|
Acholiland
The Acholi people (also spelled Acoli) are a Nilotic ethnic group of Luo peoples (also spelled Lwo), found in Magwi County in South Sudan and Northern Uganda (an area commonly referred to as Acholiland), including the districts of Agago, Amuru, Gulu, Kitgum, Nwoya, Lamwo, Pader and Omoro District. Approximately 2.1 million Acholi were counted in the Uganda census of 2014, and 45,000 more were living in South Sudan in 2000.Lewis, M. Paul (ed.)"Acholi." ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World.'' SIL International, September, 2010. Accessed 10 March 2011. Language The Acholi dialect is a Western Nilotic language, classified as Luo (or Lwo). It has similarity with Alur, Padhola language, and other Luo languages in South Sudan Shilluk, Anuak,Pari, Balanda, Boor, Thuri. Then in Kenya and Tanzania are the Joluo also known as the Luo. The ''Song of Lawino'', one of the most successful African literary works, was written by Okot p'Bitek, published in 1966 in Acholi, and later tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Peoples
The Luo, (also spelled Lwo) are several ethnically and linguistically related Nilo-Semitic ethnic groups that inhabit an area ranging from Egypt and Sudan to South Sudan and Ethiopia, through Northern Uganda and eastern Congo (DRC), into western Kenya, and the Mara Region of Tanzania. Their Luo languages belong to the western branch of the Nilotic language family. The Luo groups in South Sudan include the Shilluk, Anuak, Pari, Acholi, Balanda Boor, Thuri and Luwo. Those in Uganda include the Alur, Acholi, Jonam and Padhola. The ones in Kenya and Tanzania are the Joluo (also called Luo in Kenyan English). The Joluo and their language Dholuo are also known as the "Luo proper" by Kenya based observers, even though their dialect has more Bantu loan words than the rest. The level of historical separation between these groups is estimated at about eight centuries. Dispersion from an alleged Nilotic core region in South Sudan is presumed to have been triggered by the tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acholi Language
Acholi (also Leb Acoli, or Leb Lwo) is a Southern Luo dialect spoken by the Acholi people in the districts of Gulu, Kitgum and Pader (a region known as Acholiland) in northern Uganda. It is also spoken in South Sudan in Magwi County, Eastern Equatoria. '' Song of Lawino'', well known in African literature, was written in Acholi by Okot p'Bitek, although its sequel, ''Song of Ocol'', was written in English. Acholi, Alur, and Jo Padola have between 84 and 90 per cent of their vocabulary in common and are mutually intelligible. However, they are often counted as separate languages because their speakers are ethnically distinct. Labwor (Thur), once considered a dialect of Acholi, may not be intelligible with it. Phonology Acholi has vowel harmony: all vowels in a word have to belong to a single class (e.g. ''the cold'' vs. ''to separate''). There are two sets of five vowels, distinguished by the feature /-ATR /pʷ/ and /bʷ/ sounds may also sound as labial affrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitgum District
Kitgum District is a district in Northern Uganda. It is named after its major town of Kitgum, where the district headquarters is located. It has suffered many deaths and social disruption resulting from the 20-year civil war within the region during the late 20th century. The government moved tens of thousands of residents to internally displaced persons camps for their protection, where they were subject to raids by the rebels and also harsh conditions, including disease. Location Kitgum District is bordered by South Sudan to the north, Kaabong District to the east, Kotido District to the southeast, Agago District to the south, Pader District to the southwest and Lamwo District to the northwest. Kitgum, the largest town in the district, is located approximately , by road, northeast of Gulu, the largest city in the sub-region. This location lies approximately , by road, north of Uganda's capital, Kampala. Overview The district is composed of one county: Chua County. In 2010, La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritance of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male kin. This is sometimes distinguished from cognate kinship, through the mother's lineage, also called the spindle side or the distaff side. A patriline ("father line") is a person's father, and additional ancestors, as traced only through males. Traditionally and historically people would identify the person's ethnicity with the father's heritage and ignore the maternal ancestry in the ethnic factor. In the Bible In the Bible, family and tribal membership appears to be transmitted through the father. For example, a person is considered to be a priest or Levite, if his father is a priest or Levite, and the members of all the Twelve Tribes are called Israelites be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, meaning that their members can marry one another. Clans preceded more centralized forms of community organization and government, and exist in every country. Members may identify with a coat of arms or other symbol to show that they are an . Kinship-based groups may also have a symbolic ancestor, whereby the clan shares a "stipulated" common ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Etymology The English word "clan" is derived from old Irish meaning "children", "offspring", "progeny" or "descendants"; it is not from the word for "family" or "clan" in either Irish or Scottish Gaelic. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word "clan" was introduced into English in around 1425, as a descriptive label for the organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a political-ideological aristocracy relative to the general group. Concept In anthropological theory, one model of human social development rooted in ideas of cultural evolution describes a chiefdom as a form of social organization more complex than a tribe or a band society, and less complex than a state or a civilization. Within general theories of cultural evolution, chiefdoms are characterized by permanent and institutionalized forms of political leadership (the chief), centralized decision-making, economic interdependence, and social hierarchy. Chiefdoms are described as intermediate between tribes and states in the progressive scheme of sociopolitical development formulated by Elman Service: ''band - tribe - chiefdom - state''. A chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahr El Ghazal (region Of South Sudan)
The Bahr el Ghazal is a region of northwestern South Sudan. Its name came from the river Bahr el Ghazal. The name translates as "sea of gazelles" from Arabic. Geography Bahr el Ghazal borders the Central African Republic to the west. It is an area of swamps and ironstone plateaus inhabited mainly by the Dinka people, who make their living through subsistence farming and cattle herding plus Luwo and Fartit tribes. Administrative divisions Bahr el Ghazal consists of the following states: * Lakes * Northern Bahr el Ghazal * Warrap * Western Bahr el Ghazal * '' Abyei Area'' Between October 2015 and January 2020, the region consisted of the following states: * Eastern Lakes State * Gok State * Western Lakes State * Aweil East State * Aweil State * Tonj State * Twic State Twic State was a state in South Sudan that existed between 2 October 2015 and 22 February 2020. It was located in the Bahr el Ghazal region and it bordered Aweil East to the west, the disputed Abyei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
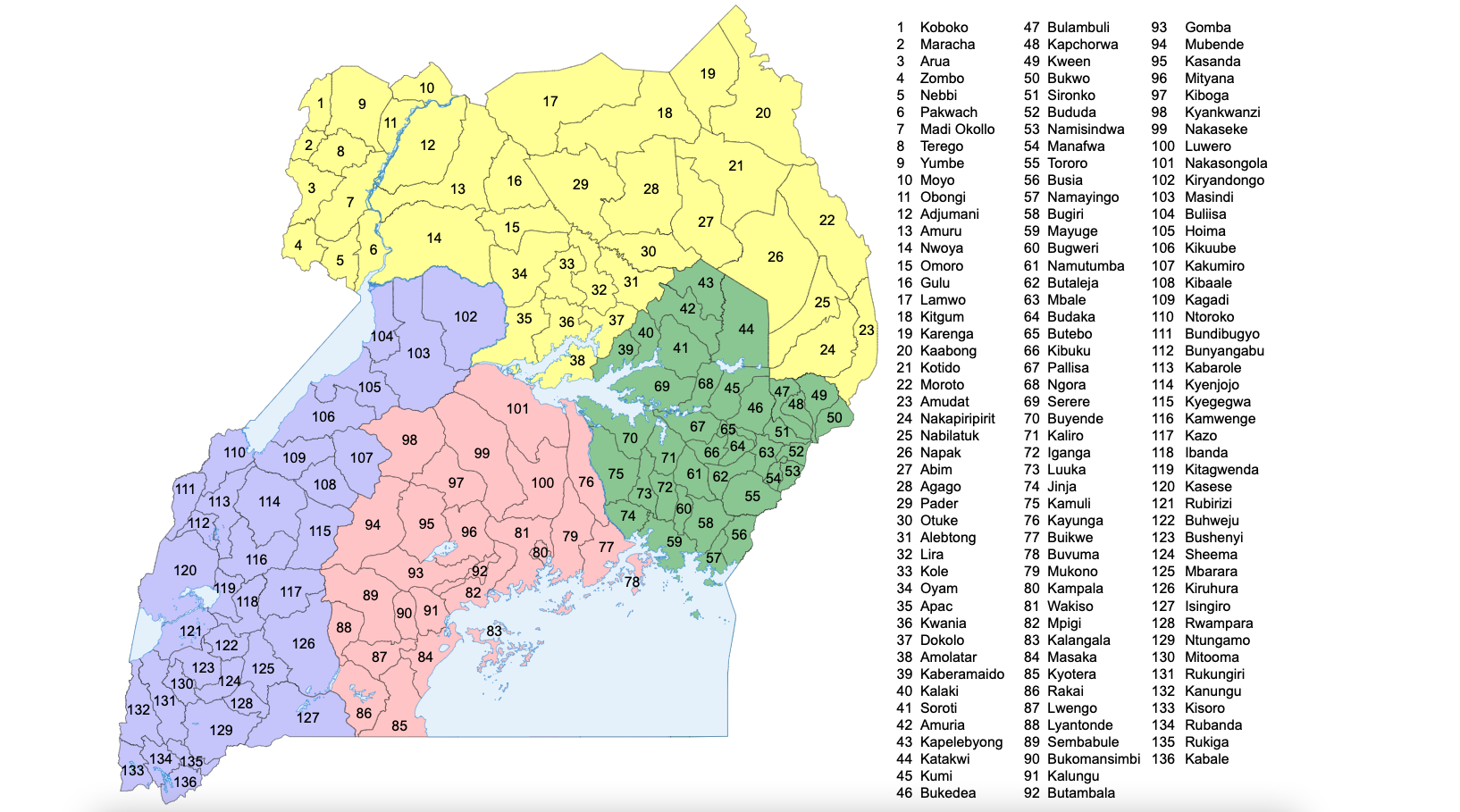
Districts Of Uganda
As of 17 November 2020, Uganda is divided into 136 districts and the capital city of Kampala, which are grouped into four administrative regions. Since 2005, the Ugandan government has been in the process of dividing districts into smaller units. This decentralization is intended to prevent resources from being distributed primarily to chief towns and leaving the remainder of each district neglected. Each district is further divided into counties and municipalities, and each county is further divided into sub-counties. The head elected official in a district is the chairperson of the Local Council five (usually written with a Roman numeral V). Below are population figures from the 2014 census (tables show population figures for districts that existed in 2014). __NOTOC__ Districts created since 2015 In September 2015, the Parliament of Uganda created 23 new districts, to be phased in over the next four years. In May 2020, Parliament approved the creation of Terego Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okot P'Bitek
Okot p'Bitek (7 June 1931 – 19 July 1982) was a Ugandan poet, who achieved wide international recognition for ''Song of Lawino'', a long poem dealing with the tribulations of a rural African wife whose husband has taken up urban life and wishes everything to be westernised. ''Song of Lawino'' was originally written in the Acholi dialect of Southern Luo, translated by the author into English, and published in 1966. It was a breakthrough work, creating an audience among anglophone Africans for direct, topical poetry in English; and incorporating traditional attitudes and thinking in an accessible yet faithful literary vehicle. It was followed by the ''Song of Ocol'' (1970), the husband's reply. The "East African Song School" or "Okot School poetry" is now an academic identification of the work following his direction, also popularly called "comic singing": a forceful type of dramatic verse monologue rooted in traditional song and phraseology. Early life Okot p'Bitek was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Of Lawino
''Song of Lawino'' ( Acholi: ''Wer pa Lawino'') is an epic poem written by Ugandan poet Okot p'Bitek. It was first published in 1966 in an English translation by the author, although Chapter 14, its final chapter, was removed. It was quickly translated into other languages. The complete poem in the original Acholi Luo language was published later in 1969. Taban Lo Liyong published an English translation of chapter 14 in 1993 as well as a new translation of the entire poem in 2001 (as ''The Defence of Lawino''). ''Song of Lawino'' has become one of the most widely read literary works originating from Sub-Saharan Africa. It has also become culturally iconic within Africa, because of its scathing display of how African society was being destroyed by the colonization of Africa. ''Song of Lawino'' was originally written in rhyming couplets and had a regular meter. The poem is told from the point of view of Lawino in the first person. p'Bitek published a follow-up poem in English, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |