|
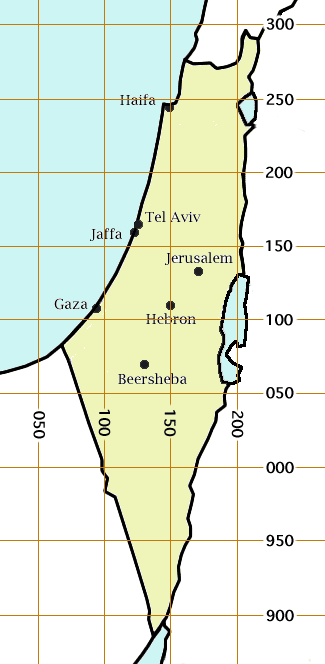
Atlit
Atlit ( he, עַתְלִית, ar, عتليت) is a coastal town located south of Haifa, Israel. The community is in the Hof HaCarmel Regional Council in the Haifa District of Israel. Off the coast of Atlit is a submerged Neolithic village. Atlit was also a Crusader outpost, the Château Pèlerin, which fell to the Mamluks in 1291. During their rule, in the 14th century, it became home to a large concentration of Oirat Mongols. During early Ottoman rule, in the 16th century, it was recorded in tax registers as a port of call and a farm. Later, in the 19th century, it was a small Arab fishing village under the influence of the local al-Madi family. An adjacent Jewish village was reestablished in 1903 under the auspices of Baron Edmond de Rothschild, which merged with the remnants of the Crusader fortress village. The Atlit detainee camp is nearby, which was used by the British to intern Jewish refugees and is now a museum. From 1950 until the unification of the municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlit Detainee Camp
The Atlit detainee camp was a concentration camp established by the authorities of Mandatory Palestine in the late 1930s on what is now the Israeli coastal plain, south of Haifa. Under British rule, it was primarily used to hold Jews and Arabs who were in administrative detention; it largely held Jewish immigrants who did not possess official entry permits. Tens of thousands of Jewish refugees were interned at the camp, which was surrounded by barbed wire and watchtowers. The camp at Atlit now has a museum that covers the history of ''aliyah'' by non-permitted Jews. It was declared a National Heritage Site by Israel in 1987. History The camp at Atlit, established by the British government in the 1930s, was surrounded by barbed wire and watchtowers. Many of the detainees during the 1930s and 1940s were Jewish refugees from German-occupied Europe. In the late 1940s, most of the inmates were Holocaust survivors. The British authorities, acceding to Arab demands to limit Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlit Yam
Atlit Yam is an ancient submerged Neolithic village off the coast of Atlit, Israel. It has been carbon-dated as to be between 8,900 and 8,300 years old. Among the features of the 10-acre site is a stone circle. History Atlit-Yam provides the earliest known evidence for an agro-pastoral-marine subsistence system on the Levantine coast. The site of Atlit Yam has been carbon-dated to be between 8,900 and 8,300 years old (calibrated dates) and belongs to the final Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. It is currently between 8–12 m (25–40 ft) beneath sea level in the Mediterranean Sea, in the Bay of Atlit, at the mouth of the Oren river on the Carmel coast. It covers an area of ca. 40,000 square meters (10 acres). Underwater excavations have uncovered rectangular houses and a well. The site was covered by the eustatic rise of sea levels after the end of the last Ice Age. It is assumed that the contemporary coastline was about 1 km (a half-mile) west of the present coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château Pèlerin
Château Pèlerin (Old French: Chastel Pelerin; la, Castrum Perigrinorum), also known as Atlit Castle and Pilgrim Castle, is a Crusader fortress located near Atlit on the northern coast of Israel, about south of Haifa. The Knights Templar began building the fortress in 1218 during the Fifth Crusade. One of the major Crusader fortresses, it could support up to 4,000 troops in siege conditions. It was abandoned by its garrison and taken over by the Mamluks in August 1291, shortly after the Fall of Acre. It remained intact for several hundred years, until suffering damage in the Galilee earthquake of 1837. In modern times, the castle is part of a training zone for Israeli Naval commandos. It has been described as the "crowning example of Crusader military architecture", although T. E. Lawrence found it lacking in elegance and imagination in terms of military architecture, setting on massiveness instead. History Construction began in early spring 1218 during the period of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah Bet
''Aliyah Bet'' ( he, עלייה ב', "Aliyah 'B'" – bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet) was the code name given to illegal immigration by Jews, most of whom were refugees escaping from Nazi Germany, and later Holocaust survivors, to Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and 1948, in violation of the restrictions laid out in the British White Paper of 1939, which dramatically increased between 1939 and 1948. With the establishment of the State of Israel in May 1948, Jewish displaced persons and refugees from Europe began streaming into the new sovereign state. In modern-day Israel it has also been called by the Hebrew term ''Ha'apala'' ( he, הַעְפָּלָה, "Ascension"). The ''Aliyah Bet'' is distinguished from the ''Aliyah Aleph'' ("Aliyah 'A'", Aleph being the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet) which refers to the limited Jewish immigration permitted by British authorities during the same period. The name ''Aliya B'' is also shortened name for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Eastern Mediterranean, southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the Economy of Israel, economic and Science and technology in Israel, technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Status of Jerusalem, Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Ruad
The fall of Ruad in 1302 was one of the culminating events of the Crusades in the Eastern Mediterranean. When the garrison on the tiny Isle of Ruad fell, it marked the loss of the last Crusader outpost on the coast of the Levant. In 1291, the Crusaders had lost their main power base at the coastal city of Acre, and the Muslim Mamluks had been systematically destroying any remaining Crusader ports and fortresses since then, forcing the Crusaders to relocate their dwindling Kingdom of Jerusalem to the island of Cyprus. In 1299–1300, the Cypriots sought to retake the Syrian port city of Tortosa, by setting up a staging area on Ruad, two miles (3 km) off the coast of Tortosa. The plans were to coordinate an offensive between the forces of the Crusaders, and those of the Ilkhanate (Mongol Persia). However, though the Crusaders successfully established a bridgehead on the island, the Mongols did not arrive, and the Crusaders were forced to withdraw the bulk of their forces to C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area in Israel. It is home to the Baháʼí Faith's Baháʼí World Centre, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a destination for Baháʼí pilgrimage. Built on the slopes of Mount Carmel, the settlement has a history spanning more than 3,000 years. The earliest known settlement in the vicinity was Tell Abu Hawam, a small port city established in the Late Bronze Age (14th century BCE). Encyclopedia Judaica, ''Haifa'', Keter Publishing, Jerusalem, 1972, vol. 7, pp. 1134–1139 In the 3rd century CE, Haifa was known as a dye-making center. Over the millennia, the Haifa area has changed hands: being conquered and ruled by the Canaanites, Israelites, Phoenicians, Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Hasmoneans, Romans, Byzant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlit From The 1871-77 Palestine Exploration Fund Survey Of Palestine
''Athlit'' is an album by ambient musician Oöphoi. It was released in 2002 on Hypnos Recordings. Track listing #"Drifting into Black Space" - 16:40 #"An Ever-Changing Horizon" - 10:30 #"On Wings Of Light" - 18:05 #"Lord Of The Starfields" - 28:31 References Oöphoi albums 2008 albums {{2002-album-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hof HaCarmel Regional Council
Hof HaCarmel Regional Council ( he, מועצה אזורית חוף הכרמל, ''Mo'atza Azorit Hof ha-Karmel'', ''lit.'' Carmel Coast Regional Council) is a regional council located in the northern Israeli coastal plain. The council serves a large area, stretching from Tirat HaCarmel in the north to Caesarea in the south. Its offices are located in Ein Carmel to the south of Haifa. The head of the council is Asif Izek, elected in 2018. Location Straddling the coast of the Mediterranean Sea to the west, the boundaries of the municipal area are: *To the north: Haifa, Tirat HaCarmel and Zevulun Regional Council *To the south: Hadera, Pardes Hanna-Karkur and Menashe Regional Council *To the east: Megiddo and Jezreel Valley regional councils as well as the Wadi Ara settlements. In the centre of the council area are the enclave towns of Binyamina, Zikhron Ya'akov, Fureidis and Jisr az-Zarqa. Communities Hof HaCarmel Regional Council contains many different types of settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haifa Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine
The Haifa Subdistrict (قضاء حيفا, נפת חיפה) was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It covered the northern Mediterranean coast of regional Palestine, southwestern Galilee, and the Wadi Ara region. It was disintegrated after the British withdrawal from the area. Prior to and during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War around half of the Arab localities were depopulated or destroyed. The entire district was captured by Israel and most of its Arab defenders were composed of the Arab Liberation Army and local militias. Its predecessor was Haifa Subdistrict, Ottoman Empire. The subdistrict was transformed into Haifa District, divided into Haifa Subdistrict and Hadera Subdistrict under Israel. Localities See also * Haifa District Haifa District ( he, מחוז חיפה, ''Mehoz Ḥeifa''; ar, منطقة حيفا) is an administrative district surrounding the city of Haifa, Israel. The district is one of the seven administrative districts of Israel, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Grid
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini-Soldner projection. The central meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative north-south coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by adding 1000 to the northern coordinate in that case. For some military purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak origin, commonly known as Baibars or Baybars ( ar, بيبرس, ''Baybars'') – nicknamed Abu al-Futuh (; English: ''Father of Conquests'', referring to his victories) – was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria in the Bahri dynasty, succeeding Qutuz. He was one of the commanders of the Egyptian forces that inflicted a defeat on the Seventh Crusade of King Louis IX of France. He also led the vanguard of the Egyptian army at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, which marked the first substantial defeat of the Mongol army and is considered a turning point in history. The reign of Baybars marked the start of an age of Mamluk dominance in the Eastern Mediterranean and solidified the durability of their military system. He managed to pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |