|
Autoinjector
An autoinjector (or auto-injector) is a medical device for injection of a premeasured dose of a particular drug. Most autoinjectors are one-use, disposable, spring-loaded syringes (prefilled syringes). By design, autoinjectors are easy to use and are intended for self-administration by patients, administration by untrained personnel, or easy use by healthcare professionals; they can also overcome the hesitation associated with self-administration using a needle. The site of injection depends on the drug, but it typically is administered into the thigh or the buttocks. Autoinjectors are sharps waste. History Automatic syringes are known since the 1910s, and many spring-loaded devices with needle protectors were patented in the first half of the 20th century, but it was not until 1970s when they became economically feasible to mass-produce (simple syrettes were used instead before). In 2023 an open source autoinjector was developed that could be digitally replicated with a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epinephrine Autoinjector
An epinephrine autoinjector (or adrenaline autoinjector, also known by the trademark EpiPen) is a medical device for injecting a measured dose or doses of epinephrine (adrenaline) by means of autoinjector technology. It is most often used for the treatment of anaphylaxis. The first epinephrine autoinjector was brought to market in 1983. Medical uses Epinephrine autoinjectors are hand-held devices carried by those who have severe allergies; the epinephrine delivered by the device is an emergency treatment for anaphylaxis. When anaphylaxis is suspected, epinephrine solution should be given as soon as possible as an intramuscular injection, in the middle of the outer side of the thigh, which corresponds to the location of the vastus lateralis muscle. The injection may be repeated every 5 to 15 minutes if there is insufficient response. A second dose is needed in 16–35% of episodes with more than two doses rarely required; in around 80% of the cases where a second dose is adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoinjector
An autoinjector (or auto-injector) is a medical device for injection of a premeasured dose of a particular drug. Most autoinjectors are one-use, disposable, spring-loaded syringes (prefilled syringes). By design, autoinjectors are easy to use and are intended for self-administration by patients, administration by untrained personnel, or easy use by healthcare professionals; they can also overcome the hesitation associated with self-administration using a needle. The site of injection depends on the drug, but it typically is administered into the thigh or the buttocks. Autoinjectors are sharps waste. History Automatic syringes are known since the 1910s, and many spring-loaded devices with needle protectors were patented in the first half of the 20th century, but it was not until 1970s when they became economically feasible to mass-produce (simple syrettes were used instead before). In 2023 an open source autoinjector was developed that could be digitally replicated with a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat closing due to swelling that can obstruct or stop breathing; severe tongue swelling that can also interfere with or stop breathing; shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, and medical shock. These symptoms typically start in minutes to hours and then increase very rapidly to life-threatening levels. Urgent medical treatment is required to prevent serious harm and death, even if the patient has used an epinephrine autoinjector or has taken other medications in response, and even if symptoms appear to be improving. Cause, mechanism, and diagnosis Common causes include allergies to insect bites and stings, allergies to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
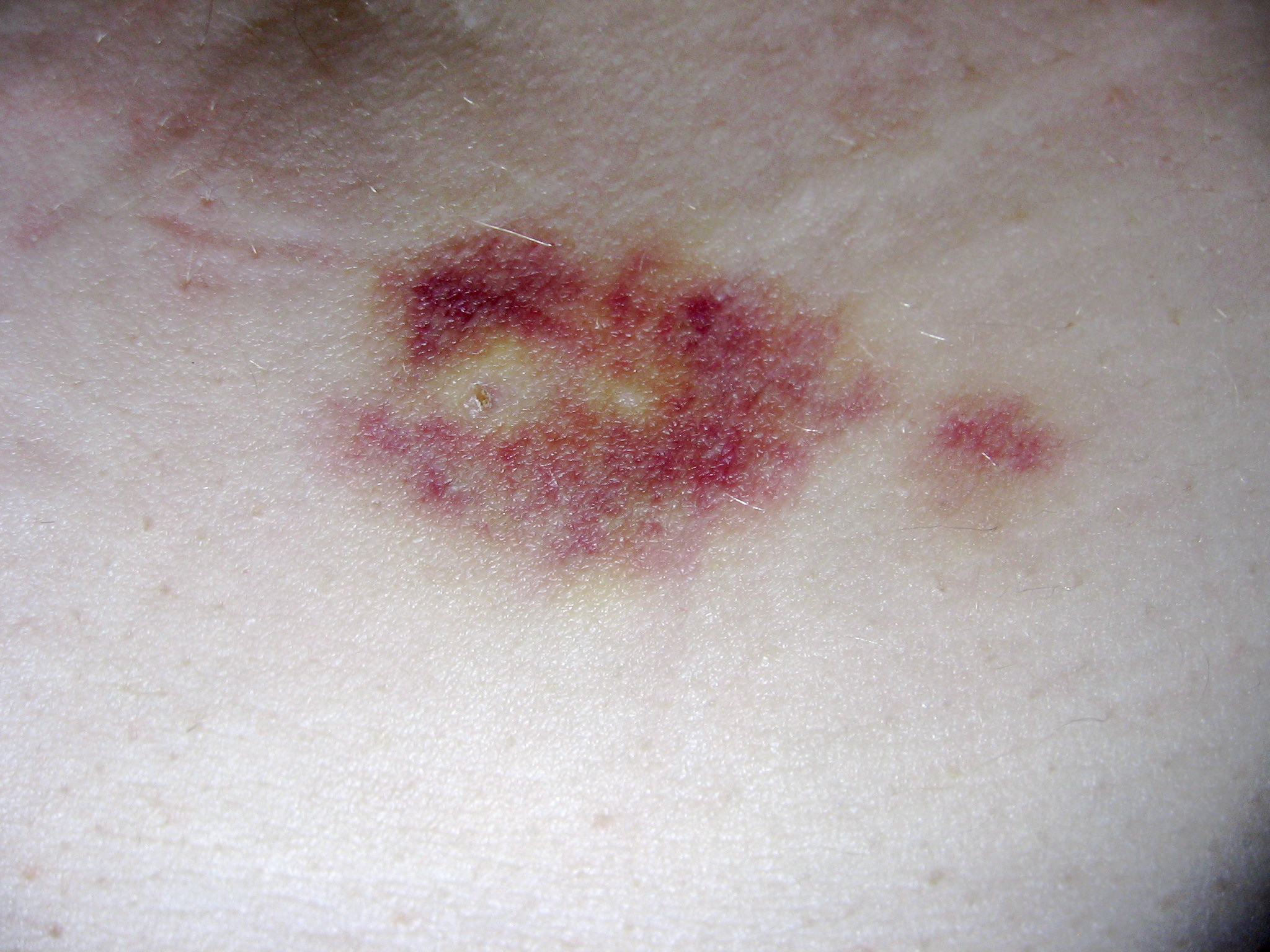
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle or tubing to direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are frequently used in clinical medicine to administer injections, infuse intravenous therapy into the bloodstream, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and draw/measure liquids. There are also prefilled syringes (disposable syringes marketed with liquid inside). The word "syringe" is derived from the Greek σῦριγξ ('' syrinx'', meaning "Pan flute", "tube"). Medical syringes Medical syringes include disposable and safety syringes, injectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrette
A syrette is a single-use device for injecting liquid through a needle. It is similar to a syringe except that it has a sealed squeeze tube instead of a rigid tube and piston. It was developed by the pharmaceutical manufacturer E.R. Squibb & Sons (eventually merged into the current day Bristol-Myers Squibb) just prior to World War II (WWII). In WWII, the morphine syrette was included in first aid kits. It had a wire loop with a guard at the end of a hollow needle that was used to break a seal where the needle was attached to the tube. The wire loop was then removed and the needle was inserted under the skin at a shallow angle and the tube slowly squeezed from the sealed end (see subcutaneous injection). After injection the used tube was often pinned to the receiving soldier's collar to inform others of the dose administered. The syrette was adopted for use by the United States Army in 1940. The US military also distributed atropine in syrettes. Chemical treatment was subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization () refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents (such as prions or viruses) present in fluid or on a specific surface or object. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure food preservation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, fluid or an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period of time slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebif
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified ''E. coli''. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses. Interferon beta has not been shown to slow the advance of disability. Interferons are not a cure for MS (there is no known cure); the claim is that interferons may slow the progress of the disease if started early and continued for the duration of the disease. Medical uses Clinically isolated syndrome The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), that is, a single attack of a single symptom. During a CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive of demyelination which should be included in the spectrum of MS phenotypes. Treatment with interferons after an initial atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nail Gun
A nail gun, nailgun or nailer is a form of hammer used to drive nails into wood or other materials. It is usually driven by compressed air ( pneumatic), electromagnetism, highly flammable gases such as butane or propane, or, for powder-actuated tools, a small explosive charge. Nail guns have in many ways replaced hammers as tools of choice among builders. The nail gun was designed by Morris Pynoos, a civil engineer by training, for his work on Howard Hughes' Hughes H-4 Hercules (known as the Spruce Goose). The wooden fuselage was nailed together and glued, and then the nails were removed. The first nail gun used air pressure and was introduced to the market in 1950 to speed the construction of housing floor sheathing and sub-floors. With the original nail gun, the operator used it while standing and could nail 40 to 60 nails a minute. It had a capacity of 400 to 600 nails. Use Nail guns use fasteners mounted in long clips (similar to a stick of staples) or collated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon Beta-1a
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified ''E. coli''. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses. Interferon beta has not been shown to slow the advance of disability. Interferons are not a cure for MS (there is no known cure); the claim is that interferons may slow the progress of the disease if started early and continued for the duration of the disease. Medical uses Clinically isolated syndrome The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), that is, a single attack of a single symptom. During a CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive of demyelination which should be included in the spectrum of MS phenotypes. Treatment with interferons after an initial atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |