. Planar techniques, such as conventional scintigraphy, are rarely used. Rather, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is more common in the US. With multihead SPECT systems, imaging can often be completed in less than 10 minutes. With SPECT, inferior and posterior a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world. Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role, because it emits readily detectable gamma rays with a photon energy of 140 keV (these 8.8 pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The relatively "short" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek language, Greek , , meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862; Lamy by electrolysis, and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the international exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year. Thallium tends to form the +3 and +1 oxidation states. The +3 state resembles that of the other elements in Boron Group, group 13 (boron, aluminium, galli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asystole
Asystole (New Latin, from Greek privative a "not, without" + ''systolē'' "contraction") is the absence of ventricular contractions in the context of a lethal heart arrhythmia (in contrast to an induced asystole on a cooled patient on a heart-lung machine and general anesthesia during surgery necessitating stopping the heart). Asystole is the most serious form of cardiac arrest and is usually irreversible. Also referred to as cardiac flatline, asystole is the state of total cessation of electrical activity from the heart, which means no tissue contraction from the heart muscle and therefore no blood flow to the rest of the body. Asystole should not be confused with very brief pauses in the heart's electrical activity—even those that produce a temporary flatline—that can occur in certain less severe abnormal rhythms. Asystole is different from very fine occurrences of ventricular fibrillation, though both have a poor prognosis, and untreated fine VF will lead to asystole. Fault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardioversion
Cardioversion is a medical procedure by which an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or other cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a sinus rhythm, normal rhythm using electricity or pharmaceutical drug, drugs. Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart at a specific moment in the cardiac cycle, restoring the activity of the electrical conduction system of the heart. (Defibrillation#Relationship to cardioversion, Defibrillation uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart at a random moment in the cardiac cycle, and is the most effective resuscitation measure for cardiac arrest associated with ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia.) Pharmacologic cardioversion, also called chemical cardioversion, uses Antiarrhythmic agent, antiarrhythmia medication instead of an electrical shock. Electrical To perform synchronized electrical cardioversion, two electrode pads are used (or, alternatively, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Agents
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
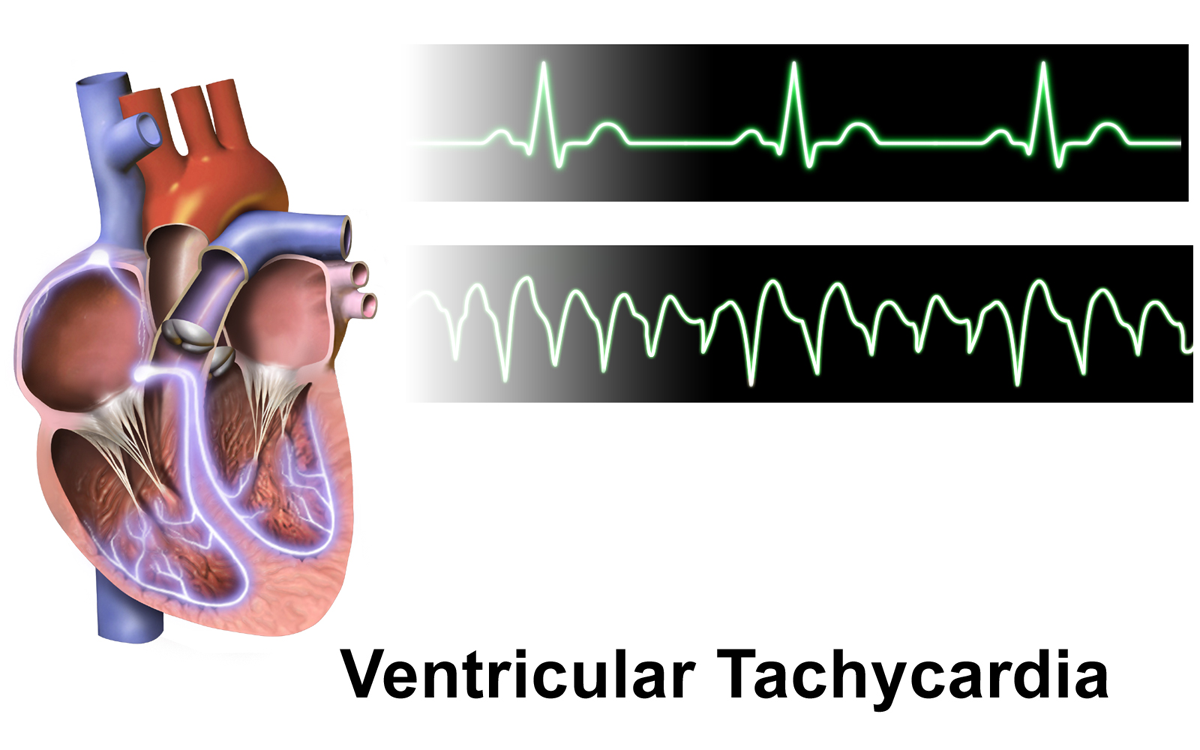
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a rate of greater than 120 beats per minute and at least three wide QRS complexes in a row. It is classified as non-sustained versus sustained based on whether it lasts les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)