|
Avaris
Avaris (Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; ; ; ) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. As the main course of the Nile migrated eastward, its position at the hub of Egypt's delta emporia made it a major capital suitable for trade. It was occupied from about the 18th century BC until its capture by Ahmose I. Etymology The name in the Egyptian language of the 2nd millennium BC was probably pronounced *Ḥaʔət-Waʕrəʔ “House of the Region” and denotes the capital of an administrative division of the land (''wʕr.t''). Today, the name ''Hawara'' survives, referring to the site at the entrance to Faiyum. Alternatively, Clement of Alexandria referred to the name of this city as "Athyria". Excavations In 1885, the Swiss Édouard Naville started the first excavations in the area around Tell-el-Daba. Between 1941 and 1942, Labib Habachi, an Egyptian Egyptologist first forwarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyksos
The Hyksos (; Egyptian language, Egyptian ''wikt:ḥqꜣ, ḥqꜣ(w)-wikt:ḫꜣst, ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''heqau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands"), in modern Egyptology, are the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC). Their seat of power was the city of Avaris in the Nile Delta, from where they ruled over Lower Egypt and Middle Egypt up to Cusae. In the ''Aegyptiaca'', a history of Egypt written by the Greco-Egyptian priest and historian Manetho in the 3rd century BC, the term Hyksos is used ethnically to designate people of probable West Semitic, Levantine origin. While Manetho portrayed the Hyksos as invaders and oppressors, this interpretation is questioned in modern Egyptology. Instead, Hyksos rule might have been preceded by groups of Canaanite peoples who gradually settled in the Nile Delta from the end of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty onwards and who may have seceded from the crumbling and unstable Egyptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamose
Kamose was the last king of the Thebes, Egypt, Theban Seventeenth dynasty of Egypt, Seventeenth Dynasty at the end of the Second Intermediate Period. Kamose is usually ascribed a reign of three years (his highest attested regnal year), although some scholars now favor giving him a longer reign of approximately five years. He was the son of Seqenenre Tao and the brother of Ahmose I, founder of the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. His mother is unknown, but is thought to be Ahhotep I. His reign is important for the decisive military initiatives he took against the Hyksos, who had come to rule much of Ancient Egypt. His father had begun the initiatives and lost his life in battle with the Hyksos. It is thought that his mother, as regent, continued the campaigns after the death of Kamose, and that his full brother made the final conquest of them and united all of Egypt. Campaigns ''Casus Belli'' Kamose was the final king in a succession of native Egyptian kings at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell El-Dab'a
Tell el-Dab'a is the modern name for the ancient city of Avaris, an archaeological site in the Nile Delta region of Egypt where the capital city of the Hyksos, once stood. Avaris was occupied by Asiatics from the end of the 12th through the 13th Dynasty consisting a mixture of cultures of Near East and Egyptian. Avaris became one of the largest city and capital of the Near East during the 14th Dynasty under the Hyksos King Nehesy, consisting of a large Asiatic population. Avaris, geological was placed within a strategic location becoming a military rival to the Egyptians. The Hyksos stayed militarily rivals to the Egyptians till their defeat and partial abandonment of Avaris at the end of the Second Intermediate Period when Ahmoses I reunified Egypt at the end of the 17th Dynasty and start of the New Kingdoms 18th Dynasty. Avaris still contained a large population of Asiatic until its full abandonment following the construction of Pi-Ramesses under Ramesses II during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose I
Ahmose I (''Amosis'', ''Aahmes''; meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh and founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt in the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. His reign is usually dated to the mid-16th century BC at the beginning of the Late Bronze Age. During his reign, Ahmose completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos, restored Theban rule over Lower- and Upper Egypt, and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia and Canaan. He then reorganized the administration of the country, reopened quarry, quarries, mining, mines and trade routes and began massive construction projects of a type that had not been undertaken since the time of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. This building program culminated in the construction of the last Egyptian pyramids, pyramid built by native Egyptian rulers. Ahmose's reign laid the foundations for the New Kingdom of Egypt, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi-Ramesses
Pi-Ramesses (; Ancient Egyptian: , meaning "House of Ramesses") was the new capital built by the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses II (1279–1213 BC) at Qantir, near the old site of Avaris. The city had served as a summer palace under Seti I (c. 1290–1279 BC), and may have been founded by Ramesses I (c. 1292–1290 BC) while he served under Horemheb. Discovery In 1884, Flinders Petrie arrived in Egypt to begin his excavations there. His first dig was at Tanis, Egypt, Tanis, where he arrived with 170 workmen. Later in the 1930s, the ruins at Tanis were explored by Pierre Montet. The masses of broken Ramesside stonework at Tanis led archaeologists to identify it as Pi-Ramesses. Yet it eventually came to be recognised that none of these monuments and inscriptions originated at the site. In the 1960s, Manfred Bietak recognised that Pi-Ramesses was known to have been located on the then-easternmost branch of the Nile. He painstakingly mapped all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labib Habachi
Labib Habachi (لبيب حبشي; April 18, 1906 – February 18, 1984) was an Egyptian egyptologist. Dr. Habachi spent 30 years in the Antiquities Department of the Egyptian Government, ending his career as Chief inspector. During this period he spent an enormous amount of time in numerous dig sites in Egypt and the Sudan. He left government work to accept a position at the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago as an Archaeological Consultant to its Nubian Expedition. Tell el-Dab'a Born to a Coptic family, between 1929 and 1939, Pierre Montet excavated at Tanis, finding the royal necropolis of the Twenty-first and Twenty-second Dynasties — the finds there almost equalled that of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings. He believed that he found the location of Avaris, and this opinion was widely accepted at the time. Yet Habachi was not convinced. In 1941-42 he worked at Tell el-Dab'a for the Egyptian Antiquities Service and came to the conclusion that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
Thebes (, , ''Thēbai''), known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome (Sceptre nome) and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a religious center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. Toponymy The Egyptian name for Thebes was ''w� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan palaces at Knossos and Phaistos are popular tourist attractions. The Minoan civilization developed from the local Neolithic culture around 3100BC, with complex urban settlements beginning around 2000BC. After 1450BC, they came under the cultural and perhaps political domination of the mainland Mycenaean Greeks, forming a hybrid culture which lasted until around 1100BC. Minoan art included elaborately decorated pottery, seals, figurines, and colorful frescoes. Typical subjects include nature and ritual. Minoan art is often described as having a fantastical or ecstatic quality, with figures rendered in a manner suggesting motion. Little is known about the structure of Minoan society. Minoan art contains no unambiguous depiction of a monarch, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
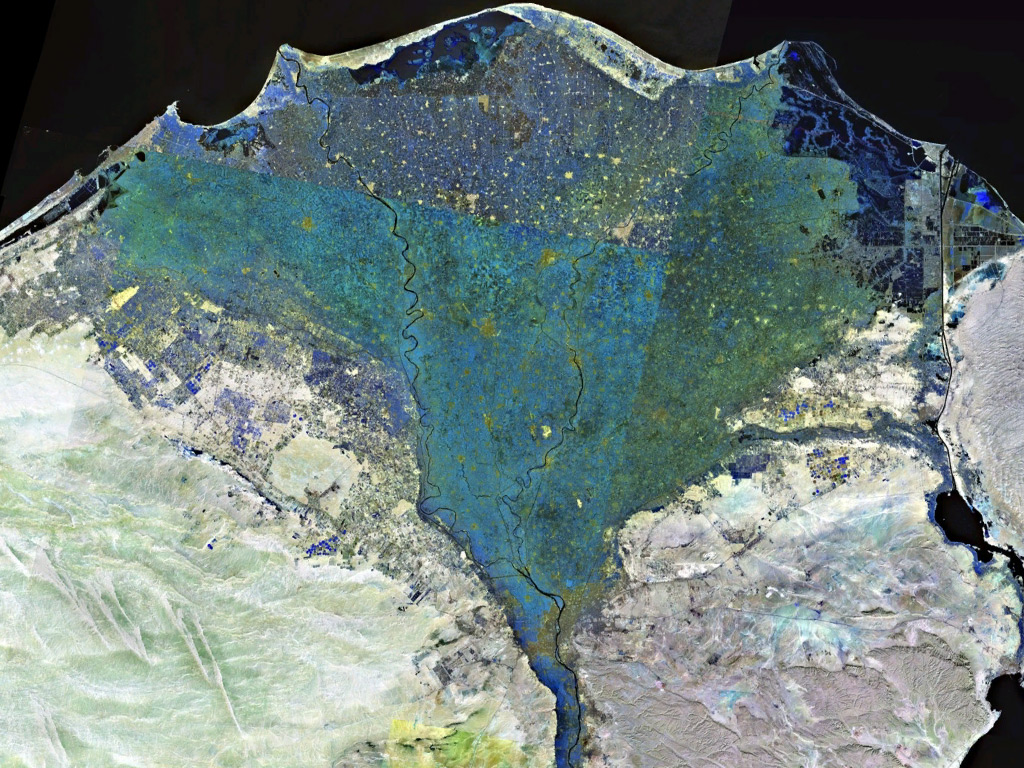
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty, he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom, which itself was the most powerful period of ancient Egypt. He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the Battle of Kadesh, generally considered a stalemate. In Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek sources, he is called Ozymandias, derived from the first part of his Egyptian-language regnal name: . Ramesses was also referred to as the "Great Ancestor" by successor pharaohs and the Egyptian people. For the early part of his reign, he focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep II
Amenhotep II (sometimes called Amenophis II and meaning "Amun is Satisfied") was the seventh pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. He inherited a vast kingdom from his father Thutmose III, and held it by means of a few military campaigns in Syria; however, he fought much less than his father, and his reign saw the effective cessation of hostilities between Egypt and Mitanni, the major kingdoms vying for power in Syria. His reign is usually dated from 1427 to 1401 BC. His consort was Tiaa, who was barred from any prestige until Amenhotep's son, Thutmose IV, came into power. Family and early life Amenhotep II was born to Thutmose III and a minor wife of the king: Merytre-Hatshepsut. He was not, however, the firstborn son of this pharaoh; his elder brother Amenemhat, the son of the great king's chief wife Satiah, was originally the intended heir to the throne since Amenemhat was designated the 'king's eldest son" and overseer of the cattle of Amun in Year 24 of Thut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |