|
Asymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptote02 Vectorial
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
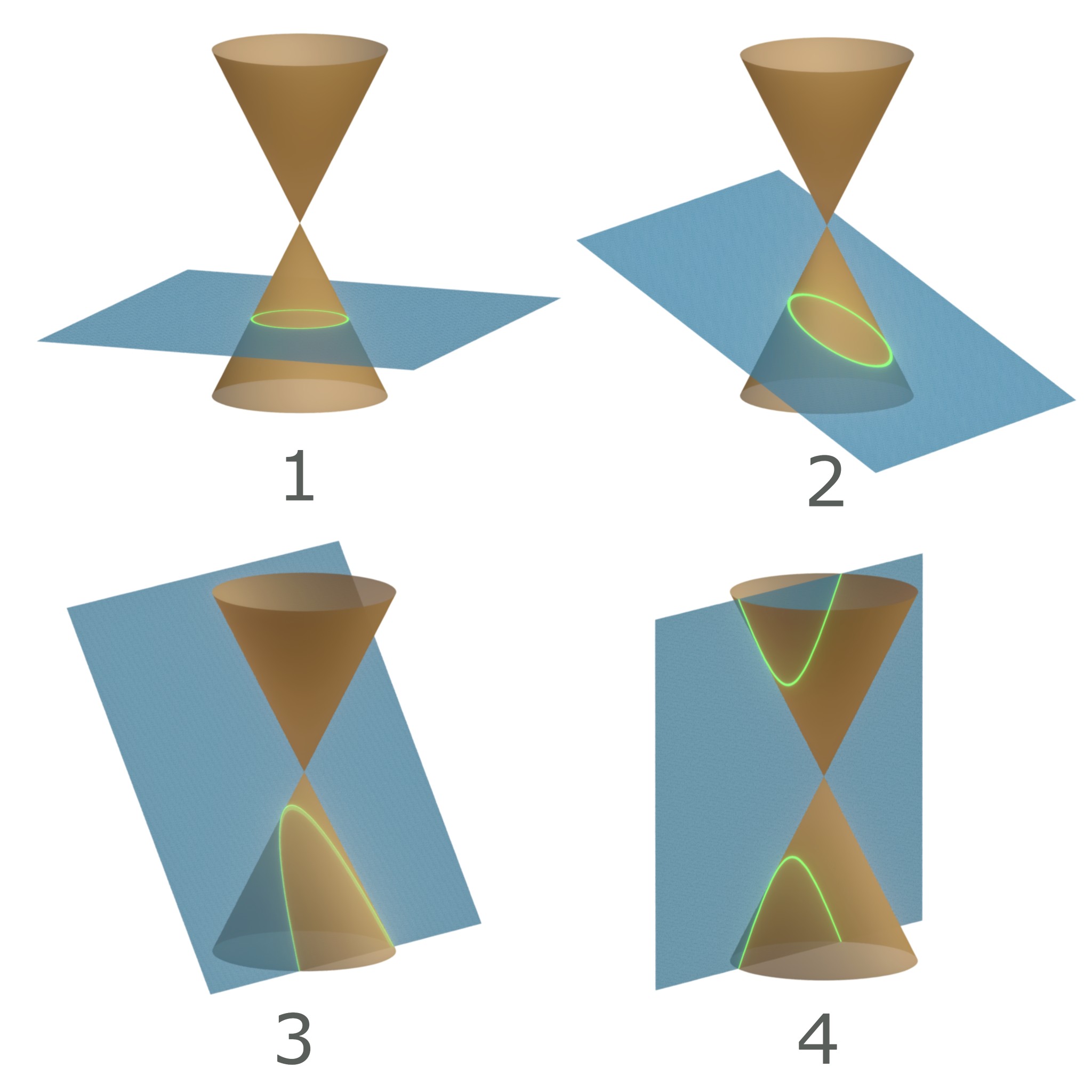
Hyperbola
In mathematics, a hyperbola (; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae ; adj. hyperbolic ) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function y(x) = 1/x in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit Of A Function
Although the function (sin ''x'')/''x'' is not defined at zero, as ''x'' becomes closer and closer to zero, (sin ''x'')/''x'' becomes arbitrarily close to 1. In other words, the limit of (sin ''x'')/''x'', as ''x'' approaches zero, equals 1. In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input. Formal definitions, first devised in the early 19th century, are given below. Informally, a function ''f'' assigns an output ''f''(''x'') to every input ''x''. We say that the function has a limit ''L'' at an input ''p,'' if ''f''(''x'') gets closer and closer to ''L'' as ''x'' moves closer and closer to ''p''. More specifically, when ''f'' is applied to any input ''sufficiently'' close to ''p'', the output value is forced ''arbitrarily'' close to ''L''. On the other hand, if some inputs very close to ''p'' are taken to outputs that stay a fixed distance apart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptotic Analysis
In mathematical analysis, asymptotic analysis, also known as asymptotics, is a method of describing limiting behavior. As an illustration, suppose that we are interested in the properties of a function as becomes very large. If , then as becomes very large, the term becomes insignificant compared to . The function is said to be "''asymptotically equivalent'' to , as ". This is often written symbolically as , which is read as " is asymptotic to ". An example of an important asymptotic result is the prime number theorem. Let denote the prime-counting function (which is not directly related to the constant pi), i.e. is the number of prime numbers that are less than or equal to . Then the theorem states that \pi(x)\sim\frac. Asymptotic analysis is commonly used in computer science as part of the analysis of algorithms and is often expressed there in terms of big O notation. Definition Formally, given functions and , we define a binary relation f(x) \sim g(x) \q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conic Sections
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a '' focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the '' eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry. Analytic geometry is used in physics and engineering, and also in aviation, Aerospace engineering, rocketry, space science, and spaceflight. It is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including Algebraic geometry, algebraic, Differential geometry, differential, Discrete geometry, discrete and computational geometry. Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and circles, often in two and sometimes three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space. As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometric shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Function
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve (sigmoid function, sigmoid curve) with equation f(x) = \frac, where For values of x in the domain of real numbers from -\infty to +\infty, the S-curve shown on the right is obtained, with the graph of f approaching L as x approaches +\infty and approaching zero as x approaches -\infty. The logistic function finds applications in a range of fields, including biology (especially ecology), biomathematics, chemistry, demography, economics, geoscience, mathematical psychology, probability, sociology, political science, linguistics, statistics, and artificial neural networks. A generalization of the logistic function is the hyperbolastic functions, hyperbolastic function of type I. The standard logistic function, where L=1,k=1,x_0=0, is sometimes simply called ''the sigmoid''. It is also sometimes called the ''expit'', being the inverse of the logit. History The logistic function was introduced in a series of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollonius Of Perga
Apollonius of Perga ( grc-gre, Ἀπολλώνιος ὁ Περγαῖος, Apollṓnios ho Pergaîos; la, Apollonius Pergaeus; ) was an Ancient Greek geometer and astronomer known for his work on conic sections. Beginning from the contributions of Euclid and Archimedes on the topic, he brought them to the state prior to the invention of analytic geometry. His definitions of the terms ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola are the ones in use today. Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz stated “He who understands Archimedes and Apollonius will admire less the achievements of the foremost men of later times.” Apollonius worked on numerous other topics, including astronomy. Most of this work has not survived, where exceptions are typically fragments referenced by other authors like Pappus of Alexandria. His hypothesis of eccentric orbits to explain the apparently aberrant motion of the planets, commonly believed until the Middle Ages, was superseded during the Renaissance. The Apol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |