|
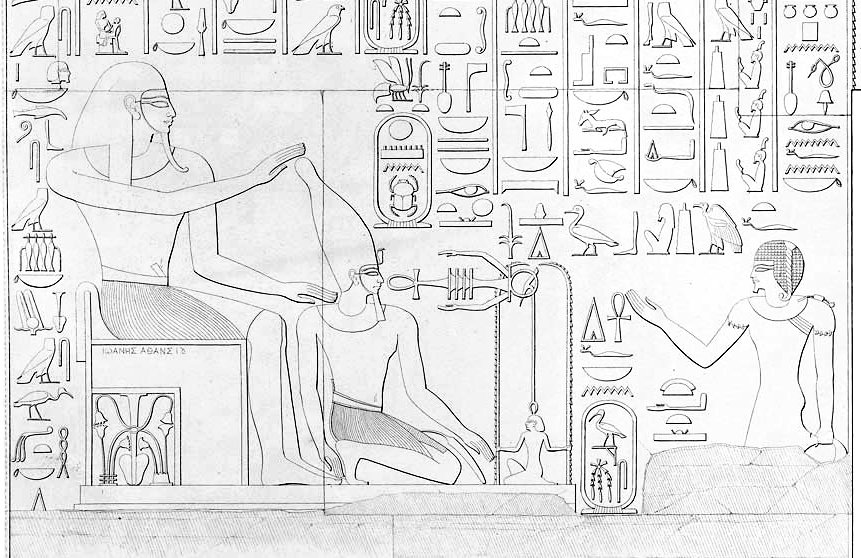
Atlanersa
Atlanersa (also Atlanarsa) was a Kushite ruler of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, reigning for about a decade in the mid-7th century BC. He was the successor of Tantamani, the last ruler of the 25th Dynasty of Egypt, and possibly a son of Taharqa or less likely of Tantamani, while his mother was a queen whose name is only partially preserved. Atlanersa's reign immediately followed the collapse of Nubian control over Egypt, which witnessed the Assyrian conquest of Egypt and then the beginning of the Late Period under Psamtik I. The same period also saw the progressive cultural integration of Egyptian beliefs by the Kushite civilization. Atlanersa may have fathered his successor Senkamanisken with his consort Malotaral, although Senkamanisken could also be his brother. He built a pyramid in the necropolis of Nuri, now conjecturally believed to be Nuri 20 and may also have started a funerary chapel in the same necropolis, now called Nuri 500. Atlanersa was the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuri
Nuri is a place in modern Sudan on the west side of the Nile, near the Fourth Cataract. Nuri is situated about 15 km north of Sanam, and 10 km from Jebel Barkal. Nuri is the second of three Napatan burial sites and the construction of pyramids at Nuri began when there was no longer enough space at El-Kurru. More than 20 ancient pyramids belonging to Nubian kings and queens are still standing at Nuri, which served as a royal necropolis for the ancient city of Napata, the first capital of the Nubian Kingdom of Kush. It is probable that, at its apex, 80 or more pyramids stood at Nuri, marking the tombs of royals. The pyramids at Nuri were built over a period of more than three centuries, from circa 670 BCE for the oldest (pyramid of Taharqa), to around 310 BCE (pyramid of king Nastasen). The earliest known pyramid (Nu. 1) at Nuri belongs to king Taharqa which measures 51.75 meters square by 40 or by 50 metres high. The pyramid of Taharqa was situated so that when obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantamani
Tantamani ( egy, tnwt-jmn, Neo-Assyrian: , grc, Τεμένθης ), also known as Tanutamun or Tanwetamani (d. 653 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Kush located in Northern Sudan, and the last pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. His prenomen or royal name was Bakare, which means "Glorious is the Soul of Re." Filiation He was the son of King Shabaka and the nephew of his predecessor Taharqa. In some sources he is said to be the son of Shebitku. Assyrian records call Tantamani a son of Shabaka and refer to his mother, Qalhata, as a sister of Taharqa. Some Egyptologists interpreted the Assyrian text as stating that Tantamani was a son of Shebitku, but it is now more common to consider Tantamani a son of Shabaka. Conflict with Ashurbanipal of Assyria Soon after the Assyrians had appointed Necho I as king and left, Tantamani invaded Egypt in hopes of restoring his family to the throne. Tantamani marched down the Nile from Nubia and reoccupied all of Egypt, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senkamanisken
Senkamanisken was a Kushite King who ruled from 640 to 620 BC at Napata. He used royal titles based on those of the ancient Egyptian pharaohs. Biography He might have been married to queens Amanimalel and Nasalsa, the latter of whom bore him two sons: Anlamani and Aspelta. Both sons would ultimately assume the Kushite throne after his death at Napata, Nubia's capital city. His pyramid is Nu.3 in Nuri. Statues of Senkamanisken have been found buried or hidden in the Jebel Barkal, presumably due to Psamtik II's attack on Kush in 592 BC. A sphinx has also been found which was inscribed with his name. Objects bearing the name of this king have also been found in Meroë indicating that he placed a degree of importance to this site which would be the political capital of the Kushite kingdom after Psamtik II's sack of Napata in 592 BC. He is the only Nubian king after the 25th Dynasty known from an inscription found in Egypt. He appears on a fragment of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal ( ar, جبل بركل) is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a flat top, and came to have religious significance for both ancient Kush and ancient Egyptian occupiers. In 2003, the mountain, together with the extensive archaeological site at its base (ancient Napata), were named as the center of a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. The Jebel Barkal area houses the Jebel Barkal Museum. History The earliest occupation of Jebel Barkal was that of the Kerma culture that was also known as Kush, but this occupation is so far known only from scattered potsherds. Around 1450 BCE, the Egyptian Pharaoh Thutmose III conquered Barkal and built a fortified settlement (Egyptian ''menenu'') there as the southern limit of the Egyptian empire. The city and region around it came to be called Napata, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenirdis II
The ancient Nubian princess Amenirdis II, daughter of the Kushite pharaoh Taharqa of the 25th Dynasty, was adopted by Shepenupet II, daughter of Piye, to become Divine Adoratrice of Amun from around 650 BC to 640 BC during the 26th Dynasty. Amenirdis adopted Nitocris, daughter of Psamtik I, to become her successor. She may have been married to one of Taharqa's sons, king Atlanersa Atlanersa (also Atlanarsa) was a Kushite ruler of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, reigning for about a decade in the mid-7th century BC. He was the successor of Tantamani, the last ruler of the 25th Dynasty of Egypt, and possibly a son of Tahar .... References * Robert Steven Bianchi, ''Daily Life Of The Nubians'', Greenwood Press 2004 * Karol Myśliwiec, ''The Twilight of Ancient Egypt: First Millennium B.C.E.'', Cornell University Press 2000 * I. E. S. Edwards, John Boardman, John B. Bury, S. A. Cook, ''The Cambridge Ancient History'', Cambridge University Press 1969 * Aidan Dodson, ''Monarchs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasalsa
Nasalsa was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is known from a shabti, some inscriptions on tablets and cups, text on the stela of Khaliut, a dedication inscription and a text from Kawa.Dows Dunham, M. F. Laming Macadam: ''Names and Relationships of the Royal Family of Napata'', Journal of Egyptian Archaeology. 35, 1949, pp.142 (Plate XVI; nr 50), 145 Dodson mentions that Nasalsa is named on the Enthronement Stela of Atlanersa and on the Election and Adoption Stelae of Aspelta. These stelae were from Gebel Barkal. Life Nasalsa was a daughter of Atlanersa, the sister-wife of Senkamanisken, and the mother of Kings Anlamani and Aspelta Aspelta was a ruler of the kingdom of Kush (c. 600 – c. 580 BCE). More is known about him and his reign than most of the rulers of Kush. He left several stelae carved with accounts of his reign. Family Aspelta was the son of Senkamanisken a ... as well as of Queen Madiqen.Aidan Dodson & Dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Monarchs Of Kush
This is an incomplete list for rulers with the title of Qore (king) or Kandake (queen) of the Kingdom of Kush. Some of the dates are only rough estimates. While the chronological list is well known, only a few monarchs have definite dates. These include those leaders who also ruled Ancient Egypt and those who ruled during famous invasions or famous trade expeditions. The others are based on estimates made by Fritz Hintze. The estimates are based on the average length of the reigns, which were then shortened or lengthened based on the size and splendour of the monarch's tomb, the assumption being that monarchs who reigned longer had more time and resources to build their burial sites. An added complication is that in recent years, there have been disputes as to which monarch belongs to which tomb. Dates are definite and accurate for the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, when Egypt was invaded and absorbed by the Kushite Empire. The dates are also certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenirdis II
The ancient Nubian princess Amenirdis II, daughter of the Kushite pharaoh Taharqa of the 25th Dynasty, was adopted by Shepenupet II, daughter of Piye, to become Divine Adoratrice of Amun from around 650 BC to 640 BC during the 26th Dynasty. Amenirdis adopted Nitocris, daughter of Psamtik I, to become her successor. She may have been married to one of Taharqa's sons, king Atlanersa Atlanersa (also Atlanarsa) was a Kushite ruler of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, reigning for about a decade in the mid-7th century BC. He was the successor of Tantamani, the last ruler of the 25th Dynasty of Egypt, and possibly a son of Tahar .... References * Robert Steven Bianchi, ''Daily Life Of The Nubians'', Greenwood Press 2004 * Karol Myśliwiec, ''The Twilight of Ancient Egypt: First Millennium B.C.E.'', Cornell University Press 2000 * I. E. S. Edwards, John Boardman, John B. Bury, S. A. Cook, ''The Cambridge Ancient History'', Cambridge University Press 1969 * Aidan Dodson, ''Monarchs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanimalel
Amanimalel (also Amanimalēl and Amanimalil) was a Kushite queen of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, likely a spouse of king Senkamanisken living in the second half of the 7th century BC. She is mostly known from one or possibly two statues of her of very high quality. Chronology and family Amanimalel lived in the second half of the 7th century BC. Several date have been proposed for her queenship based on those estimated for Senkamanisken's rule: 643–623 BC, or 642–623 BC. Amanimalel is presumed to have been a queen consort of Senkamanisken, who was also married to queen Nasalsa and, possibly, Masalaye. As such, Amanimalel could be the mother of queens Asata and Madekan who espoused kings Aspelta and Anlamani, respectively. These possibilities are debated however because of the lack of direct evidence on the matter. Amanimalel's parents are equally uncertain, she could be a daughter of Atlanersa. Attestations Amanimalel is attested by a high lifesize statue of the que ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Conquest Of Egypt
The Assyrian conquest of Egypt covered a relatively short period of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 673 BCE to 663 BCE. The conquest of Egypt not only placed a land of great cultural prestige under Assyrian rule but also brought the Neo-Assyrian Empire to its greatest extent. Context The Egyptians and Kushites had begun agitating peoples within the Assyrian empire in an attempt to gain a foothold in the region. As a result, in 701 BCE, Hezekiah of Judah, Lule king of Sidon, Sidka, king of Ascalon and the king of Ekron formed an alliance with Egypt against Assyria. The Neo-Assyrian ruler Sennacherib (705–681 BC) attacked the rebels, conquering Ascalon, Sidon and Ekron and defeating the Egyptians and driving them from the region. He marched toward Jerusalem, destroying 46 towns and villages (including the heavily defended city of Lachish) in his path. This is graphically described in Isaiah 10; exactly what happened next is unclear (the Bible says an angel of the Lord killed 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-fifth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXV, alternatively 25th Dynasty or Dynasty 25), also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt that occurred after the Nubian invasion. The 25th dynasty was a line of pharaohs who originated in the Kingdom of Kush, located in present-day northern Sudan and Upper Egypt. Most of this dynasty's kings saw Napata as their spiritual homeland. They reigned in part or all of Ancient Egypt for nearly a century, from 744 to 656 BC. The 25th dynasty was highly Egyptianized, using the Egyptian language and writing system as their medium of record and exhibiting an unusual devotion to Egypt's religious, artistic, and literary traditions. Earlier scholars have ascribed the origins of the dynasty to immigrants from Egypt, particularly the Egyptian Amun priests. The third intermediate-period Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedun
Dedun (or Dedwen) was a Nubian god worshipped during ancient times in ancient Egypt and Sudan and attested as early as 2400 BC. There is much uncertainty about his original nature, especially since he was depicted as a lion, a role which usually was assigned to the son of another deity. Nothing is known of the earlier Nubian mythology from which this deity arose, however. The earliest known information in Egyptian writings about Dedun indicates that he already had become a god of incense by the time of the writings. Since at this historical point, incense was an extremely expensive luxury commodity and Nubia was the source of much of it, he was quite an important deity. The wealth that the trade in incense delivered to Nubia led to his being identified by them as the god of prosperity, and of wealth in particular. He is said to have been associated with a fire that threatened to destroy the other deities, however, leading many Nubiologists to speculate that there may have been a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |