|
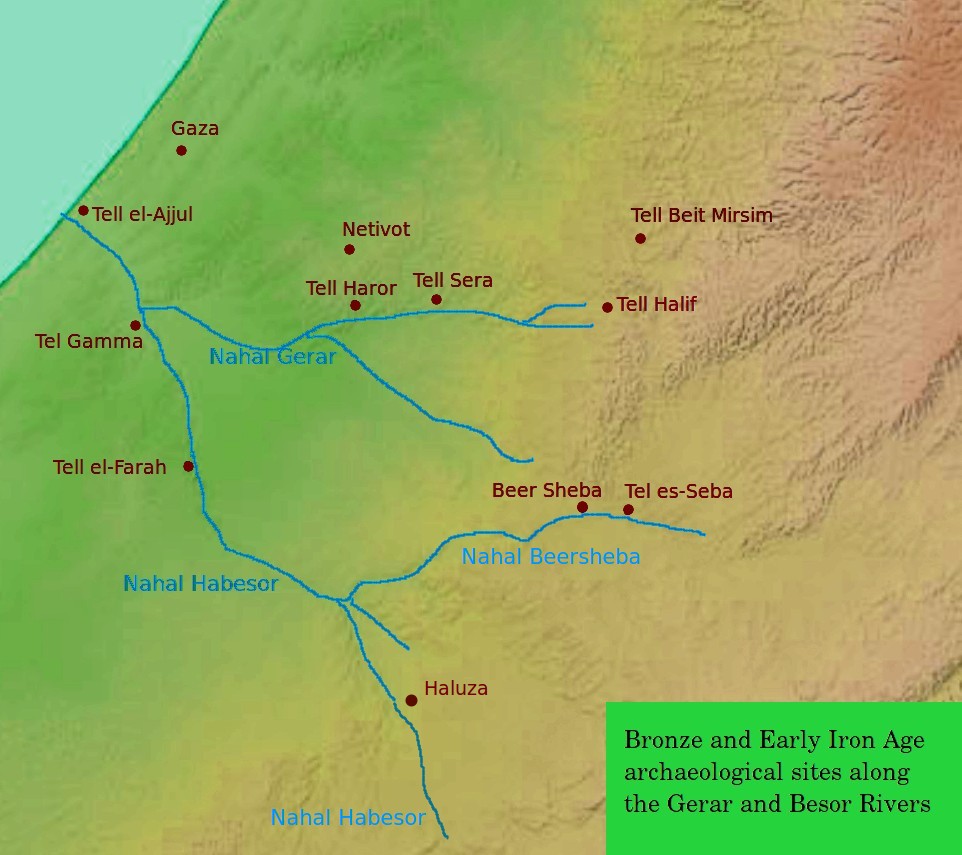
Avdat
Avdat or Ovdat (), and Abdah or Abde (), are the modern names of an archaeological site corresponding to the ancient Nabataean, Roman and Byzantine settlement of Oboda (''tabula Peutingeriana''; Stephanus Byzantinus) or Eboda (Ptolemaeus 5:16, 4)"Avedat (Ovdat; Ar. "Abde")" in ''Encyclopaedia Judaica'' 2008, The Gale Group. Via Jewish Virtual Library, accessed 11 May 2024. in the Negev desert in southern Israel. It was inhabited with intermissions between the 3rd century BCE and the mid-7th century CE by Nabataeans, in their time becoming the most important city on the Incense Route after Petra, then by Ancient Rome , Roman army veterans, and Byzantines, surviving only for a few years into the Timeline of Palestine region#Early Muslim period , Early Muslim period.Yedioth Ahronoth (6 October 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
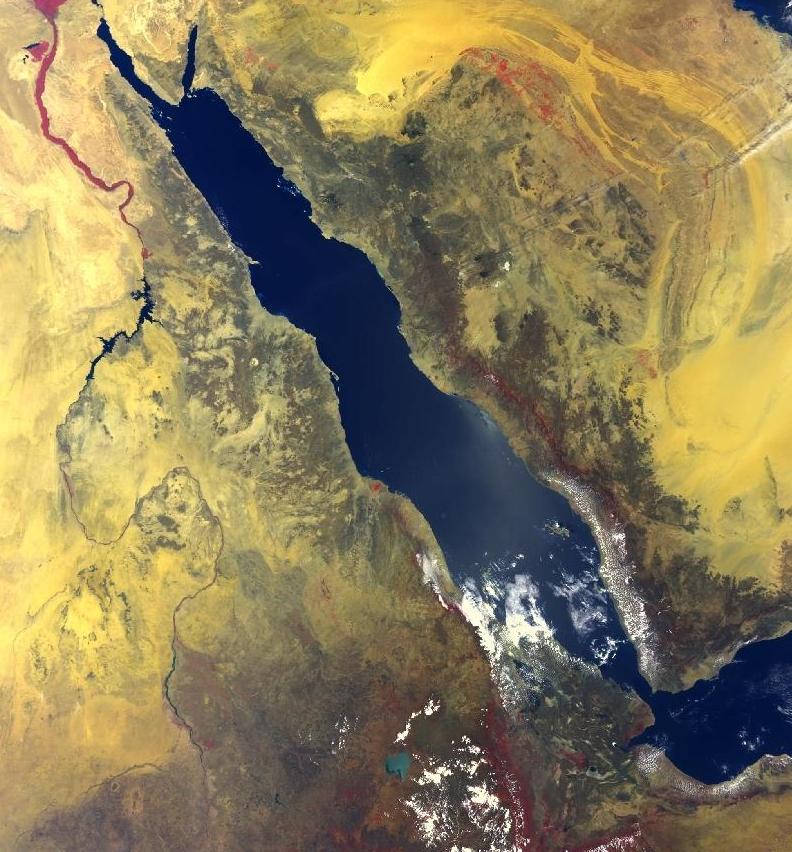
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad, Israel, Arad, and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Negev Bedouin, Bedouin towns, including Rahat, Tel Sheva, and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman Empire, Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Emirate of Transjordan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivta
Shivta (), originally Sobata () or Subeita (), is an ancient city in the Negev Desert of Israel located 43 kilometers southwest of Beersheba. Shivta was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in June 2005, as part of the Incense Route and the Desert Cities of the Negev, together with Haluza/Elusa, Avdat and Mamshit/ Mampsis. The name Shivta is a modern Hebraization, given by the Negev Naming Committee in the early 1950s. The Greek name Sobata was mentioned in the Nessana papyri. History Long considered a classical Nabataean town on the ancient spice route, archaeologists are now considering the possibility that Shivta was a Byzantine agricultural colony and a way station for pilgrims en route to the Saint Catherine's Monastery in the Sinai Peninsula. A few Roman-period ruins have been discovered, but most of the archaeological findings date to the Byzantine period. Shivta's water supply was based on surface runoff collected in large reservoirs. Roman period Roman ruins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamshit
Mampsis (Medieval Greek: Μάμψις) or Memphis (Ancient Greek: Μέμφις), today Mamshit (), Kurnub (Arabic: كرنب), is a former Nabataean caravan stop and Byzantine city. In the Nabataean period, Mampsis was an important station on the Incense Road, connecting Southern Arabia through Edom, the Arabah and Ma'ale Akrabim, to the Mediterranean ports, as well as to Jerusalem via Beersheba and Hebron. The city covers and is the smallest but best restored ancient city in the Negev Desert. The once-luxurious houses feature unusual architecture not found in any other Nabataean city. The reconstructed city gives the visitor a sense of how Mampsis once looked. Entire streets have survived intact, and there are also large groups of Nabataean buildings with open rooms, courtyards, and terraces. The stones are carefully chiseled and the arches that support the ceiling are remarkably well constructed. The Incense Route - Desert Cities in the Negev, including Mampsis, Haluza, Av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elusa (Haluza)
The ancient city of Halasa or Chellous (), Elusa () in the Byzantine period, was a city in the Negev near present-day Kibbutz Mash'abei Sadeh that was once part of the Nabataean Incense Route. It lay on the route from Petra to Gaza.Carta's Official Guide to Israel, 1983. Today it is known as Haluza (), and during periods of Arab habitation it was known as al-Khalūṣ (; Early Muslim period) and Al-Khalasa (; 20th century). In the 5th century it was surrounded by vineyards and was famous for its wines. Due to its historic importance, UNESCO declared Haluza a World Heritage Site along with Mamshit, Avdat and Shivta. Name in ancient sources The city is called 'Chellous' (Χελλοὺς) in the Greek text of Judith, i, 9 (seJdt 1:9in NABRE), a work probably dating to the 1st century BCE. It is also mentioned in the 2nd century CE by Ptolemy, Peutinger's Table, Stephanus Byzantius (fl. 6th century; as being formerly in the province of Arabia Petraea, but "now" in Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christianity during the Byzantine period. They h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incense Route
The incense trade route was an ancient network of major land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant and Egypt through Northeast Africa and Arabia to India and beyond. These routes collectively served as channels for the trading of goods such as Arabian frankincense and myrrh; Indian spices, precious stones, pearls, ebony, silk and fine textiles; and from the Horn of Africa, rare woods, feathers, animal skins, Somali frankincense, gold, and slaves. The incense land trade from South Arabia to the Mediterranean flourished between roughly the 3rd century BC and the 2nd century AD. Early history The Egyptians had traded in the Red Sea, importing spices, gold and exotic wood from the " Land of Punt" and from Arabia.Rawlinson 2001: 11–12 Indian goods were brought in Arabian and Indian vessels to Aden. Rawlinson identifies the lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makhtesh Ramon
Makhtesh Ramon (; ''lit.'' Ramon Crater/ Makhtesh; ; ''lit.'' The Ruman Wadi) is a geological feature of Israel's Negev desert. Located some 85 km south of Beersheba, the landform is the world's largest "erosion cirque" (steephead valley or box canyon). The formation is 40 km long, 2–10 km wide and 500 meters deep. Despite its appearance it is not an impact crater from a meteor nor a volcanic crater formed by a volcanic eruption. The only settlement in the area is the small town of Mitzpe Ramon (מצפה רמון, "Ramon Lookout") located on the northern edge of the depression. Today the area forms Israel's largest national park, the Ramon Nature Reserve. Formation Hundreds of millions of years ago, the Negev was covered by the Tethys ocean. Slowly, it started to recede northwards leaving behind a hump-shaped hill. The hump was slowly flattened by water and climatic forces. Approximately 5 mya, the Arava Rift Valley was formed, with rivers changing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obodas I
Obodas I (Nabataean Aramaic: ''ʿŌbōdaṯ''; ) was king of the Nabataeans from 96 to 85 BC. After his death, Obodas was worshiped as a deity. The king's name as transcribed in Arabic is ', which means "submission, obedience or worship (of god)". Life Obodas was the successor of Aretas II, from whom he inherited the war with the Hasmonean kingdom. He defeated them around 93 BCE on the Golan Heights. Then he ambushed Alexander Jannaeus near Gadara (Umm Qais), just east of the Sea of Galilee. Using camel cavalry, he forced Jannaeus into a valley where he completed the ambush, thereby getting revenge for the Nabateans' loss of Gaza. Moab and Gilead, two mountains east of the Dead Sea and the Jordan River, were returned. Around 86 BCE, the Seleucid ruler, Antiochus XII Dionysus, invaded Nabatea. During the Battle of Cana, Antiochus was slain and his demoralized army perished in the desert. The Nabataeans, seeing how Obodas defeated both the Hasmoneans and the Greeks, started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arabs, Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabah
The Arabah/Araba () or Aravah/Arava () is a loosely defined geographic area in the Negev Desert, south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east. The old meaning, which was in use up to around the early 20th century, covered almost the entire length of what today is called the Jordan Rift Valley, running in a north–south orientation between the southern end of the Sea of Galilee and the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba of the Red Sea at Aqaba–Eilat. This included the Jordan River Valley between the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea, the Dead Sea itself, and what today is commonly called the Arava Valley. The contemporary use of the term is restricted to this southern section alone. Geography The Arabah is in length, from the Gulf of Aqaba to the southern shore of the Dead Sea. Topographically, the region is divided into three sections. From the Gulf of Aqaba northward, the land gradually rises over a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darb Es-Sultan
Darb may refer to: Places * Darb, Armenia * Darb, Andika, Iran * Darb, Bagh-e Malek, Iran * Darb, Izeh, Iran * Darb-e Bagh, Iran * Darb-e Juqa, Iran * Al Darb (), Jizan Region, Saudi Arabia; a governorate Other uses * , botanical abbreviation for British botanist Otto Vernon Darbishire (1870–1934) * Darb (sword), a Thai/Lao single-edge sword / martial arts weapon See also * * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |