|
Arsites
Arsites (; ; ) was Persian satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia in the Achaemenid Empire in the 4th century BC. His satrapy also included the region of Paphlagonia. In 340 BC, he sent a mercenary force under the leadership of the Athenian Apollodorus to defend Perinthos, which was besieged by Philip II of Macedon, possibly at Artaxerxes III's request. The operation was successful and prevented a further advance of Philip into Asia Minor. In the spring of 334 BC, however, Alexander the Great, after crossing the Hellespont, set foot in Asia Minor in the dominion of Arsites. Arsites then took part in the satrap coalition to counter the attacker. In the consequent war-council of Zelea he was foremost in opposing the scorched earth plan presented by the mercenary Memnon. In the battle of the Granicus, he commanded the Paphlagonian cavalry in the left Persian wing just to the right of Arsames and Memnon of Rhodes Memnon of Rhodes (Greek: Μέμνων ὁ Ῥόδιος; 380 – 33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Granicus
The Battle of the Granicus in May 334 BC was the first of three major battles fought between Alexander the Great of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon and the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The battle took place on the road from Abydos (Hellespont), Abydus to Dascylium, at the crossing of the Granicus in the Troad region, which is now called the Biga Çayı, Biga River in Turkey. In the battle Alexander defeated the field army of the Persian satraps of Asia-Minor, Asia Minor, which defended the river crossing. After this battle, the Persians were forced on the defensive in the cities that remained under their control in the region. Background After winning the Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC), Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, King Philip II of Macedon forced most of the Greek states into a military alliance, the League of Corinth, Hellenic League. Its goal was to make war on the Persian Achaemenid Empire to avenge the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC. He managed to convince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
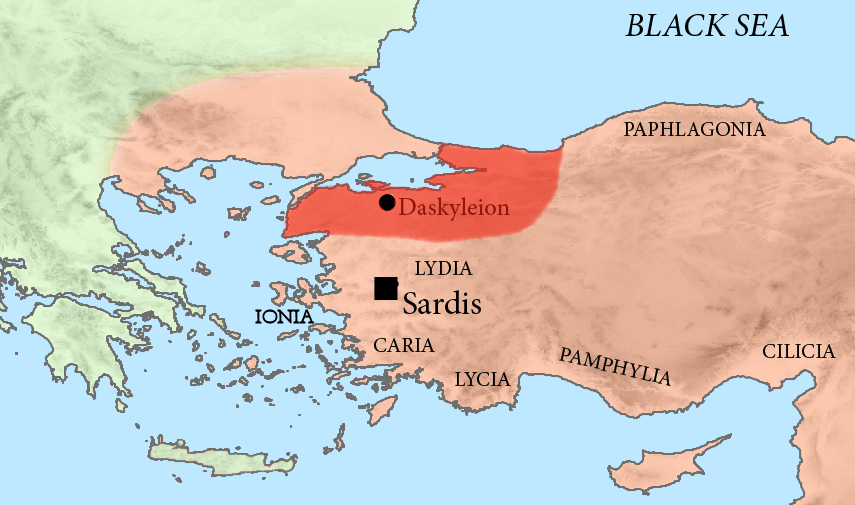
Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia () or Lesser Phrygia () was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of the Hellespont. Its capital was Dascylium, and for most of its existence it was ruled by the hereditary Persian Pharnacid dynasty. Together with Greater Phrygia, it made up the administrative provinces of the wider Phrygia region. History The satrapy was created in the beginning of the fifth century BC, during the time of administrative reorganisations of the territories in western Asia Minor, which were amongst the most important Achaemenid territories. The first Achaemenid ruler of Hellespontine Phrygia was Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BC), who was appointed by Cyrus the Great and continued under Cambises. He was killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of neighbouring Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, Mitrobates was succeeded by Oebares II (c.493), son of Megabazus. Artabazus then became satrap circa 479 BC and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsames (satrap Of Cilicia)
Arsames (Old Persian ''Aršāma'', ) was an Achaemenid Persian satrap of Cilicia in 334/3 BC. He succeeded Mazaeus in this position. He took part in the Battle of Granicus where he fought with his cavalry on the left wing, along with Arsites and Memnon of Rhodes. He was able to survive that battle and flee to the capital of Cilicia Tarsus. There he was planning a scorched-earth policy according to that of Memnon which caused the native Cilician soldiers to abandon their posts. He also decided to burn Tarsus to the ground so as not to fall in the hands of Alexander but was prevented from doing so by the speedy arrival of Parmenion with the light armored units who took the city. After that, Arsames fled to Darius who was at this time in Syria. He was slain at the battle of Issus (modern-day Turkey) in 333 BC.Alexander of Macedon, 356-323 B.C.: a historical biography By Peter Green He was succeeded by Balacrus, a bodyguard of Alexander the Great Alexander III of Macedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorched Earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and infrastructure. Its use is possible by a retreating army to leave nothing of value worth taking, to weaken the attacking force or by an advancing army to fight against unconventional warfare. Scorched earth against non-combatants has been banned under the Additional Protocol II, 1977 Geneva Conventions. Origin of the term The term was found in English in a 1937 report on the Second Sino-Japanese War. The retreating Chinese forces burned crops and destroyed infrastructure, including cities, to sabotage the logistics of the advancing Japanese forces. Military theory Clausewitz wrote in ''Principles of War'': Clausewitz wrote in ''On War'': Historic examples Notable historic examples of successful scorched-earth tactics include the fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
334 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 334 ( CCCXXXIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Optatus and Caesonius (or, less frequently, year 1087 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 334 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Flavius Dalmatius puts down a revolt in Cyprus, led by Calocaerus. Calocaerus is brought to Tarsus (Cilicia), and executed. * The Goths protect the Danube frontier against an invasion by the Vandals. * Emperor Constantine the Great reauthorises gladiatorial combat. Births * Huiyuan, Chinese Buddhist teacher and founder of Donglin Temple (d. 416) * Sabbas the Goth, Christian reader and saint (d. 372) * Virius Nicomachus Flavianus, Roman historian and politician (d. 394) Deaths * December 5 – Li Ban, Chinese emperor of Cheng-Han (b. 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Iranian People
The 4th century was the time period from 301 CE (represented by the Roman numerals CCCI) to 400 CE (CD) in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two-emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Satraps Of Hellespontine Phrygia
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex infrastructu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Fragmente Der Griechischen Historiker
''Die Fragmente der griechischen Historiker'', commonly abbreviated ''FGrHist'' or ''FGrH'' (''Fragments of the Greek Historians''), is a collection by Felix Jacoby of the works of those ancient Greek historians whose works have been lost, but of which we have citations, extracts or summaries. It is mainly founded on Karl Wilhelm Ludwig Müller's previous ''Fragmenta Historicorum Graecorum'' (1841–1870). The work was started in 1923 and continued by him till his death in 1959. The project was divided into six parts, of which only the first three were published. The first included the mythographers and the most ancient historians (authors 1-63); the second, the historians proper (authors 64–261); the third, the autobiographies, local histories and works on foreign countries (authors 262-856). Parts I-III come to fifteen volumes, but Jacoby never got to write part IV (biography and antiquarian literature) and V (historical geography). A pool of editors is currently trying to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nearchos
Nearchus or Nearchos (; – 300 BC) was one of the Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at the mouth of the Tigris River following the Indian campaign of Alexander the Great, in 326–324 BC. Early life A native of Lato in Crete and son of Androtimus, his family settled at Amphipolis in Macedonia at some point during Philip II's reign (we must assume after Philip took the city in 357 BC), at which point Nearchus was probably a young boy. He was almost certainly older than Alexander, as were Ptolemy, Erigyius, and the others of the ‘boyhood friends’; so depending on when Androtimus came to Macedonia Nearchus was quite possibly born in Crete. Nearchus, along with Ptolemy, Erigyius and Laomedon, and Harpalus, was one of Alexander's ‘mentors’ – and he was exiled by Philip as a result of the Pixodarus affair (A 3.6.5; P 10.3). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calas (general)
Calas or Callas (Greek Κάλας or Κάλλας; lived 4th century BC) was an ancient Greek, son of Harpalus of Elimiotis and first cousin to Antigonus, king of Asia. Asian campaign of Philip II Calas held a command in the army which Philip II sent into Anatolia under Parmenion and Attalus, 336 BC, to further his cause among the Greek cities there. In 335 BC Calas was defeated in a battle in the Troad by Memnon of Rhodes, but took refuge in Rhaeteum. Campaigns of Alexander the Great At the Battle of the Granicus in 334 BC he led the Thessalian cavalry in Alexander's army, and was appointed by him in the same year to the satrapy of the Lesser or Hellespontine Phrygia, to which Paphlagonia was soon after added. Excluding a failed attempt to conquer Bithynia, we do not hear of Calas: it would seem, however, that he died before the treason and flight of his father in 325, as we know from Arrian that Demarchus succeeded him in the satrapy of the Hellespontine Phrygia during Alex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, between 60 and 30 BC. The history is arranged in three parts. The first covers mythic history up to the destruction of Troy, arranged geographically, describing regions around the world from Egypt, India and Arabia to Europe. The second covers the time from the Trojan War to the death of Alexander the Great. The third covers the period to about 60 BC. ''Bibliotheca'', meaning 'library', acknowledges that he was drawing on the work of many other authors. Life According to his own work, he was born in Agyrium in Sicily (now called Agira). With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about his life and doings beyond his written works. Only Jerome, in his '' Chronicon'' under the "year of Abraham 1968" (49 BC), writes, "D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memnon Of Rhodes
Memnon of Rhodes (Greek: Μέμνων ὁ Ῥόδιος; 380 – 333 BC) was a prominent Rhodian Greek commander in the service of the Achaemenid Empire. Related to the Persian aristocracy by the marriage of his sister to the satrap Artabazus II, together with his brother Mentor he served the Persian king for most of his life, and played an important role during the invasion of Alexander the Great and the decades before that. Carl Otis Schuster notes that though often inaccurately described as "simply a mercenary", Memnon was arguably the toughest defender of the Persian Empire Alexander had to face, and was nearly successful in putting a halt to him. Biography Under the governor of Phrygia Not much is known about Memnon's early life. Born 380 BC in Rhodes, Memnon would serve the Achaemenid Empire for most of his life. He started his career in 358 BC by serving together with his brother Mentor under the Persian satrap (governor) Artabazos II. During his service to the Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |