|
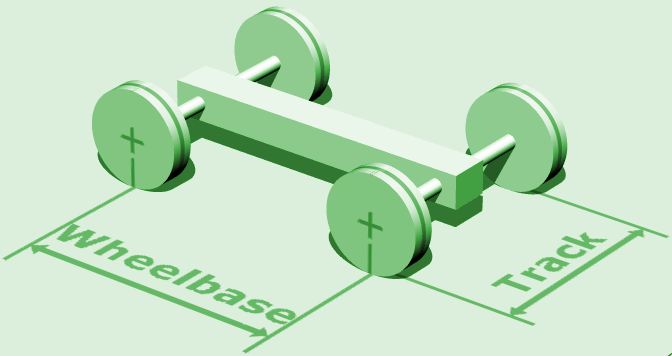
Axle Track
In Car, automobiles (and other wheeled vehicles which have two wheels on an axle), the axle track is the distance between the hub Flange, flanges on an axle. Wheel track, track width or simply track refers to the distance between the centerline of two wheels on the same axle. In the case of an axle with dual wheels, the centerline of the dual wheel assembly is used for the wheel track specification. Axle and wheel track are commonly measured in millimetres or inches. Common usage Despite their distinct definitions, ''axle track'', (not to be frequently and incorrectly used interchangeably as ''wheel track'' and ''track width''), normally refers to the distance between the centerline of the wheels. For a vehicle with two axles, the term can be expressed as ''front track'' and ''rear track''. For a vehicle with more than two axles, the axles are normally numbered for reference. Offset wheel track In vehicles with Wheel_sizing#Offset, offset wheels, wheel track is distinct from axle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheelbase And Track
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track (rail Transport)
Railway track ( and UIC terminology) or railroad track (), also known as permanent way () or "P way" ( and Indian English), is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, sleepers ( railroad ties in American English) and ballast (or slab track), plus the underlying subgrade. It enables trains to move by providing a dependable, low-friction surface on which steel wheels can roll. Early tracks were constructed with wooden or cast-iron rails, and wooden or stone sleepers. Since the 1870s, rails have almost universally been made from steel. Historical development The first railway in Britain was the Wollaton wagonway, built in 1603 between Wollaton and Strelley in Nottinghamshire. It used wooden rails and was the first of about 50 wooden-railed tramways built over the subsequent 164 years. These early wooden tramways typically used rails of oak or beech, attached to wooden sleepers with iron or wooden nails. Gravel or small stones were pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of Mechanical engineering, mechanical, Electrical engineering, electrical, Electronic engineering, electronic, Software engineering, software, and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles, and trucks and their respective engineering subsystems. It also includes modification of vehicles. Manufacturing domain deals with the creation and assembling the whole parts of automobiles is also included in it. The automotive engineering field is research intensive and involves direct application of mathematical models and formulas. The study of automotive engineering is to design, develop, fabricate, and test vehicles or vehicle components from the concept stage to production stage. Production, development, and manufacturing are the three major functions in this field. Disciplines Automobile engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Profile
The rail profile is the cross-sectional shape of a Railway track#Rail, rail as installed on a railway or railroad, perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section Profile (engineering), (profile) approximate to an I-beam, but asymmetric about a horizontal axis (however see #Grooved rail, grooved rail below). The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel. It took many decades to improve the quality of the materials, including the change from iron to steel. Minor flaws in the steel that may pose no problems in other applications can lead to broken rails and dangerous derailments when used on railway tracks. By and large, the heavier the rails and the rest of the track work, the heavier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the transverse distance be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OO Gauge
OO gauge or OO scale (also, 00 gauge and 00 scale) is the most popular standard gauge model railway standard in the United Kingdom, outside of which it is virtually unknown. OO gauge is one of several 4 mm-scale standards (4 mm to , or 1:76.2), and the only one to be marketed by major manufacturers. The OO track gauge of (same as the 1:87 HO scale) corresponds to prototypical gauge of , rather than standard gauge. However, since the 1960s, other gauges in the same scale have arisen – 18.2 mm ( EM) and 18.83 mm ( Scalefour) — to reflect the desire of some modellers for greater scale accuracy. Origin Double-0 scale model railways were launched by Bing in 1921 as "The Table Railway", running on track and scaled at 4 mm to the foot. In 1922, the first models of British prototypes appeared. Initially all locomotives were powered by clockwork, but the first electric power appeared in 1923. "OO" describes models with a scale of 4 mm = 1 foot (1:76) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HO Scale
HO or H0 is a rail transport modelling scale using a 1:87 scale (3.5 mm to 1 foot). It is the most popular scale of model railway in the world. The rails are spaced apart for modelling standard gauge tracks and trains in HO. The name HO comes from 1:87 scale being ''half'' that of O scale, which was originally the smallest of the series of older and larger 0, 1, 2 and 3 gauges introduced by Märklin around 1900. Rather than referring to the scale as "half-zero" or "H-zero", English-speakers have consistently pronounced it and have generally written it with the letters HO. In other languages it also remains written with the letter H and number 0 (zero); in German it is thus pronounced as . In Japan, many models are produced using 1:80 scale proportions (16.5mm track is still used). History After the First World War there were several attempts to introduce a model railway about half the size of 0 scale that would be more suitable for smaller home layouts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for longer and heavier freight trains, companies are increasingly using distributed power: single or multiple locomotives placed at the front and rear and at intermediate points throughout the train under the control of the leading locomotive. Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first used in 1814 to distinguish between self-propelled and stationary steam engines. Classifications Prior to locomotives, the motive force for railways had been generated by various lower-technology methods such as human power, horse power, Gravity railroad, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Stock
The term rolling stock in the rail transport industry refers to railway vehicles, including both powered and unpowered vehicles: for example, locomotives, Railroad car#Freight cars, freight and Passenger railroad car, passenger cars (or coaches), and Railroad car#Non-revenue cars, non-revenue cars. Passenger vehicles can be un-powered, or self-propelled, Railcar, single or Multiple unit, multiple units. In North America, Australia and other countries, the term consist ( ) is used to refer to the rolling stock comprising a train, a list containing specific information for each car of a train, or a group of locomotives. In the United States, the term ''rolling stock'' has been expanded from the older broadly defined "trains" to include wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways. The word ''stock'' in the term is used in a sense of inventory. Rolling stock is considered to be a liquid asset, or close to it, since the value of the vehicle can be readily estimated and then ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport Modelling
Railway modelling (UK, Australia, New Zealand, and Ireland) or model railroading (US and Canada) is a hobby in which rail transport systems are Model building, modelled at a reduced Scale (ratio), scale. The scale models include locomotives, rolling stock, streetcars, rail tracks, tracks, Railway signal, signalling, Crane (machine), cranes, and landscapes including: countryside, roads, bridges, buildings, vehicles, harbors, urban landscape, model figures, lights, and features such as rivers, hills, tunnels, and canyons. The earliest model railways were the 'carpet railways' in the 1840s. The first documented model railway was the Railway of the Prince Imperial (French: Chemin de fer du Prince Impérial) built in 1859 by Emperor Napoleon III for his then 3-year-old son, also Louis-Napoléon, Prince Imperial, Napoleon, in the grounds of the Château de Saint-Cloud in Paris. It was powered by clockwork and ran in a figure-of-eight. Electric trains appeared around the start of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheeled Vehicle
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be moved easily facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Wheels are also used for other purposes, such as a ship's wheel, steering wheel, potter's wheel, and flywheel. Common examples can be found in transport applications. A wheel reduces friction by facilitating motion by rolling together with the use of axles. In order for a wheel to rotate, a moment must be applied to the wheel about its axis, either by gravity or by the application of another external force or torque. Terminology The English word ''wheel'' comes from the Old English word , from Proto-Germanic , from Proto-Indo-European , an extended form of the root . Cognates within Indo-European in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |