|
Arrokoth
Arrokoth ( minor-planet designation 486958 Arrokoth; provisional designation ), formerly nicknamed Ultima Thule, is a trans-Neptunian object located in the Kuiper belt. Arrokoth became the farthest and most primitive object in the Solar System visited by a spacecraft when the NASA space probe ''New Horizons'' conducted a flyby on 1 January 2019. Arrokoth is a contact binary long, composed of two planetesimals and across, that are joined along their major axes. With an orbital period of about 298 years and a low orbital inclination and eccentricity, Arrokoth is classified as a cold classical Kuiper belt object. Arrokoth was discovered on 26 June 2014 by astronomer Marc Buie and the New Horizons Search Team using the Hubble Space Telescope as part of a search for a Kuiper belt object for the ''New Horizons'' mission to target in its first extended mission; it was chosen over two other candidates to become the primary target of the mission. Name When Arrokoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with a team led by Alan Stern, the spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. On January 19, 2006, ''New Horizons'' was launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station by an Atlas V rocket directly into an Earth-and-solar escape trajectory with a speed of about . It was the fastest (average speed with respect to Earth) man-made object ever launched from Earth. It is not the fastest speed recorded for a spacecraft, which as of 2021 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Reconnaissance Imager
Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) is a telescope aboard the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft for imaging. LORRI has been used to image Jupiter, its moons, Pluto and its moons, and Arrokoth since its launch in 2006. LORRI is a reflecting telescope of Ritchey-Chrétien design, and it has a main mirror diameter of 208 mm (8.2 inches) across. LORRI has a narrow field of view, less than a third of a degree. Images are taken with a CCD capturing data with 1024 × 1024 pixels. LORRI is a telescopic panchromatic camera integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft, and it is one of seven major science instruments on the probe. LORRI does not have any moving parts and is pointed by moving the entire ''New Horizons'' spacecraft. Operations LORRI was used to calculate albedos for Pluto and Charon. LORRI is also used for navigation, especially to more precisely determine the location of a flyby target. In 2018, ''New Horizons'' spacecraft used navigation data from LORRI for its pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
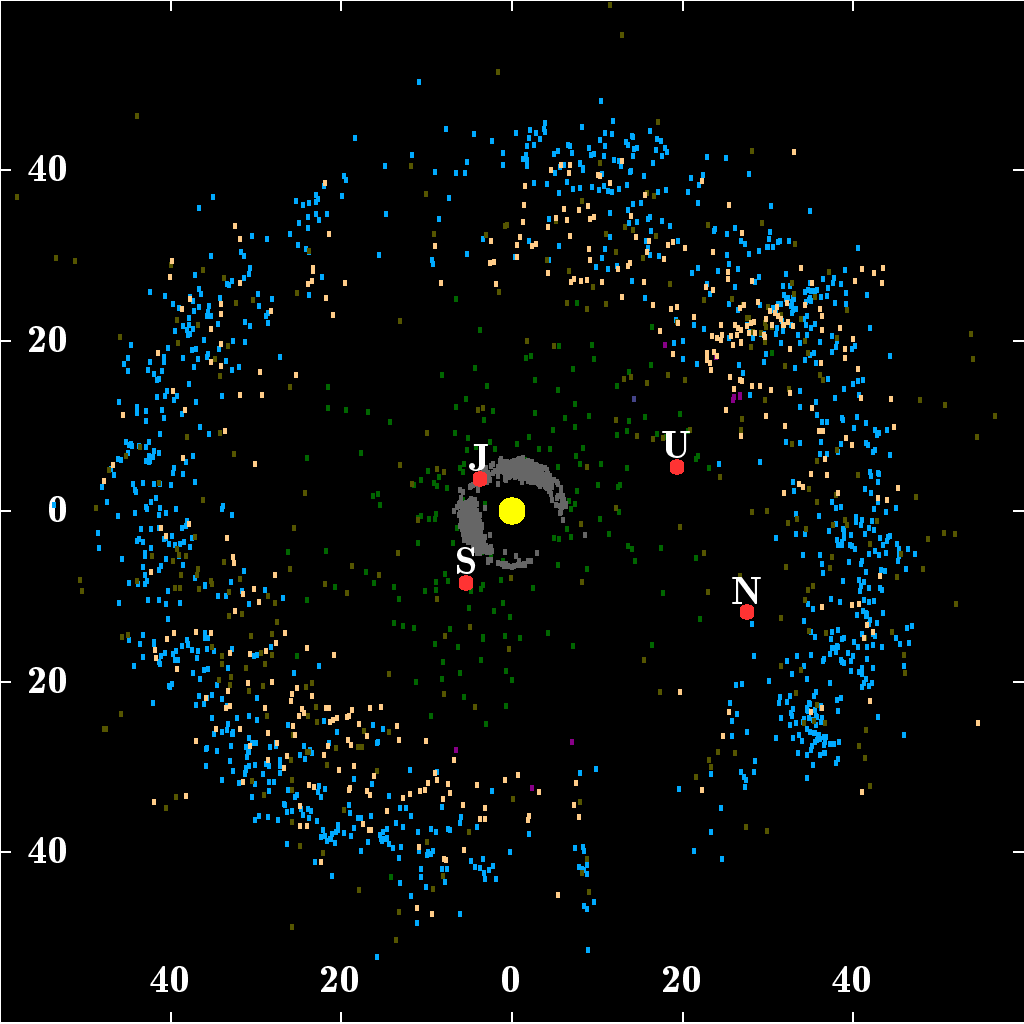
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region. The Kuiper belt was named after Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper, although he did not predict its existence. In 1992, minor planet (15760 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Kuiper Belt Object
A classical Kuiper belt object, also called a cubewano ( "QB1-o"), is a low-eccentricity Kuiper belt object (KBO) that orbits beyond Neptune and is not controlled by an orbital resonance with Neptune. Cubewanos have orbits with semi-major axes in the 40–50 AU range and, unlike Pluto, do not cross Neptune's orbit. That is, they have low- eccentricity and sometimes low-inclination orbits like the classical planets. The name "cubewano" derives from the first trans-Neptunian object (TNO) found after Pluto and Charon: 15760 Albion, which until January 2018 had only the provisional designation (15760) 1992 QB1. Similar objects found later were often called "QB1-o's", or "cubewanos", after this object, though the term "classical" is much more frequently used in the scientific literature. Objects identified as cubewanos include: * 15760 Albion (aka 1992 QB1 and gave rise to term 'Cubewano') * 136472 Makemake, the largest known cubewano and a dwarf planet * 50000 Quaoar and 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph (New Horizons)
Ralph is a science instrument aboard the robotic ''New Horizons'' spacecraft, which was launched in 2006. Ralph is a visible and infrared imager and spectrometer to provide maps of relevant astronomical targets based on data from that hardware. Ralph has two major subinstruments, LEISA and MVIC. MVIC stands for ''Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera'' and is a color imaging device, while LEISA originally stood for ''Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array'' and is an infrared imaging spectrometer for spaceflight. LEISA observes 250 discrete wavelengths of Infrared, infrared light from 1.25 to 2.5 micrometers. MVIC is a Push broom scanner, pushbroom scanner type of design with seven channels, including red, blue, near-infrared (NIR), and methane. Overview Ralph is one of seven major instruments aboard ''New Horizons'' which was launched in 2006 and flew by the dwarf planet Pluto in 2015. At Pluto, Ralph enables the observation of many aspects including: *geology of Pluto *form *struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Binary (small Solar System Body)
A contact binary is a small Solar System body such as a minor planet or a comet that is composed of two bodies that have gravitated toward each other until they touch, resulting in a bilobated, peanut-like overall shape. Contact binaries are often rubble piles but distinct from real binary systems such as binary asteroids. The term is also used for stellar contact binaries. An example of what is thought to be a contact binary is the Kuiper belt object 486958 Arrokoth, which was imaged by the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft during its flyby in January 2019. Description Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko and Comet Tuttle are most likely contact binaries, while asteroids suspected of being contact binaries include the unusually elongated 624 Hektor and the bilobated 216 Kleopatra and 4769 Castalia. 25143 Itokawa, which was photographed by the ''Hayabusa'' probe, also appears to be a contact binary which has resulted in an elongated, bent body. Asteroid 4179& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Neptunian Object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has a semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (au). Typically, TNOs are further divided into the classical and resonant objects of the Kuiper belt, the scattered disc and detached objects with the sednoids being the most distant ones. As of October 2020, the catalog of minor planets contains 678 numbered and more than 2,000 unnumbered TNOs. The first trans-Neptunian object to be discovered was Pluto in 1930. It took until 1992 to discover a second trans-Neptunian object orbiting the Sun directly, 15760 Albion. The most massive TNO known is Eris, followed by Pluto, , , and . More than 80 satellites have been discovered in orbit of trans-Neptunian objects. TNOs vary in color and are either grey-blue (BB) or very red (RR). They are thought to be composed of mixtures of rock, amorphous carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System about 4.6 billion years ago, they aid study of its formation. Formation A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the so-called planetesimal hypotheses, the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis and that of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form from cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form ever-larger bodies. Once a body reaches around a kilometer in size, its constituent grains can attract each other directly through mutual gravity, enormously aiding further growth into moon-sized protoplanets. Smaller bodies must instead rely on Brownian motion or turbulence to cause the collisions leading to sticking. The mechanics of collisions and mechanisms of sticking are intricate. Alternatively, planetesimals may for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Neptunian Object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has a semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (au). Typically, TNOs are further divided into the classical and resonant objects of the Kuiper belt, the scattered disc and detached objects with the sednoids being the most distant ones. As of October 2020, the catalog of minor planets contains 678 numbered and more than 2,000 unnumbered TNOs. The first trans-Neptunian object to be discovered was Pluto in 1930. It took until 1992 to discover a second trans-Neptunian object orbiting the Sun directly, 15760 Albion. The most massive TNO known is Eris, followed by Pluto, , , and . More than 80 satellites have been discovered in orbit of trans-Neptunian objects. TNOs vary in color and are either grey-blue (BB) or very red (RR). They are thought to be composed of mixtures of rock, amorphous carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minor Planets Visited By Spacecraft
The following tables list all minor planets and comets that have been visited by robotic spacecraft. List of minor planets visited by spacecraft A total of 17 minor planets (asteroids, dwarf planets, and Kuiper belt objects) have been visited by space probes. Moons (not directly orbiting the Sun) and planets are not minor planets and thus are not included in the table below. File:Small Asteroids and Comets Visited by Spacecraft.jpg, Minor planets and comets visited by spacecraft as of 2019 (except Pluto, Ceres, and Vesta), to scale File:Asteroidsscale.jpg, The comparative sizes of the first eight asteroids visited by spacecraft Incidental flybys In addition to the above listed objects, four asteroids have been imaged by spacecraft at distances too large to resolve features (over 100,000 km), and are labeled as such. List of comets visited by spacecraft Spacecraft visited by comets Comet C/2013 A1 passed close by planet Mars in October 2014, closer than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)