|
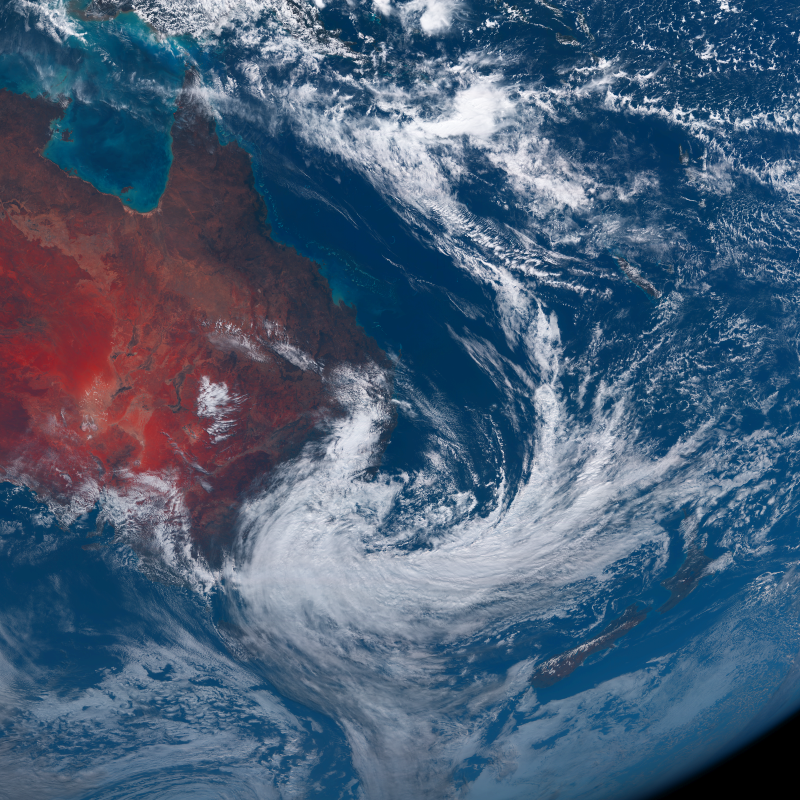
Australian East Coast Low
Australian east coast lows (known locally as east coast lows, maritime lows, and east coast cyclones) are extratropical cyclones or low-pressure systems on the coast of southeastern Australia that may be caused by both mid-latitude and tropical influences over a variety of levels in the atmosphere.East coast lows and climate change in Australia The Earth Systems and Climate Change Hub These storms should not be confused with s which typically affect the northern half of the continent. The most intense of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface Trough (meteorology), trough of Low-pressure area, low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Northern Hemisphere, to the east in the Southern Hemisphere, Southern), at the leading edge of its cold air Advection#Meteorology, advection pattern—known as the cyclone's dry "conveyor belt" flow. Temperature differences across the boundary can exceed from one side to the other. When enough moisture is present, rain can occur along the boundary. If there is significant Convective instability, instability along the boundary, a Squall line, narrow line of thunderstorms can form along the frontal zone. If instability is weak, a broad shield of rain can move in behind the Weather front, front, and evaporative cooling of the rain can increase the temperature difference across the front. Cold fronts are stronger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Coast (New South Wales)
The South Coast refers to the narrow coastal belt from the Shoalhaven district in the north to the state border with Victoria in the south in the south-eastern part of the State of New South Wales, Australia. It is bordered to the west by the coastal escarpment of the Southern Tablelands, and is largely covered by a series of national parks, namely Jervis Bay National Park, Eurobodalla National Park, and Beowa National Park. To the east is the coastline of the Pacific Ocean, which is characterised by rolling farmlands, small towns and villages along a rocky coastline, interspersed by numerous beaches and lakes. The South Coast includes Shoalhaven district in the north and the Bega Valley in the more remote south as well as the Eurobodalla Shire and the Commonwealth Jervis Bay Territory which is adjacent to the City of Shoalhaven Local Government Area. Some definitions of the region include the Illawarra, but it is often seen as a separate and distinct region of New Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladstone, Queensland
Gladstone () is a coastal city in the Gladstone Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the Gladstone urban area had a population of 45,185 people. It is by road north-west of the state capital, Brisbane, and south-east of Rockhampton, Queensland, Rockhampton. Situated between the Calliope River, Calliope and Boyne River (Central Queensland), Boyne Rivers, Gladstone is home to Queensland's largest multi-commodity shipping port, the Port of Gladstone. Gladstone is the largest town within the Gladstone Region and the headquarters of Gladstone Regional Council is located in Gladstone. History Before European settlement, the Gladstone region was home of the Gooreng Gooreng, Toolooa (or Tulua), Meerooni and Baiali (or Byellee) Aboriginal tribes. In May 1770, , under the command of James Cook, sailed by the entrance to Gladstone Harbour under the cover of darkness. Matthew Flinders, during his 1801–1803 circumnavigation of Australia, became the first recorded European to sigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SL 96P 2021-02-22 0165Z
SL may refer to: Arts and entertainment * SL (rapper), a rapper from London * ''Second Life'', a multi-user 3D virtual world * Sensei's Library, an Internet site dedicated to the game of Go * Subdominant leittonwechselklänge * Leica SL, a mirrorless system camera by Leica Camera AG Business and organizations * Sociedad Limitada, the Spanish version of a private limited company Politics * Serbian Left (''Srpska levica''), a political party in Serbia * Stronnictwo Ludowe, a defunct Polish political party * Soyons Libres, a French political party Transportation and vehicles * SL Corporation, a Korean auto parts company * Rio Sul Serviços Aéreos Regionais (IATA code SL), a Brazilian airline * Salt Lake City Southern Railroad (reporting mark SL) * Stor-Oslo Lokaltrafikk, a public transport operator in Akershus, Norway * Storstockholms Lokaltrafik, the public transport operator in Stockholm, Sweden * Thai Lion Air (IATA airline code SL) * Mercedes-Benz SL-Class, an automobile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoptic Scale Meteorology
In meteorology, the synoptic scale (also called the large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions (e.g. extratropical cyclones). Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps (such as surface weather analyses) are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word '' synoptic'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "seen together". The Navier–Stokes equations applied to atmospheric motion can be simplified by scale analysis in the synoptic scale. It can be shown that the main terms in horizontal equations are Coriolis force and pressure gradient terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Meteorology
Mesoscale meteorology is the study of weather systems and processes at horizontal scales of approximately to several hundred kilometres. It is smaller than synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic-scale systems (1,000 km or larger) but larger than Microscale meteorology, microscale (less than 1 km). At the small end, it includes storm-scale phenomena (the size of an individual thunderstorm). Examples of mesoscale weather systems are sea breezes, squall lines, and mesoscale convective complexes. Vertical velocity often equals or exceeds horizontal velocities in mesoscale meteorological systems due to nonhydrostatic processes such as buoyant acceleration of a rising thermal or acceleration through a narrow mountain pass. Classification The History of weather forecasting, earliest networks of weather observations in the late 1800s and early 1900s could detect the movement and evolution of larger, synoptic scale, synoptic-scale systems like high pressure area, high and low-pressure area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Cyclogenesis
Explosive cyclogenesis (also referred to as a weather bomb, meteorological bomb, explosive development, bomb cyclone, or bombogenesis) is the rapid deepening of an extratropical cyclonic low-pressure area. The change in pressure needed to classify something as explosive cyclogenesis is latitude dependent. For example, at 60° latitude, explosive cyclogenesis occurs if the central pressure decreases by or more in 24 hours. This is a predominantly maritime, winter event, but also occurs in continental settings. This process is the extratropical equivalent of the tropical rapid deepening. Although their cyclogenesis is entirely different from that of tropical cyclones, bomb cyclones can produce winds of , the same order as the first categories of the Saffir–Simpson scale, and yield heavy precipitation. Even though only a minority of bomb cyclones become this strong, some weaker ones can also cause significant damage. History In the 1940s and 1950s, meteorologists at the Bergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECL25 06 13
ECL may refer to: Science and technology * Electrochemiluminescence * Enhanced chemiluminescence * Emitter-coupled logic * Enterochromaffin-like cell Computing * ECL programming language, an extensible programming language * ECL (data-centric programming language) * Embeddable Common Lisp Sport * East Cornwall League, an English football league * Eastern Colored League, a defunct American baseball league * Eastern Counties Football League, in England * European Cricket League, a professional cricket league organized by ICC member federations * UEFA Europa Conference League, annual football club competition organised by UEFA * European Champions League (table tennis), annual table tennis club competition * Entertainers Cricket League (Cricket), an Indian cricket league organized by social media celebrities Other uses * Eccleston Park railway station, in England * Ecolab, a sanitation supply company * École centrale de Lyon, a graduate engineering school in Lyon, France * Educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and ''sphere, sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Core
A cold-core low, also known as an upper level low or cold-core cyclone, is a cyclone aloft which has an associated cold pool of air residing at high altitude within the Earth's troposphere, without a weather front, frontal structure. It is a low pressure system that strengthens with height in accordance with the thermal wind relationship. If a weak surface circulation forms in response to such a feature at subtropical latitudes of the eastern north Pacific Ocean, Pacific or north Indian Ocean, Indian oceans, it is called a subtropical cyclone. Cloud cover and rainfall mainly occurs with these systems during the day. Severe weather, such as tornadoes, can occur near the center of cold-core lows. Cold lows can help spawn cyclones with significant weather impacts, such as polar lows, and Kármán vortex street, Kármán vortices. Cold lows can lead directly to the development of tropical cyclones, owing to their associated cold pool of air aloft or by acting as additional outflow (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABC News (Australia)
ABC News, also known as ABC News and Current Affairs, is a public news service produced by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation. The service covers both local and world affairs, broadcasting both nationally as ABC News, and across the Asia-Pacific under the ''ABC Australia'' title. The division of the organisation ABC News, Analysis and Investigations is responsible for all news-gathering and coverage across the Australian Broadcasting Corporation's various television, radio, and online platforms. Some of the services included under the auspices of the division are its 24-hour news channel ABC News Australia TV Channel (formerly ABC News 24), the long-running radio news programs, '' AM'', '' The World Today'', and '' PM''; ABC NewsRadio, a 24-hour continuous news radio channel; and radio news bulletins and programs on ABC Local Radio, ABC Radio National, ABC Classic FM, and Triple J. ABC News Online has an extensive online presence which includes many written news ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |