|
Acute Abdomen
An acute abdomen refers to a sudden, severe abdominal pain. It is in many cases a medical emergency, requiring urgent and specific diagnosis. Several causes need immediate surgical treatment. Differential diagnosis The differential diagnosis of acute abdomen includes: # Acute appendicitis # Acute peptic ulcer and its complications # Acute cholecystitis # Acute pancreatitis # Acute intestinal ischemia (see section below) # Acute diverticulitis # Ectopic pregnancy with tubal rupture # Ovarian torsion # Acute peritonitis (including hollow viscus perforation) # Acute ureteric colic # Bowel volvulus # Bowel obstruction # Acute pyelonephritis # Adrenal crisis # Biliary colic # Abdominal aortic aneurysm # Familial Mediterranean fever # Hemoperitoneum # Ruptured spleen # Kidney stone # Sickle cell anaemia # Carcinoid Peritonitis Acute abdomen is occasionally used synonymously with peritonitis. While this is not entirely incorrect, peritonitis is the more specific term, refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear. Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important. Differential diagnosis The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndrome (8%), urinary tract problems (5%), inflammation of the stomach (5%) and constipation (5%). In about 30% of cases, the cause is not determined. About 10% of cases have a more serious cause including gallbladder (gallstones or biliary dyskine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biliary Colic
Biliary colic, also known as symptomatic cholelithiasis, a gallbladder attack or gallstone attack, is when a colic (sudden pain) occurs due to a gallstone temporarily blocking the cystic duct. Typically, the pain is in the right upper part of the abdomen, and can be severe. Pain usually lasts from 15 minutes to a few hours. Often, it occurs after eating a heavy meal, or during the night. Repeated attacks are common. Gallstone formation occurs from the precipitation of crystals that aggregate to form stones. The most common form is cholesterol gallstones. Other forms include calcium, bilirubin, pigment, and mixed gallstones. Other conditions that produce similar symptoms include appendicitis, stomach ulcers, pancreatitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Treatment for gallbladder attacks is typically surgery to remove the gallbladder. This can be either done through small incisions or through a single larger incision. Open surgery through a larger incision is associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Colon
''Ascending'' is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints.HarperCollins, Avon, HarperCollins Canada, SFBC/Avon; paperback edition 2001, Eos Books. It is the fifth novel in Gardner's " League of Peoples" series. It is a direct sequel to the first novel in the series, ''Expendable'', in that it picks up the dual story of Festina Ramos, Explorer turned admiral, and the transparent glass woman Oar, where the earlier novel left off. Backstory Through the course of ''Ascending'', Gardner adds depth, detail, and perspective to the conceptual background he has established for the "League of Peoples" series. In particular, he explains how human beings and other species in the galaxy are contacted by, and become a part of, the larger galactic community. Sometime in the middle of the 21st century, humanity encounters a mysterious group of beings who call themselves merely "citizens of the Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Bowel
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the small intestines (can be compressed by the SMA at this location, leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebound Tenderness
Blumberg's sign (also referred to as rebound tenderness or Shchetkin–Blumberg's sign) is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. (The latter is referred to simply as ''abdominal tenderness''.) It is indicative of peritonitis. It was named after German surgeon Jacob Moritz Blumberg. Procedure The abdominal wall is compressed slowly and then rapidly released. A positive sign is indicated by presence of pain upon removal of pressure on the abdominal wall. Clinical significance The sign indicates aggravation of the parietal peritoneum by stretching or moving. Positive Blumberg's sign is indicative of peritonitis, which can occur in diseases like appendicitis, and may occur in ulcerative colitis with rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. However, in recent years the value of rebound tenderness has been questioned, since it may not add any diagnostic value beyond the observation that the patient h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, physician assistant, a certified nur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
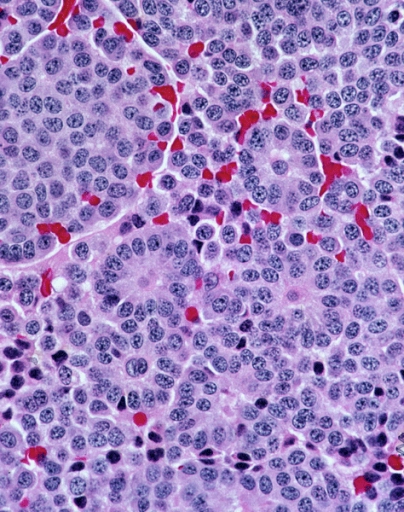
Carcinoid
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle-cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
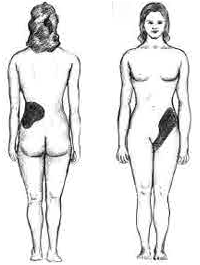
Ruptured Spleen
A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injury to the spleen. The rupture of a normal spleen can be caused by trauma, such as a traffic collision. Signs and symptoms In minor injuries with little bleeding, there may be abdominal pain, tenderness in the epigastrium and pain in the left flank. Often there is a sharp pain in the left shoulder, known as Kehr's sign. In larger injuries with more extensive bleeding, signs of hypovolemic shock are most prominent. This might include a rapid pulse, low blood pressure, rapid breathing, paleness, and anxiety. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured spleen is blunt abdominal trauma, such as in traffic collisions or sports accidents. Direct, penetrating injuries, for example, stab or gunshot wounds are rare. Non-traumatic causes are less common. These include infectious diseases, medical procedures such as colonoscopy, haematological diseases, medications, and pregnancy. In less than one percent of cases of infecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |