|
Astreopora Myriophthalma
''Astreopora myriophthalma'', sometimes known as porous star coral, is a species of hard coral found in shallow water in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is a common species with a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "Least-concern species, least concern". Description ''A. myriophthalma'' is a colonial species which forms massive hemispherical or boulder-shaped colonies. The corallites are conical and evenly distributed over the surface; each has a circular, upright or outwardly-pointing opening. The colour of this coral varies but may be plain or mottled and cream, yellow or brownish-blue. It is similar in appearance to ''Astreopora gracilis'' and ''Astreopora listeri''. Distribution and habitat ''A. myriophthalma'' has a wide distribution in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans. Its range extends from East Africa and the Red Sea through Indonesia and northern Australia to Japan, the Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biological evolution occurred and proceeded in accordance with Naturalism (philosophy), natural laws. Lamarck fought in the Seven Years' War against Prussia, and was awarded a commission for bravery on the battlefield. Posted to Monaco, Lamarck became interested in natural history and resolved to study medicine.#Packard, Packard (1901), p. 15. He retired from the army after being injured in 1766, and returned to his medical studies. Lamarck developed a particular interest in botany, and later, after he published the three-volume work ''Flore françoise'' (1778), he gained membership of the French Academy of Sciences in 1779. Lamarck became involved in the Jardin des Plantes and was appointed to the Chair of Botany in 1788. When the French Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marine Fauna Of Oceania
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine current power * Marine debris * Marine energy * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fauna Of The Red Sea
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and ''funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word for a boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cnidarians Of The Indian Ocean
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroids, sea anemones, corals and some of the smallest marine parasites. Their distinguishing features are an uncentralized nervous system distributed throughout a gelatinous body and the presence of cnidocytes or cnidoblasts, specialized cells with ejectable flagella used mainly for envenomation and capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living, jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians are also some of the few animals that can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes, which are specialized stinging cells used to cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acroporidae
Acroporidae is a family of small polyped stony corals in the phylum Cnidaria. The name is derived from the Greek ''"akron"'' meaning "summit" and refers to the presence of a corallite at the tip of each branch of coral. They are commonly known as staghorn corals and are grown in aquaria by reef hobbyists. Description Staghorn corals are the dominant group of reef builders. They come in many shapes and sizes and can be highly variable in colour and form, even within the same species. Most are either a branching variant or a wall/ table top variant shaped and some are encrusting (growing over rock structures). Their colours vary between browns, whites, pinks, blues, yellows, greens and purple, depending not only on species but also on the growing conditions. Identification is difficult and requires close examination of the corallites and a biochemical and genetic analysis. There is a corallite at the tip of each branch and, with the exception of '' Astreopora'', these are small wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coral Disease
Coral diseases are transmissible Pathogen, pathogens that cause the degradation of coral colonies. Coral cover in reef ecosystems has decreased significantly for a diverse set of reasons, ranging from variable environmental conditions to mechanical breakdowns from storms. In recent years, diseases that infect and kill coral have shown to be a threat to the health of coral reefs. Since the first coral disease was reported in 1965, many different kinds of diseases have popped up in mostly Caribbean, Caribbean waters. These diseases are diverse, including pathogens of bacteria, Fungus, fungi, Virus, viruses, and Protozoa, protozoans. Coral diseases have widespread implications, impacting entire Ecosystem, ecosystems and Community (ecology), communities of organisms. Researchers are working to understand these diseases, and how potential treatments could stop these pathogens from causing the widespread death of corals in a way that permanently impacts the community structure of reefs. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to loss of Symbiosis, symbiotic algae and Photosynthesis, photosynthetic pigments. This loss of pigment can be caused by various stressors, such as changes in water temperature, light, salinity, or nutrients. A bleached coral is not necessarily dead, and some corals may survive. However, a bleached coral is under stress, more vulnerable to starvation and disease, and at risk of death. The leading cause of coral bleaching is Effects of climate change on oceans, rising ocean temperatures due to climate change. Bleaching occurs when coral polyp (zoology), polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are Photosynthesis, photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is Toxicity, toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
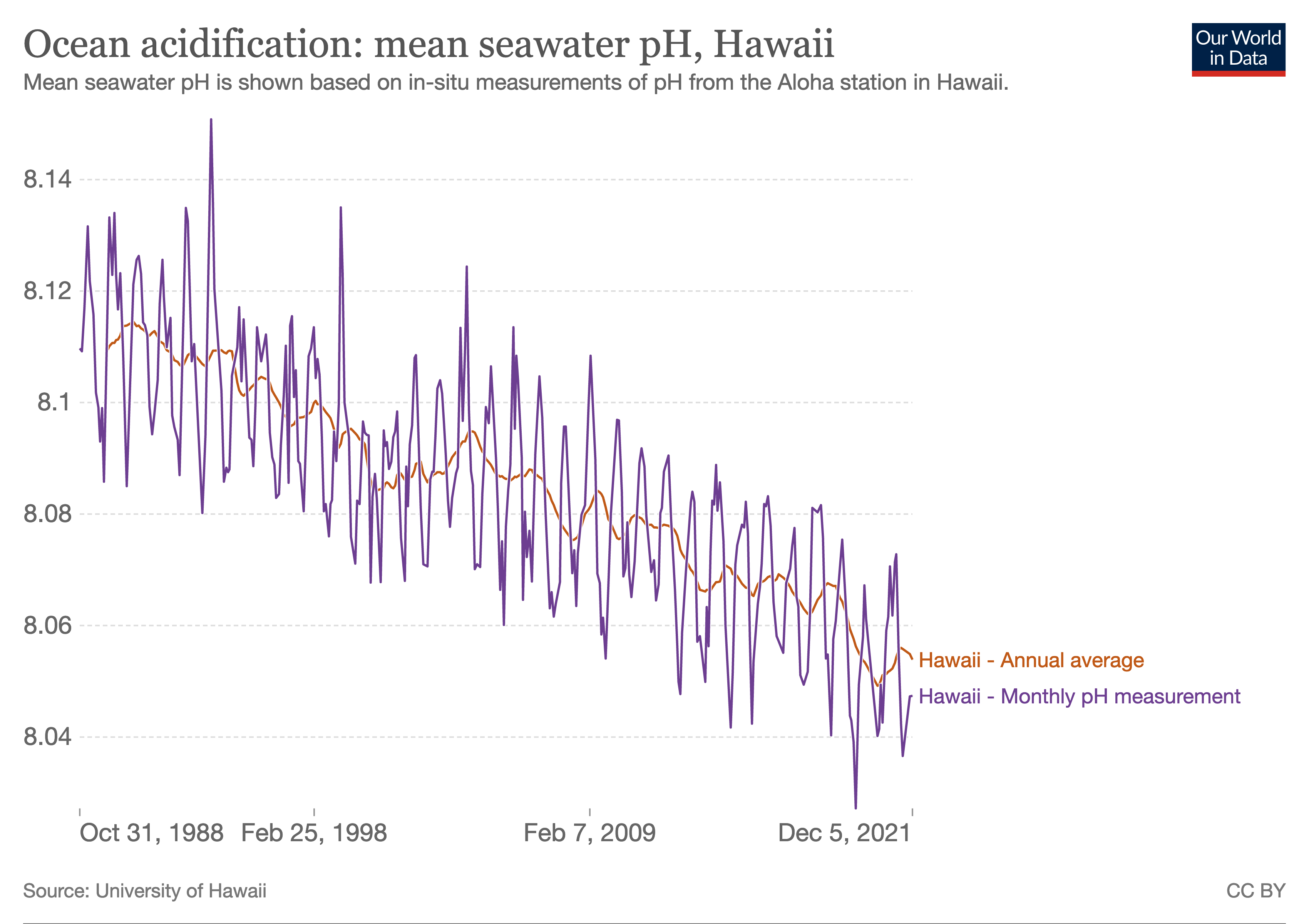
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ocean acidification, with Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide () levels exceeding 422 ppm (). from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This chemical reaction produces carbonic acid () which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (). The presence of free hydrogen ions () lowers the pH of the ocean, increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). Marine biogenic calcification, Marine calcifying organisms, such as Mollusca, mollusks and corals, are especially vulnerable because they rely on calcium carbonate to build shells and skeletons. A change in pH by 0.1 represents a 26% increase in hydrogen ion concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleus) to ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged (protonated) substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by Organic compound, organic or other groups (indicated by R). Not only is ammonium a source of nitrogen and a key metabolite for many living organisms, but it is an integral part of the global nitrogen cycle. As such, human impact in recent years could have an effect on the biological communities that depend on it. Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted acids (proton donors): : The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |