|
Aziridine
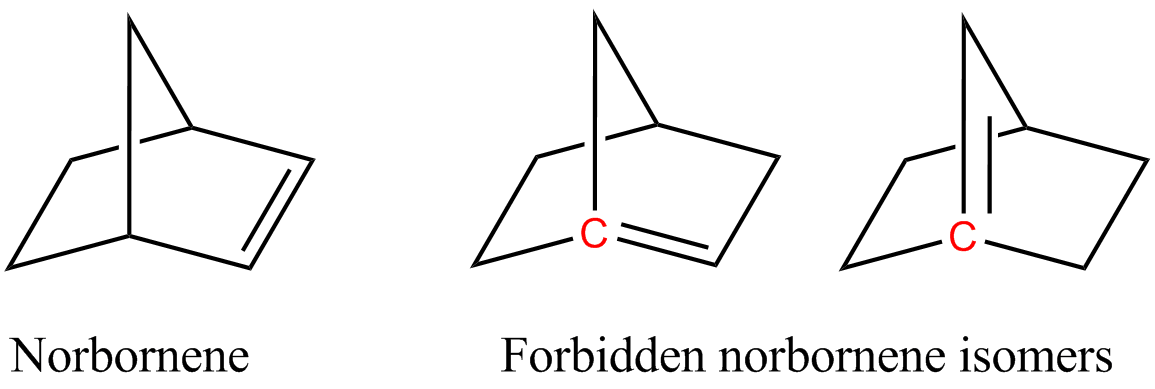
Aziridine is an organic compound consisting of the three-membered heterocycle . It is a colorless, toxic, volatile liquid that is of significant practical interest. Aziridine was discovered in 1888 by the chemist Siegmund Gabriel. Its derivatives, also referred to as aziridines, are of broader interest in medicinal chemistry. Structure The bond angles in aziridine are approximately 60°, considerably less than the normal hydrocarbon bond angle of 109.5°, which results in angle strain as in the comparable cyclopropane and ethylene oxide molecules. A banana bond model explains bonding in such compounds. Aziridine is less basic than acyclic aliphatic amines, with a pKa of 7.9 for the conjugate acid, due to increased s character of the nitrogen free electron pair. Angle strain in aziridine also increases the barrier to nitrogen inversion. This barrier height permits the isolation of separate ''invertomers'', for example the ''cis'' and ''trans'' invertomers of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aziridines
220 px, chemotherapy.html" ;"title="Mitomycin C, an aziridine, is used as a chemotherapy">chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity. In organic chemistry, aziridines are organic compounds containing the aziridine functional group (chemical structure ), a three-membered heterocycle with one amine () and two methylene bridges (). The parent compound is aziridine (or ethylene imine), with molecular formula . Several drugs feature aziridine rings, including zoldonrasib, thiotepa, mitomycin C, porfiromycin, and azinomycin B (carzinophilin). Structure The bond angles in aziridine are approximately 60°, considerably less than the normal hydrocarbon bond angle of 109.5°, which results in angle strain as in the comparable cyclopropane and ethylene oxide molecules. A banana bond model explains bonding in such compounds. Aziridine is less basic than acyclic aliphatic amines, with a pKa of 7.9 for the conjugate acid, due to increased s character of the nitrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenker Synthesis
The Wenker synthesis is an organic reaction converting a beta amino alcohol to an aziridine with the help of sulfuric acid. It is used industrially for the synthesis of aziridine itself. The original Wenker synthesis of aziridine itself takes place in two steps. In the first step ethanolamine is reacted with sulfuric acid at high temperatures (250 °C) to form the sulfate monoester. This salt is then reacted with sodium hydroxide in the second step forming aziridine. The base (chemistry), base abstracts an amine proton enabling it to nucleophilic displacement, displace the sulfate group. A modification of this reaction involving lower reaction temperatures (140–180 °C) and therefore reduced charring increases the yield of the intermediate. The Wenker synthesis protocol using ''trans''-2-aminocyclooctanol, available from reaction of ammonia with the epoxide of cyclooctene, gives a mixture of cyclooctenimine (the Wenker aziridine product) and cyclooctanone (a competing Hofmann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylenimine
Polyethylenimine (PEI) or polyaziridine is a polymer with repeating units composed of the amine group and two carbon Aliphatic_compound, aliphatic ''CHCH'' spacers. Linear polyethyleneimines contain all Amines#Classification_of_amines, secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain primary, secondary and tertiary amino groups. Totally branched, dendrimeric forms were also reported. PEI is produced on an industrial scale and finds many applications usually derived from its polyelectrolyte, polycationic character. Properties The linear PEI is a semi-crystalline solid at room temperature while branched PEI is a fully amorphous polymer existing as a liquid at all molecular weights. Linear polyethyleneimine is soluble in hot water, at low pH, in methanol, ethanol, or chloroform. It is insoluble in cold water, benzene, Diethyl ether, ethyl ether, and acetone. Linear polyethylenimine has a melting point of around 67 °C. Both linear and branched polyethylneimine c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borirane
Borirane is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C2 H4 BH. This colourless, flammable gas is the simplest borirane, a three-membered ring consisting of two carbon and one boron atom. It can be viewed as a structural analog of aziridine, with boron replacing the nitrogen atom of aziridine. Borirane is isomer In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...ic with ethylideneborane. This compound has five isomers. References {{Reflist Boron heterocycles Gases Three-membered rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energies chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Inversion
In chemistry, pyramidal inversion (also umbrella inversion) is a fluxional process in compounds with a pyramidal molecule, such as ammonia (NH3) "turns inside out". It is a rapid oscillation of the atom and substituents, the molecule or ion passing through a planar transition state. For a compound that would otherwise be chiral due to a stereocenter, pyramidal inversion allows its enantiomers to racemize. The general phenomenon of pyramidal inversion applies to many types of molecules, including carbanions, amines, phosphines, arsines, stibines, and sulfoxides. Energy barrier The identity of the inverting atom has a dominating influence on the barrier. Inversion of ammonia is rapid at room temperature, inverting 30 billion times per second. Three factors contribute to the rapidity of the inversion: a low energy barrier (24.2 kJ/mol; 5.8 kcal/mol), a narrow barrier width (distance between geometries), and the low mass of hydrogen atoms, which combine to give a furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana Bond
In organic chemistry, a bent bond, also known as a banana bond, is a type of covalent chemical bond with a geometry somewhat reminiscent of a banana. The term itself is a general representation of electron density or configuration resembling a similar "bent" structure within small ring molecules, such as cyclopropane (C3H6) or as a representation of double or triple bonds within a compound that is an alternative to the sigma and pi bond model. Small cyclic molecules Bent bonds are a special type of chemical bonding in which the ordinary hybridization state of two atoms making up a chemical bond are modified with increased or decreased s-orbital character in order to accommodate a particular molecular geometry. Bent bonds are found in strained organic compounds such as cyclopropane, oxirane and aziridine. In these compounds, it is not possible for the carbon atoms to assume the 109.5° bond angles with standard sp3 hybridization. Increasing the p-character to sp5 (i.e. s-den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis Isomer
CIS may refer to: Computing * Card information structure, formatting and organization data stored on a PC card * Center for Internet Security, cybersecurity benchmarks, controls, practices and tools * Center for Internet and Society (other) * Comodo Internet Security suite * CompuServe Information Service, a US commercial online service * Computer and information science, a field that emphasizes both computing and informatics * Computer information systems, technologies which process data to solve business problems * Configuration interaction singles, a quantum-chemical method for computing electronic states * Contact image sensor, a technology developed for optical flatbed scanners * Continuous ink system, for ink-jet printers Education * Calcutta International School, in India * Canadian International School (other) ** Canadian International School (Bangalore) ** Canadian International School Vietnam ** Canadian International School of Sanya, in Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoethanol
Aminoethanol may refer to: * 1-Aminoethanol * Ethanolamine Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorl ... (2-aminoethanol, ETA, or MEA) {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans Isomer
Trans- is a Latin prefix meaning "across", "beyond", or "on the other side of". Used alone, trans may refer to: Sociology * Trans, a sociological term which may refer to: ** Transgender, people who identify themselves with a gender that differs from their sex societally designated/assigned at birth ** Transsexual, people who seek to transition from their birth-assigned sex to another via therapy and/or surgery ** Trans*, a broader term for identities including transgender and transsexual Arts, entertainment, and media * Trans (festival), a former festival in Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Trans (1982 film), a Venezuelan short documentary film * ''Trans'' (1998 film), an American film * Trans Corp, an Indonesian business unit of CT Corp in the fields of media, lifestyle, and entertainment ** Trans Media, a media subsidiary of Trans Corp *** Trans TV, an Indonesian television network *** Trans7, an Indonesian television network Literature * '' Trans: G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |