|
Aztec Numerals
The Aztec or Nahuatl script is a pre-Columbian writing system that combines ideographic writing with Nahuatl specific phonetic logograms and syllabic signs which was used in central Mexico by the Nahua people in the Epiclassic and Post-classic periods. It was originally thought that its use was reserved for elites; however, the topographical codices and early colonial catechisms, recently deciphered, were used by ''tlacuilos'' (scribes), ''macehuallis'' (peasants), and ''pochtecas'' (merchants). Origin The Aztec writing system derives from writing systems used in Central Mexico, such as Zapotec script. Mixtec writing is also thought to descend from Zapotec. The first Oaxacan inscriptions are thought to encode Zapotec, partially because of numerical suffixes characteristic of the Zapotec languages. Structure and use Aztec was pictographic and ideographic proto-writing, augmented by phonetic rebuses. It also contained syllabic signs and logograms. There was no alphabet, but pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuatl Language
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations Nahuatl language in the United States, in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican chronology, Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. Following the Spanish conquest, Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin script, and Nahuatl became a literary language. Many chronicles, gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebus
A rebus ( ) is a puzzle device that combines the use of illustrated pictures with individual letters to depict words or phrases. For example: the word "been" might be depicted by a rebus showing an illustrated bumblebee next to a plus sign (+) and the letter "n". It was a favourite form of Heraldry, heraldic expression used in the Middle Ages to denote surnames. For example, in its basic form, three salmon (fish) are used to denote the surname "Salmon (surname), Salmon". A more sophisticated example was the rebus of Bishop Walter Hart, Walter Lyhart (d. 1472) of Norwich, consisting of a stag (or Deer, hart) lying down in a conventional representation of water. The composition alludes to the name, profession or personal characteristics of the bearer, and speaks to the beholder ''Non verbis, sed rebus'', which Latin expression signifies "not by words but by things" (''res, rei'' (f), a thing, object, matter; ''rebus'' being ablative plural). Rebuses within heraldry Rebuses are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The PARI Journal
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieroglyph
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters.In total, there were about 1,000 graphemes in use during the Old Kingdom period; this number decreased to 750–850 during the Middle Kingdom, but rose instead to around 5,000 signs during the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, ''Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction'' (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Egyptian hieroglyphs are the ultimate ancestor of the Phoenician alphabet, the first widely adopted phonetic writing system. Moreover, owing in large part to the Greek and Aramaic sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damago Soto
The Reverend Damago Soto of Concordia, Vera Cruz, Mexico, was a minister who supposedly discovered the key to interpreting Aztec The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ... writings. References Culture of Mexico Mexican Christians {{Mexico-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
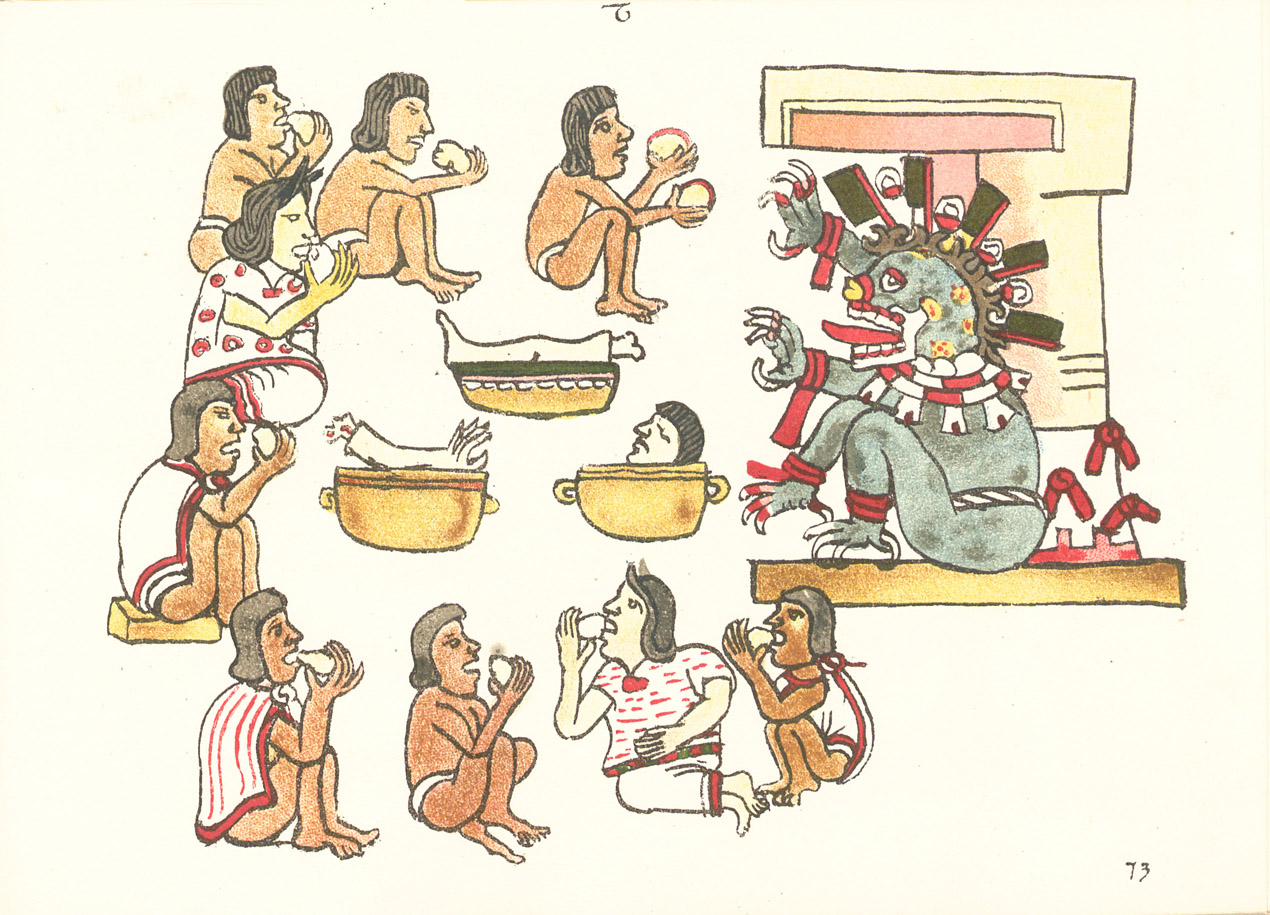
Aztec Codices
Aztec codices ( , sing. ''codex'') are Mesoamerican manuscripts made by the pre-Columbian Aztec, and their Nahuatl-speaking descendants during the colonial period in Mexico. Most of their content is pictorial in nature and they come from the multiple Indigenous groups from before and after Spanish contact. Differences in styles indicate regional and temporal differences. The types of information in manuscripts fall into several broad categories: calendar or time, history, genealogy, cartography, economics/tributes, census and cadastral, and property plans. Codex Mendoza and the Florentine Codex are among the important and popular colonial-era codices. The Florentine Codex, for example is known for providing a Nahuatal narrative of the Spanish Conquest from the viewpoint of the Indigenous people, instead of Europeans. History Before the start of the Spanish colonization of the Americas, the Mexica and their neighbors in and around the Valley of Mexico relied on painted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Zumárraga
Juan de Zumárraga, OFM (1468 – June 3, 1548) was a Spanish Basque Franciscan prelate and the first Bishop of Mexico. He was also the region's first inquisitor. He wrote ''Doctrina breve'', the first book published in the Western Hemisphere by a European, printed in Mexico City in 1539. Biography Origins and arrival in New Spain Zumárraga was born in 1468 or 1469 of a noble family, in Durango in the Biscay province in Spain. He entered the Franciscan Order, and in 1527 was custodian of the convent of Abrojo. Shortly afterwards he was appointed one of the judges of the court for the examination of witches in the Basque province. From his writings it would appear that he looked upon witches merely as women possessed of hallucinations. By this time more detailed accounts of the importance of the conquest of Hernán Cortés began to be received, and on December 20, 1527, Zumárraga was recommended by Charles V for the post of first bishop of Mexico. Without having been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
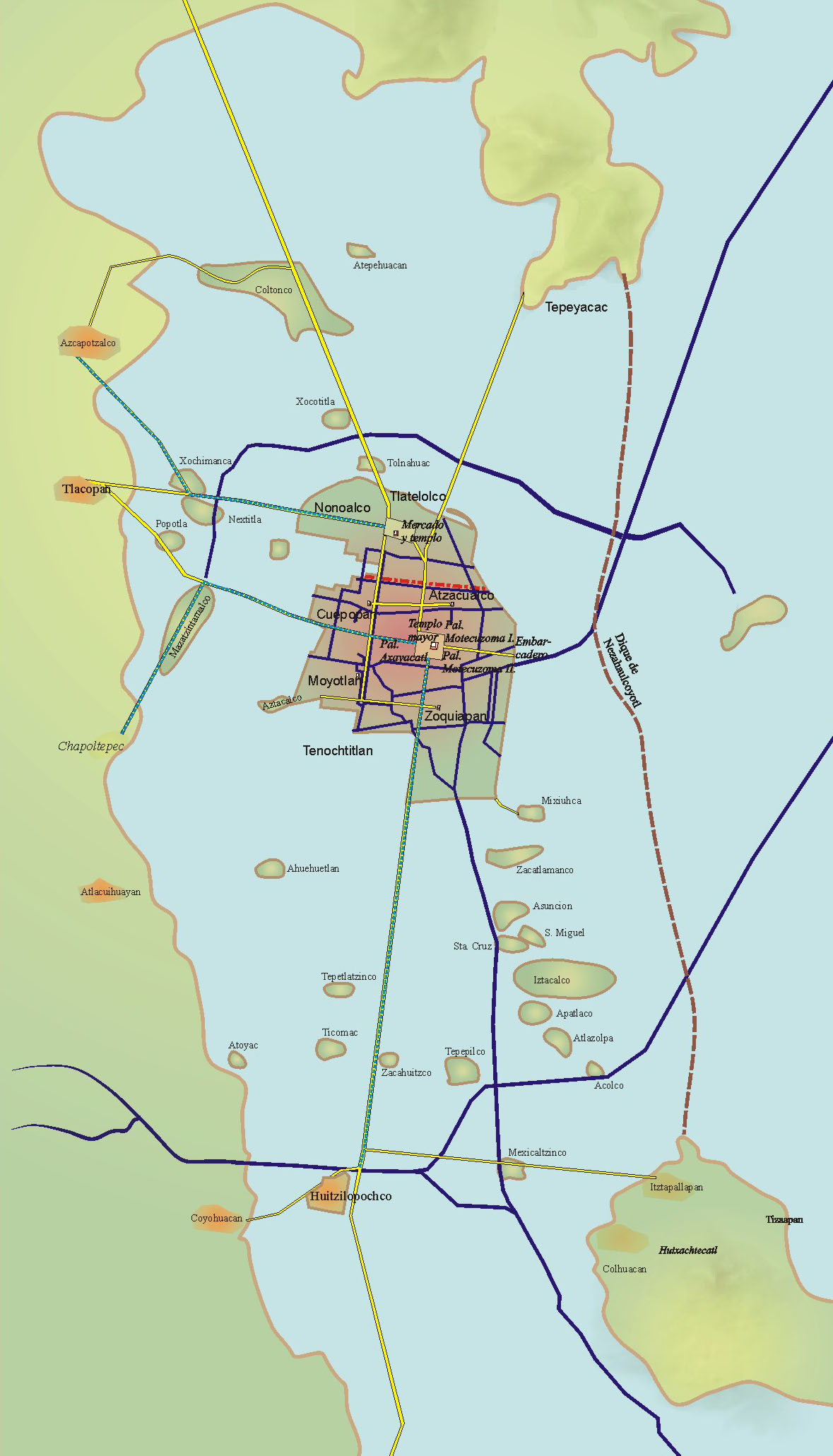
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texcoco De Mora
Texcoco de Mora (, Otomi: ) is a city located in the State of Mexico, 25 km northeast of Mexico City. Texcoco de Mora is the municipal seat of the municipality of Texcoco. In the pre-Hispanic era, this was a major Aztec city on the shores of Lake Texcoco. After the Conquest, the city was initially the second most important after Mexico City, but its importance faded over time, becoming more rural in character. Over the colonial and post-independence periods, most of Lake Texcoco was drained and the city is no longer on the shore and much of the municipality is on lakebed. Numerous Aztec archeological finds have been discovered here, including the 125 tonne stone statue of Chalchiuhtlicue, which was found near San Miguel Coatlinchán and now resides at the Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City. Much of Texcoco's recent history involves the clash of the populace with local, state and federal authorities. The most serious of these is the continued attempts to deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'idea' + 'to write') is a symbol that is used within a given writing system to represent an idea or concept in a given language. (Ideograms are contrasted with phonogram (linguistics), phonograms, which indicate sounds of speech and thus are independent of any particular language.) Some ideograms are more arbitrary than others: some are only meaningful assuming preexisting familiarity with some convention; others more directly resemble their signifieds. Ideograms that represent physical objects by visually illustrating them are called ''pictograms''. * Numeral system, Numerals and List of mathematical symbols, mathematical symbols are ideograms, for example ⟨1⟩ 'one', ⟨2⟩ 'two', ⟨+⟩ 'plus', and ⟨=⟩ 'equals'. * The ampersand ⟨&⟩ is used in many languages to represent the word ''and'', originally a stylized Ligature (writing), ligature of the Latin word . * Other typographical examples include ⟨§⟩ 'sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllabary
In the Linguistics, linguistic study of Written language, written languages, a syllabary is a set of grapheme, written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) mora (linguistics), morae which make up words. A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (optional) consonant sound (simple onset (linguistics), onset) followed by a vowel sound (nucleus (syllable), nucleus)—that is, a CV (consonant+vowel) or V syllable—but other phonogram (linguistics), phonographic mappings, such as CVC, CV- tone, and C (normally nasals at the end of syllables), are also found in syllabaries. Types A writing system using a syllabary is ''complete'' when it covers all syllables in the corresponding spoken language without requiring complex orthography, orthographic / graphemic rules, like implicit codas ( ⇒ /C1VC2/), silent vowels ( ⇒ /C1V1C2/) or echo vowels ( ⇒ /C1V1C2/). This loosely corresponds to ''shallow'' orthographies in alphabetic writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Numerals
The Mayan numeral system was the system to represent numbers and calendar dates in the Maya civilization. It was a vigesimal (base-20) positional notation, positional numeral system. The numerals are made up of three symbols: Zero number#The Americas, zero (a shell), 1 (number), one (a dot) and 5 (number), five (a bar). For example, thirteen is written as three dots in a horizontal row above two horizontal bars; sometimes it is also written as three vertical dots to the left of two vertical bars. With these three symbols, each of the twenty vigesimal digits could be written. Numbers after 19 were written vertically in powers of twenty. The Mayan used powers of twenty, just as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system uses powers of ten. For example, thirty-three would be written as one dot, above three dots atop two bars. The first dot represents "one twenty" or "1×20", which is added to three dots and two bars, or thirteen. Therefore, (1×20) + 13 = 33. : Upon reaching 202 or 400 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |