|
Assimilado
''Assimilado'' or ''assimilada'' (if female), literally "assimilated", was a status assigned from the 1910s to the 1960s to those African subjects of the colonial Portuguese Empire who had reached a level of "civilization", according to Portuguese legal standards, that theoretically qualified them for full rights as Portuguese citizens. Portuguese colonizers claimed the goal of their assimilation practices to be the "close union of races of different degrees of civilization that help and support each other loyally"; however, this notion of a "close union" differed from its practical application in the cultural and social spheres of the colonies of Portuguese Angola, Portuguese Mozambique and Portuguese Guinea.Heywood, Linda (2000). ''Contested Power in Angola, 1840s to the Present'', pp. 92-93. Rochester: University of Rochester Press. . Formation in Portuguese lawmaking Assimilation ideals begin Portugal, along with France, was one of the only Africa colonizers which intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
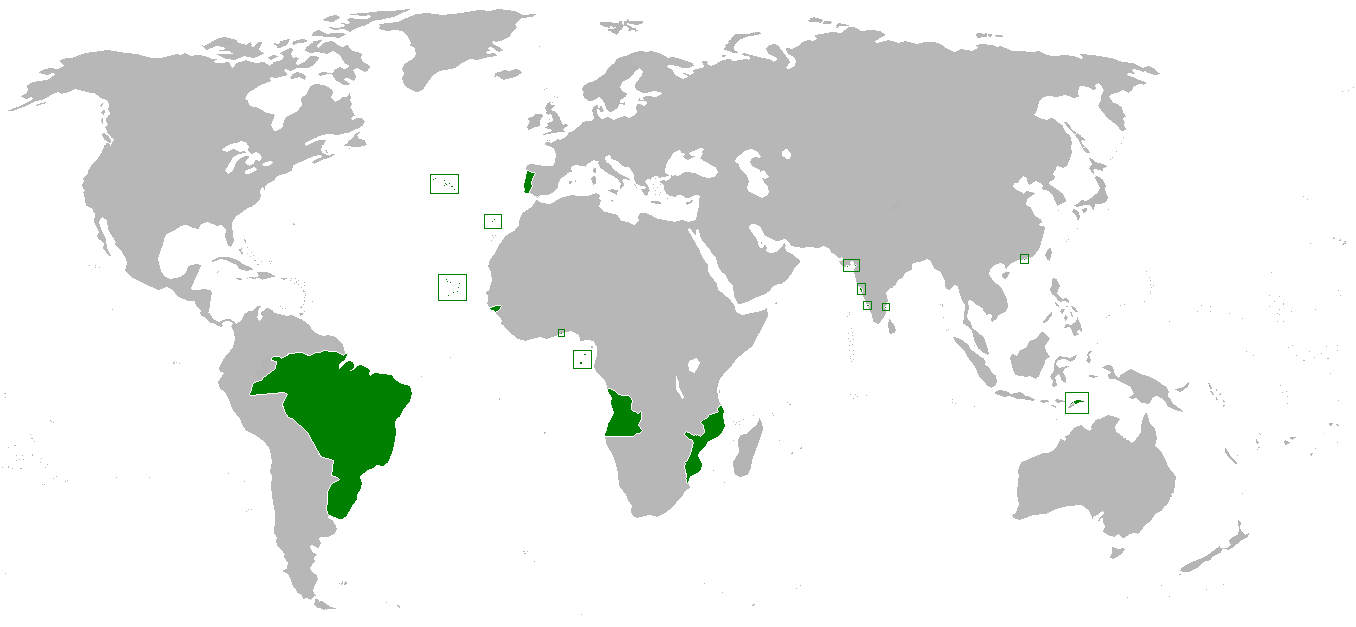
Portuguese Angola
In southwestern Africa, Portuguese Angola was a historical Evolution of the Portuguese Empire, colony of the Portuguese Empire (1575–1951), the overseas province Portuguese West Africa of Estado Novo (Portugal), Estado Novo Portugal (1951–1972), and the State of Angola of the Portuguese Empire (1972–1975). It became the independent People's Republic of Angola in 1975. In the 16th and 17th century Portugal ruled along the coast and engaged in military conflicts with the Kingdom of Kongo, but in the 18th century Portugal gradually managed to colonise the interior highlands. Other polities in the region included the Kingdom of Ndongo, Kingdom of Lunda, and Mbunda Kingdom. Full control of the entire territory was not achieved until the beginning of the 20th century, when agreements with other European powers during the Scramble for Africa fixed the colony's interior borders. History The history of Portuguese presence on the territory of contemporary Angola lasted from the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portuguese Mozambique
Portuguese Mozambique () or Portuguese East Africa () were the common terms by which Mozambique was designated during the period in which it was a Portuguese Empire, Portuguese overseas province. Portuguese Mozambique originally constituted a string of Portuguese possessions along the south-east African coast, and later became a unified province, which now forms the Republic of Mozambique. Portuguese trading settlements—and later, territories—were formed along the coast and into the Zambezi basin from 1498 when Vasco da Gama first reached the Mozambican coast. Lourenço Marques (explorer), Lourenço Marques explored the area that is now Maputo Bay in 1544. The Portuguese increased efforts for occupying the interior of the colony after the Scramble for Africa, and secured political control over most of its territory in 1918, facing the resistance of some Africans during the process. Some territories in Mozambique were handed over in the late 19th century for rule by chartered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea (), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a Portuguese overseas province in West Africa from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as Guinea-Bissau. Slave trade The Portuguese Crown commissioned its navigators to explore the Atlantic coast of West Africa in the 1430s, to find sources of gold. At that time the gold trade was controlled by Morocco. Muslim caravans across the Sahara also carried salt, kola nut, kola, textiles, fish, grain, and slaves. The navigators first passed the obstruction of Cape Bojador in 1437 and were able to explore the West African coast as far as Sierra Leone by 1460 and colonize the Portuguese Cape Verde, Cape Verde islands beginning in 1456.C.R. Boxer, (1977). The Portuguese seaborne empire, 1415–1825, pp. 26–7, 30 London, Hutchinson & Co. The gold ultimately came from the upper reaches of the Niger River, Niger and Volta Rivers and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Front For The Liberation Of Angola
The National Front for the Liberation of Angola (; Abbreviation, abbreviated FNLA) is a political party and former militant organisation that fought for Angolan independence from Portugal in the Angolan War of Independence, war of independence, under the leadership of Holden Roberto. Founded in 1954 as the UniĂŁo dos Povos do Norte de Angola guerrilla movement, it was known after 1959 as the UniĂŁo dos Povos de Angola (UPA) guerrilla movement, and from 1961 as the FNLA guerrilla movement. Ahead of the first multiparty elections in 1992, the FNLA was reorganized as a political party. The FNLA received 2.4% of the votes and had five Members of Parliament elected. In the Angolan parliamentary election, 2008, 2008 parliamentary election, the FNLA received 1.11% of the vote, winning three out of 220 seats. History Origin In 1954, the United People of Northern Angola (UPNA) was formed as a separatist movement for the Kongo people, Bakongo tribe who wished to re-establish its 16th-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pluricontinentalism
Pluricontinentalism () was a geopolitical concept, positing that Portugal was a transcontinental country and a unitary nation-state consisting of continental Portugal and its overseas provinces. With origins as early as the 14th century, pluricontinentalism gained official state sponsorship in the Estado Novo regime. It was the idea that Portugal was not a colonial empire (Portuguese Empire) but a singular nation-state spread across continents (hence the name). As such, overseas possessions were a part of Portuguese identity. The first time that Portugal was a pluricontinental country was during the reign of Maria I of Portugal, with the creation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, when the Portuguese court was living in Brazil and Rio de Janeiro served as the capital for the country. The idea of pluricontinentalism quickly collapsed following the Carnation Revolution in 1974. People associated with pluricontinentalism * AntĂłnio Vieira * LuĂs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assimilation (French Colonialism)
Assimilation was a major ideological component of French colonialism during the 19th and 20th centuries. The French government promoted the concept of cultural assimilation to colonial subjects in the French colonial empire, claiming that by adopting French culture they would ostensibly be granted the full rights enjoyed by French citizens and be legally considered "French". Colonial settlements established by the French, such as the Four Communes in French West Africa, were created with the assimilation concept in mind, and while Africans living in such settlements were theoretically granted the full rights of French citizens, discriminatory policies from various French colonial administrations denied most of these rights to "full-blooded Africans". Definition The concept of assimilation in French colonial discourse was based on the idea of spreading French culture to France's colonies in the 19th and the 20th centuries. Colonial subjects living in French colonies were consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ilustrado
The Ilustrados (, "erudite", "learned" or "enlightened ones") constituted the Filipino intelligentsia ( educated class) during the Spanish colonial period in the late 19th century. Elsewhere in New Spain (of which the Philippines were part), the term '' gente de razĂłn'' carried a similar meaning. They were late Spanish-colonial-era middle to upper class Filipinos, many of whom were educated in Spain and exposed to Spanish liberal and European nationalist ideals. The ''ilustrado'' class was composed of Philippine-born and/or raised intellectuals and cut across ethnolinguistic and racial lines—'' mestizos'' ''(''both '' de Sangleyes and de Español), insulares, and indios'', among others—and sought reform through "a more equitable arrangement of both political and economic power" under Spanish tutelage. Stanley Karnow, in his '' In Our Image: America's Empire in the Philippines'', referred to the ''ilustrados'' as the "rich Intelligentsia" because many we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lusosphere
The Portuguese-speaking world, also known as the Lusophone world () or the Lusophony (''Lusofonia''), comprises the countries and territories in which the Portuguese language is an official, administrative, cultural, or secondary language. This article provides details regarding the geographical distribution of all Portuguese-speakers or Lusophones, regardless of legislative status. Portuguese is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world and is an official language of countries on four continents. Statistics Native speakers This table depicts the native speakers of the language, which means that the table includes people who have been exposed to the Portuguese language from birth and, thus, excludes people who use the language as a second language (L2). Status by country Spread of Portuguese During a period of Portuguese discoveries and through a large colonial empire, the language was spread to areas in Africa, the Americas, and Asia, beyond East Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lusotropicalism
Lusotropicalism () is a term and "quasi-theory" developed by Brazilian sociologist Gilberto Freyre to describe the distinctive character of Portuguese imperialism overseas, proposing that the Portuguese were better colonizers than other European nations. Miguel Vale de AlmeidaPortugal’s Colonial Complex: From Colonial Lusotropicalism to Postcolonial Lusophony/ref> Freyre theorized that because of Portugal's warmer climate, and having been inhabited by Celts, Romans, Visigoths, Moors and several other peoples in pre-modern times, the Portuguese were more humane, friendly, and adaptable to other climates and cultures. He saw "Portuguese-based cultures as cultures of ecumenical expansion" and suggested that "Lusotropical culture was a form of resistance against both the 'barbaric' Soviet communist influence, and the also 'barbarian' process of Americanization and capitalist expansion." In addition, by the early 20th century, Portugal was by far the European colonial power with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa and various islands in Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, while at its greatest extent in 1820, covering 5.5 million square km ( million square miles), making it among the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Composed of colonialism, colonies, Factory (trading post)#Portuguese feitorias (c. 1445), factories, and later Territory#Overseas territory, overseas territories, it was the longest-lived colonial empire in history, from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa in 1415 to the handover of Macau to China in 1999. The power and influence of the Kingdom of Portugal would eventually expand across the globe. In the wake of the Reconquista, Portuguese maritime exploration, Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
White Man's Burden
"The White Man's Burden" (1899), by Rudyard Kipling, is a poem about the Philippine–American War (1899–1902) that exhorts the United States to assume colonial control of the Filipino people and their country.'' In "The White Man's Burden", Kipling encouraged the American annexation and colonisation of the Philippine Islands, a Pacific Ocean archipelago purchased in the three-month Spanish–American War (1898). As an imperialist poet, Kipling exhorts the American reader and listener to take up the enterprise of empire yet warns about the personal costs faced, endured, and paid in building an empire; nonetheless, American imperialists understood the phrase "the white man's burden" to justify imperial conquest as a civilising mission that is ideologically related to the continental expansion philosophy of manifest destiny of the early 19th century. With a central motif of the poem being the superiority of white men, it has long been criticised as a racist poem. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Évolué
In the Belgian colonial empire, Belgian and French colonial empires, an (, 'evolved one' or 'developed one') was an African who had been Europeanised through education and cultural assimilation, assimilation and had accepted European values and patterns of behavior. spoke French and followed European rather than indigenous laws, usually held White-collar worker, white-collar jobs (though rarely higher than clerks), and lived primarily in urban areas. Belgian colonies In the Belgian Congo (modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo), most s emerged from the Congolese who filled skilled positions (such as clerks and nurses) made available by the economic boom in the country following World War II. Colonial administrators defined an as "a man having broken social ties with his group, [and] having entered another system of motivations, another system of values." While there were no universal criteria for determining status, it was generally accepted that one would have "a good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |