|
Arsamenes
Arsamenes () was a prince of ancient Persia, the son of Darius the Great. We know very little about him today other than that he was, according to the historian Herodotus, the commander of the Utians (or "Utii") and Mycae people (or "Myci") in the army of Xerxes I Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ... during the Second Persian invasion of Greece. Herodotus does not mention who Arsamenes's mother was, so we do not know whether Xerxes was his brother or half-brother. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Arsamenes Family of Darius the Great Persian people of the Greco-Persian Wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius The Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West Asia, parts of the Balkans (Skudra, Thrace–Achaemenid Macedonia, Macedonia and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia) and the Caucasus, most of the Black Sea's coastal regions, Central Asia, the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, Indus Valley in the far east, and portions of North Africa and Northeast Africa including History of Persian Egypt, Egypt (), eastern ancient Libya, Libya, and coastal The Sudans, Sudan. Darius ascended the throne by overthrowing the Achaemenid monarch Bardiya (or ''Smerdis''), who he claimed was in fact an imposter named Gaumata. The new king met with rebellions throughout the empire but quelled each of them; a major event in Darius's life was his expedition to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
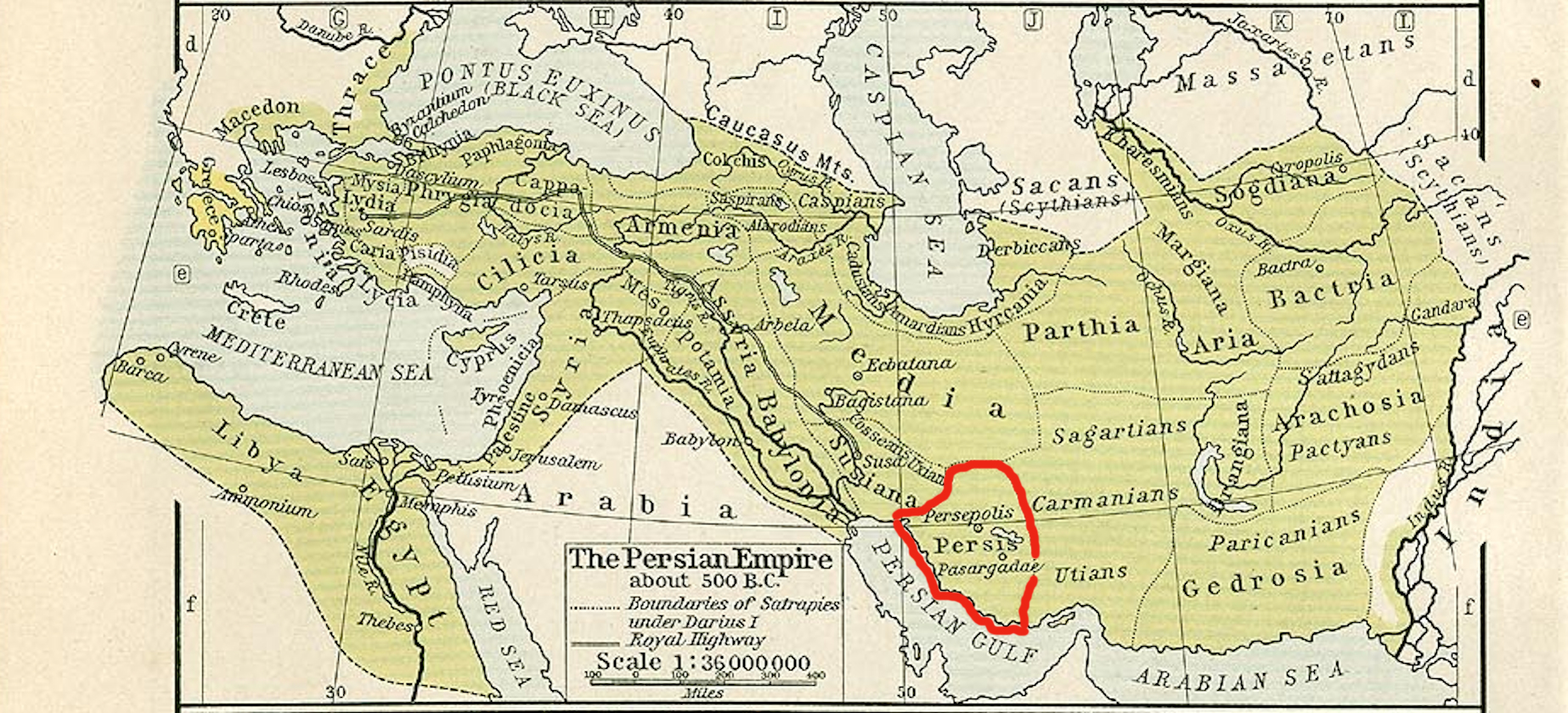
Utians
The Utians or Utii were ancient western Iranic nomadic camel-driving people, known to us primarily through the writings of the ancient Greek historian Herodotus. Herodotus describes them as "dressed in skin with the hair on". There exists little independent record of these people, and it is somewhat unclear whom Herodotus was referring to. He describes them as forming part of the 14th province of the Persian empire, sharing this province with other peoples named Sagartians, Sarangians, Thamanaeans, Mycians, and the unnamed inhabitants of the islands of the Erythraean Sea. Herodotus also describes them as serving in the army of Xerxes I, under the command of Arsamenes, son of Darius the Great, during the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 481 BCE. On the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great, a land in Southern Persis called "Vautiya" or "Yautiya" is described. Some scholars have suggested that might be the same as the homeland of the people Herodotus called "Utians". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Persia
The history of Iran (also known as Persia) is intertwined with Greater Iran, which is a socio-cultural region encompassing all of the areas that have witnessed significant settlement or influence exerted by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian languages chiefly the Persians and the Persian language. Central to this region is the Iranian plateau, now largely covered by modern Iran. The most pronounced impact of Iranian history can be seen stretching from Anatolia in the west to the Indus Valley in the east, including the Levant, Mesopotamia, the Caucasus, and parts of Central Asia. To varying degrees, it also overlaps or mingles with the histories of many other major civilizations, such as India, China, Greece, Rome, and Egypt. Iran is home to one of the world's oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and urban settlements dating back to 4000 BC. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was the son of Darius the Great and Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great. In Western history, Xerxes is best known for his Second Persian invasion of Greece, invasion of Greece in 480 BC, which ended in Persian defeat. Xerxes was designated successor by Darius over his elder brother Artobazan and inherited a large, multi-ethnic empire upon his father's death. He consolidated his power by crushing revolts in Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt, Egypt and Babylonian revolts (484 BC), Babylon, and renewed his father's campaign to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical Athens, Athens and its allies for their interference in the Ionian Revolt. In 480 BC, Xerxes personally led a large army and crossed the Dardanelles, Hellespont into Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Persian Invasion Of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece (492–490 BC) at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes. The invasion began in spring 480 BC, when the Persian army crossed the Hellespont and marched through Thrace and Macedon to Thessaly. The Persian advance was blocked at the pass of Thermopylae by a small Allied force under King Leonidas I of Sparta; simultaneously, the Persian fleet was blocked by an Allied fleet at the straits of Artemisium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histories (Herodotus)
The ''Histories'' (, ''Historíai''; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicles beforehand). ''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars between the Persian Empire and the Polis, Greek city-states in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Persians) on the one hand, and freedom (the Athenians and the confederacy of Greek city-states which united against the invaders) on the other. ''The Histories'' was at some point divided into the nine scroll, books that appear in modern editions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in the United Kingdom that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, CRC Press, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research and Dovepress. It is a division of Informa, a United Kingdom-based publisher and conference company. Overview Founding The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis (chemist), William Francis joined Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Publications included the ''Philosophical Magazine''. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. Acquisitions and mergers In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Of Darius The Great
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary purpose of Attachment theory, attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as Matrifocal family, matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), wikt:conjugal, conjugal (a married couple with children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or Extended family, extended (in addition to parents, spouse and children, may include Grandparent, grandparents, Aunt, aunts, Uncle, uncles, or Cousin, cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |