|
Argyle, Manitoba
Argyle is a small hamlet located in the Canadian province of Manitoba. Argyle is in Manitoba's Interlake Region. It is part of the Rural Municipality of Rockwood (but just across the road from the Rural Municipality of Woodlands to the west). It is approximately 30 km from Manitoba's capital, Winnipeg. Nearby are the towns of Stonewall, Balmoral, Teulon, Grosse Isle, Gunton, Rosser, Stony Mountain and Selkirk. The major industry is agriculture, where mixed farming prevails. Many residents work in Winnipeg or surrounding towns. Geographical location The Principal Meridian of Canada, (Cartographic centre of Canada) dividing Eastern and Western Canada also marked the division between the Argyle and Brant Districts, as well as the mark between neighboring Rockwood and Woodlands Municipalities. As the local residents were living on either side of the Prime Meridian, several institutions derive their name by combining the words: Brant-Argyle. The Prime Meridian was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
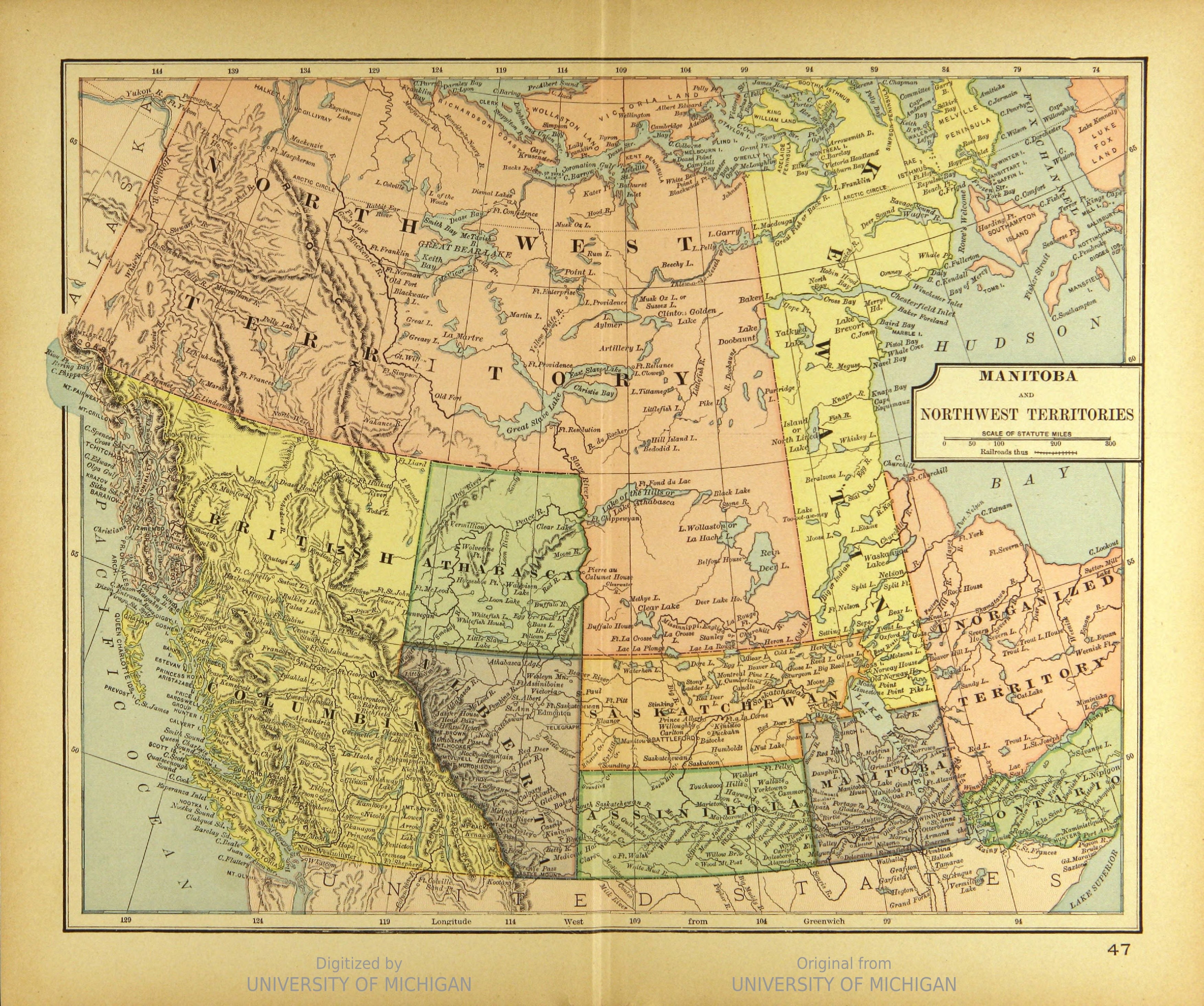
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021. Manitoba has a widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra and the Hudson Bay coastline in the Northern Region, Manitoba, north to dense Boreal forest of Canada, boreal forest, large freshwater List of lakes of Manitoba, lakes, and prairie grassland in the central and Southern Manitoba, southern regions. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, English and French North American fur trade, fur traders began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert's Land, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson's Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balmoral, Manitoba
Balmoral is an unincorporated village north of Winnipeg located within the boundaries of the Rural Municipality of Rockwood, Manitoba. The Post Office opened in 1879 to service the early settlers who began arriving in the area in 1874. There was also a Canadian Pacific railway point on 6-15-2E. The community was named after Balmoral Castle in Scotland. A School District was located on SW7-15-2E. The community was originally known as ''Quickfall''. See also * List of communities in Manitoba Communities in the province of Manitoba, Canada include incorporated municipalities, unincorporated communities and First Nations communities. Types of incorporated municipalities include urban municipalities, rural municipalities and local ... References * ''Geographic Names of Manitoba - Balmoral'' (pg. 17) published by the Millennium Bureau of Canada ''Balmoral, Manitoba'' Unincorporated communities in Manitoba {{Manitoba-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitoba Provincial Road 322
Provincial Road 322 (PR 322) is a north–south highway in both the Interlake and Winnipeg Metro regions of Manitoba, Canada. It connects the communities of Grosse Isle, Argyle, Woodroyd, and Erinview. Route description PR 322 begins in the Rural Municipality of Rosser in the town of Grosse Isle at an intersection with PTH 6 (Northern Woods and Water Route. It heads north through town along Road 1E, crossing both the Prairie Dog Central Railway and PR 321, where it enters the Rural Municipality of Rockwood, before leaving Grosse Isle and continuing north through rural farmland for the several kilometres. After passing by the Manitoba Hydro training facility, the highway has a junction with PTH 67 before continuing on through more rural areas to enter Argyle and join a concurrency (overlap) with PR 323. The pair head due west through the centre of town before becoming unpaved as the road leaves Argyle and enters the Woodlands. PR 322 splits off and heads north sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitoba Highway 67
Provincial Trunk Highway 67 (PTH 67) is a short provincial highway in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It runs as an east-west route just north of Winnipeg city limits between PTH 6 near the village of Warren to PTH 9 at the gate to Lower Fort Garry. PTH 67 is the main highway through the town of Stonewall. The speed limit Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed, express ... is 100 km/h (60 mph). History PTH 67 first appeared on the 1963 Manitoba Highway Map. Originally, it was a short connector highway spanning through Stonewall between PTH 6 and PTH 7. Between PTH 7 and PTH 9, the highway was known as Provincial Road 223 (PR 223) after the provincial government implemented the Secondary Highway system in 1966. PTH 67 was extended on to PR 223 (which was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a list of regions of Canada, Canadian region that includes the four western provinces and territories of Canada, provinces just north of the Canada–United States border namely (from west to east) British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The people of the region are often referred to as "Western Canadians" or "Westerners", and though diverse from province to province are largely seen as being collectively distinct from other Canadians along cultural, linguistic, socioeconomic, geographic and political lines. They account for approximately 32% of Canada's total population. The region is further subdivided geographically and culturally between British Columbia, which is mostly on the western side of the Canadian Rockies and often referred to as the "British Columbia Coast, west coast", and the "Prairie Provinces" (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Canada
Eastern Canada (, also the Eastern provinces, Canadian East or the East) is generally considered to be the region of Canada south of Hudson Bay/ Hudson Strait and east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces (from east to west): Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. Eastern Canada overlaps into other geographic regions; Ontario and Quebec, Canada's two largest provinces, define Central Canada, while the other provinces in Eastern Canada constitute Atlantic Canada. New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island are also known as the Maritime provinces. Capitals Ottawa, Canada's capital, is located in Eastern Canada, within the province of Ontario. The capitals of the provinces are in the list below: * Newfoundland and Labrador - St. John's * Nova Scotia - Halifax * Prince Edward Island - Charlottetown * New Brunswick - Fredericton * Quebec - Quebec City * Ontario - Toronto Definitions The Canadian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Meridian
A principal meridian is a meridian used for survey control in a large region. Canada The Dominion Land Survey of Western Canada took its origin at the First (or Principal) Meridian, located at 97°27′28.41″ west of Greenwich, just west of Winnipeg, Manitoba. This line is exactly ten miles west of the Red River at the Canada–United States border. Six other meridians were designated at four-degree intervals westward, with the seventh located in British Columbia; the second and fourth meridians form the general eastern border and the western border of Saskatchewan. United States In the United States Public Land Survey System, a principal meridian is the principal north–south line used for survey control in a large region, and which divides townships between east and west. The meridian meets its corresponding baseline at the point of origin, or initial point, for the land survey. For example, the Mount Diablo Meridian, used for surveys in California and Nevada, runs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Farming
Mixed farming is a type of farming which involves both the growing of crops and the raising of livestock. Such agriculture occurs across Asia and in countries such as India, Malaysia, Indonesia, Afghanistan, South Africa, China, Central Europe, Nordic countries, Canada, and Russia. Though at first it mainly served domestic consumption, countries such as the United States and Japan now use it for commercial purposes. The cultivation of crops alongside the rearing of animals for meat or eggs or milk defines mixed farming. For example, a mixed farm may grow cereal crops, such as wheat or rye, and also keep cattle, sheep, pigs or poultry. Often the dung from the cattle serves to fertilize the crops. Also some of the crops might be used as fodder for the livestock. Before horses were commonly used for haulage, many young male cattle on such farms were often not butchered as surplus for meat but castrated and used as bullocks to haul the cart and the plough. More info * Monocult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selkirk, Manitoba
Selkirk is a city in the western Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Manitoba, located on the Red River of the North, Red River about northeast of Winnipeg, the provincial capital. It has a population of 10,504 as of the 2021 census. The mainstays of the local economy are tourism, a steel mill, and a psychiatric hospital. A vertical lift bridge over the Red River connects Selkirk with the smaller town of East Selkirk, Manitoba, East Selkirk. The city is connected to Winnipeg via Manitoba Provincial Highway 9, Highway 9 and is served by the Canadian Pacific Railway. The city was named in honour of the Scotsman Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, who obtained the grant to establish a colony in the Red River area in 1813. History The present-day city is near the centre of the area purchased by the Earl of Selkirk from the Hudson's Bay Company. The first settlers of the Red River Colony arrived in 1813. Although the settlers negotiated a treaty with the Sau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stony Mountain, Manitoba
Stony Mountain is a small community in Manitoba, Canada approximately north of Winnipeg on Provincial Highway 7. The town is in the Rural Municipality of Rockwood and is the location of Stony Mountain Ski Area. The Stony Mountain Institution and Rockwood Institution prisons are in Stony Mountain. It is the birthplace of hockey hall of famer Babe Pratt. . . Retrieved on January 6, 2009. Demographics In the conducted by |
Rosser, Manitoba
Rosser is a List of rural municipalities in Manitoba, rural municipality (RM) in the Canadian province of Manitoba, lying adjacent to the northwest side of Winnipeg, Manitoba, Winnipeg and part of the Winnipeg Metro Region. Its population as of the 2016 Canadian Census, 2016 Census was 1,372. It is situated along Manitoba Highway 6, Provincial Trunk Highway 6, and Winnipeg's Perimeter Highway (Winnipeg), Perimeter Highway. CentrePort Canada lies primarily in the eastern part of the RM, inside the Perimeter Highway. A small portion of Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport also lies within the RM of Rosser. Water services are provided by the Cartier Regional Water Cooperative. The CentrePort distribution line serves CentrePort development and the RM of Rosser. Water sourced from the Assiniboine River is treated at Headingley, Manitoba, Headingley before being sent out through distribution channels. Near the community of Rosser is the Dorsey Converter Station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |