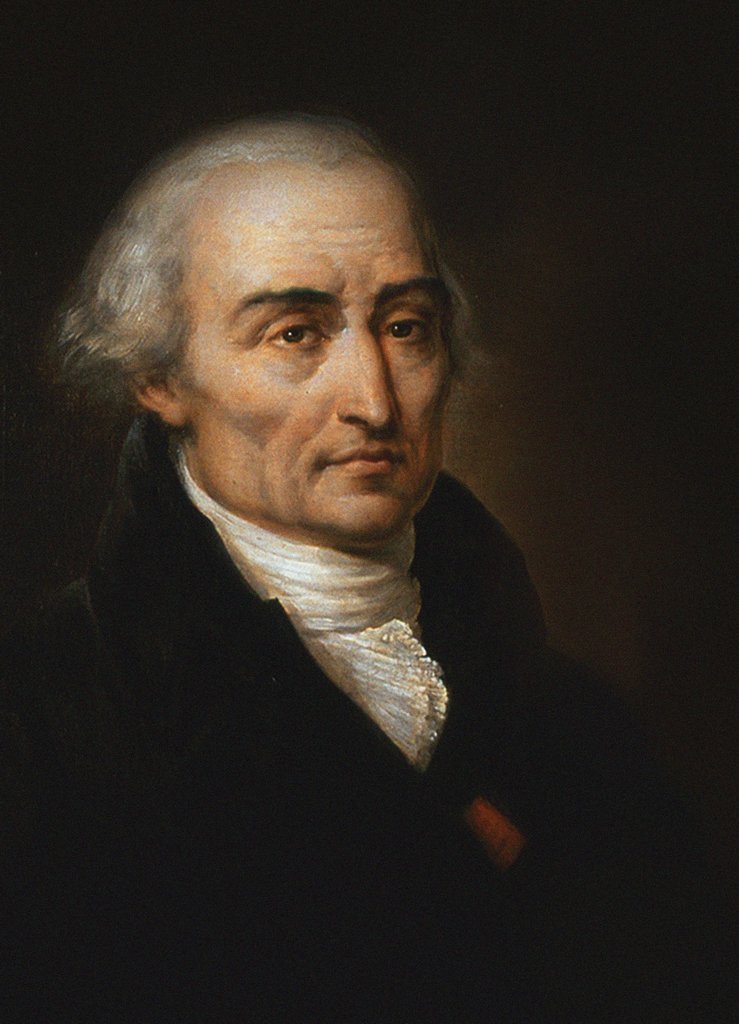|
Atanasije Stojković
Atanasije Stojković ( sr-Cyrl, Атанасије Стојковић, ; 20 September 1773 – 25 September 1832) was a Serbian, Austrian and Russian writer, pedagogue, scholar, physicist, mathematician and astronomer. He is considered the founder of Russian meteoritics. Stojković was the president of the Imperial University of Kharkov from 1807 to 1809 and from 1811 to 1813. Early life and education Stojković was born in Ruma, then part of the Austrian Empire (now modern-day Serbia) on 20 September 1773. He finished grammar school in his native village of Ruma in Srem. From 1789 to 1794 he attended the ''École polytechnique'' at Buda and later the University of Göttingen until 1798. His education (at Buda and Göttingen) was funded by the Metropolitan of the Serbian Orthodox Church at Sremski Karlovci, Stevan Stratimirović, and subsequently in Sremski Karlovci itself, where Stojković proposed to take orders. Upon graduation and on returning home, however, he abandoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Đurković
Pavle or Pavel Đurković (1772 – 1830) was a Serbian painter, portraitist and iconographer who distinguished himself in the iconography of monasteries and portraits of great personalities (mostly Serbs). His greatest work was the iconostasis of the church in Vršac and Bela Crkva from around 1792. Đurković "icon painter from Buda", because from 1793. he painted icons on the iconostasis of the White Church of Saint Peter and Paul. Biography Đurković was born in Baja, Kingdom of Hungary. He traveled to large cities and towns and portrayed wealthier citizens. Thus, in 1811, he made a portrait of Archimandrite Pavle Hadžić. In 1812, he worked in Zemun for the Karamata family, and in 1816 he portrayed Vuk Karadžić and Lukijan Musicki in Šišatovac. In 1820, he painted Metropolitan Stratimirović in Sremski Karlovci. After 1820, he traveled to Wallachia and Russia, painting along the way, and settled in Odessa, where his work went very well, where he progressed as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jena
Jena (; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a population of about 110,000. Jena is a centre of education and research. The University of Jena (formally the Friedrich Schiller University) was founded in 1558 and had 18,000 students in 2017 and the Ernst-Abbe-Hochschule Jena serves another 5,000 students. Furthermore, there are many institutes of the leading German research societies. Jena was first mentioned in 1182 and stayed a small town until the 19th century, when industry developed. For most of the 20th century, Jena was a world centre of the optical industry around companies such as Carl Zeiss AG, Carl Zeiss, Schott AG, Schott and Jenoptik (since 1990). As one of only a few medium-sized cities in Germany, it has some high-rise buildings in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known today for his association with Charles Darwin and as the author of ''Principles of Geology'' (1830–33), which presented to a wide public audience the idea that the earth was shaped by the same natural processes still in operation today, operating at similar intensities. The philosopher William Whewell dubbed this gradualism, gradualistic view "uniformitarianism" and contrasted it with catastrophism, which had been championed by Georges Cuvier and was better accepted in Europe. The combination of evidence and eloquence in ''Principles'' convinced a wide range of readers of the significance of "deep time" for understanding the earth and environment. Lyell's scientific contributions included a pioneering explanation of climate change, in which shifting boundaries between oceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Desnoyers
Jules Pierre François Stanislaus Desnoyers (8 October 18001 September 1887) was a French geologist and archaeologist. Life Desnoyers was born at Nogent-le-Rotrou, in the department of Eure-et-Loir. Becoming interested in geology at an early age, he was one of the founders of the Geological Society of France in 1830. In 1834, he was appointed librarian of the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris. He was elected a Foreign Member of the Geological Society of London in 1864. Parts of his collection of rare books in the earth sciences was bought by the United States Geological Survey Library at an auction in 1885. He was the Secretary of the Historical Society since its founding. Speleological activities Desnoyers was a spelunker. His article on caves for the ''Dictionnaire universel d’histoire naturelle'' (1841-1849) of Charles Henry Dessalines d'Orbigny broke new ground, emphasizing the role of hydrological phenomena in limestone and gypsum caves. He explored the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard Paul Deshayes
Gerard is a masculine forename of Proto-Germanic origin, variations of which exist in many Germanic and Romance languages. Like many other early Germanic names, it is dithematic, consisting of two meaningful constituents put together. In this case, those constituents are ''gari'' > ''ger-'' (meaning 'spear') and -''hard'' (meaning 'hard/strong/brave'). Common forms of the name are Gerard (English, Scottish, Irish, Dutch, Polish and Catalan); Gerrard (English, Scottish, Irish); (Italian, and Spanish); ( Portuguese); (Italian); (Northern Italian, now only a surname); (variant forms and , now only surnames, French); ( Irish); Gerhardt and Gerhart/ Gerhard/ Gerhardus (German, Dutch, and Afrikaans); ( Hungarian); ( Lithuanian) and / ( Latvian); (Greece). A few abbreviated forms are Gerry and Jerry (English); (German) and (Afrikaans and Dutch); (Afrikaans and Dutch); (Afrikaans); (Dutch) and ( Bulgarian). The introduction of the name 'Gerard' into the English lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ami Boué
Ami Boué (16 March 179421 November 1881) was a geologist of French Huguenot origin. Born at Hamburg, he was trained in Edinburgh and across Europe. He travelled across Europe, studying geology, as well as ethnology, and is considered to be among the first to produce a geological map of the world. Career Boué was born in Hamburg where his grandfather Jacques Chapeaurouge had settled in 1705 and established a shipping company which grew. Born in a wealthy home, Boué studied in Hamburg and Geneva before going to study medicine at Edinburgh from 1814 to 1817. Here he came under the influence of Robert Jameson, whose teachings in geology and mineralogy inspired his future career. Boué was thus led to make geological expeditions to various parts of Scotland and the Hebrides, and after taking his degree of M.D. in 1817 he settled for some years in Paris. In 1820 he issued his ''Essai géologique sur l'Écosse'', in which the eruptive rocks in particular were carefully described. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteor
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere, creating a streak of light via its rapid motion and sometimes also by shedding glowing material in its wake. Although a meteor may seem to be a few thousand feet from the Earth, meteors typically occur in the mesosphere at altitudes from . The root word ''meteor'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''meteōros'', meaning "high in the air". Millions of meteors occur in Earth's atmosphere daily. Most meteoroids that cause meteors are about the size of a grain of sand, i.e. they are usually millimeter-sized or smaller. Meteoroid sizes can be calculated from their mass and density which, in turn, can be estimated from the observed meteor trajectory in the upper atmosphere. Meteors may occur in meteor shower, showers, which arise when Earth passes throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an Italian and naturalized French mathematician, physicist and astronomer. He made significant contributions to the fields of mathematical analysis, analysis, number theory, and both classical mechanics, classical and celestial mechanics. In 1766, on the recommendation of Leonhard Euler and Jean le Rond d'Alembert, d'Alembert, Lagrange succeeded Euler as the director of mathematics at the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, Prussia, where he stayed for over twenty y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Charles Le Monnier
Pierre Charles Le Monnier (; 20 November 1715 – 31 May 1799) was a French astronomer. His name is sometimes given as Lemonnier. Biography Le Monnier was born in Paris, where his father Pierre Lemonnier (physicist), Pierre (1675–1757), also an astronomer, was professor of philosophy at the college d'Harcourt. His first recorded astronomical observation was made before he was sixteen, and the presentation of an elaborate lunar map resulted in his admission to the French Academy of Sciences, on 21 April 1736, aged only 20. He was chosen in the same year to accompany Pierre Louis Maupertuis and Alexis Clairaut on their French Geodesic Mission to Lapland, geodetical expedition for arc measurement, measuring a meridian arc of approximately one degree (angle), degree's length to Torne Valley in Lapland (Finland), Lapland. In 1738, shortly after his return, he explained, in a memoir read before the academy, the advantages of John Flamsteed's mode of determining right ascensions. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |