|
Argentine General Election, 1995
The Argentine general election of 1995 was held on 14 May. Voters chose both the President and their legislators and with a turnout of 82.1%. It became the first election in post-1983 Argentina to use the direct vote system, as the electoral college was abolished by 1995. Background The Justicialist Party had been founded in 1945 by Juan Perón, largely on the promise of greater self-reliance, increased state ownership in the economy and a shift in national policy to benefit "the other half" of Argentine society. Taking office on Perón's ticket in 1989 amid the worst crisis in a hundred years, President Carlos Menem had begun the systematic sell-off of Argentina's array of State enterprises, which had produced nearly half the nation's goods and services. Following 18 months of very mixed results, in February 1991 Menem reached out to his Foreign Minister, Domingo Cavallo, whose experience as an economist included a brief but largely positive stint as the nation's Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Saúl Menem
Carlos Saúl Menem (2 July 1930 – 14 February 2021) served as the 50th president of Argentina for ten years, from 1989 to 1999. He identified as Peronist, serving as President of the Justicialist Party for 13 years (from 1990 to 2001 and again from 2001 to 2003), and his political approach became known as Menemism. Born in Anillaco, La Rioja, to a Syrian family, Menem was raised as a Muslim,"Carlos Menem" ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' but later converted to to pursue a political career. Menem became a Peronist during a visit to Buenos Aires. He was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973, deposed and detained following the |
Democratic Progressive Party (Argentina)
The Democratic Progressive Party () is a political party in Argentina, principally active in Santa Fe. History Following the adoption of the Sáenz Peña Law (which established universal and compulsory suffrage for native-born male citizens) in 1912, the conservative elite that had ruled Argentina saw itself in need of a strong, centralized and organic party in order to compete against the growing threat of the Radical Civic Union and the Socialist Party. As a response to this need, the PDP was founded by Santa Fe senator Lisandro de la Torre at the Savoy Hotel in Buenos Aires on December 14, 1914. It was made up of members of eight different provincial conservative parties. However, the conservative elite of Buenos Aires Province, the largest and wealthiest in the country, were not convinced by the reformist Reformism is a political tendency advocating the reform of an existing system or institution – often a political or religious establishment – as opposed to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivos, Buenos Aires
Olivos is a neighborhood in Vicente López Partido, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is bordered to the south by Vicente López neighborhood and Florida; to the east by the River Plate; to the north by La Lucila and Martínez, and to the west by Munro. Olivos is the municipal seat of Vicente López Partido, and it is also seat of the Argentina presidencial residence. History A well-known stop along the Buenos Aires- Córdoba trade route for much of the 18th century, one of the area's first landowners, Domingo de Acassuso, began cultivating olive trees around 1720 and the spot was officially named ''Olivos'' ("Olive Trees") on 19 February 1770. Much of the area was later purchased by Viceroy Antonio de Olaguer y Feliú and by a German immigrant, Hernán Wineberg, who sold a large tract in 1860 for the construction of the Ferrocarril Central Argentino through the area. The 1863 inaugural of the local railway station, one of Argentina's first, began attracting homeow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raúl Alfonsín
Raúl Ricardo Alfonsín (; 12 March 1927 – 31 March 2009) was an Argentine lawyer and statesman who served as President of Argentina from 10 December 1983 to 8 July 1989. He was the first democratically elected president after the 7-years National Reorganization Process. Ideologically, he identified as a Radicalism (historical), radical and a social democrat, serving as the leader of the Radical Civic Union from 1983 to 1991, 1993 to 1995, 1999 to 2001, with his political approach being known as "Alfonsinism". Born in Chascomús, Buenos Aires Province, Alfonsín began his studies of law at the National University of La Plata and was a graduate of the University of Buenos Aires. He was affiliated with the Radical Civic Union (UCR), joining the faction of Ricardo Balbín after the party split. He was elected a deputy in the legislature of the Buenos Aires province in 1958, during the presidency of Arturo Frondizi, and a national deputy during the presidency of Arturo Umber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Constitution
The Constitution of the Argentine Nation () is the Constitution, basic governing document of Argentina, and the primary source of existing Law of Argentina, law in Argentina. Its Argentine Constitution of 1853, first version was written in 1853 by a constitutional assembly which gathered in Santa Fe, Argentina, Santa Fe; the doctrinal basis was taken in part from the United States Constitution. It was then reformed in 1860, 1866, 1898, 1949, 1957 (which mainly repealed the 1949 reform), and the current version is the 1994 reform of the Argentine Constitution, reformed text of 1994. It's the List of national constitutions, seventh oldest national constitution currently in effect being ratified on May 1, 1853. The Argentine Constitution consists of a preamble and two normative parts: * Preamble * First part: Declarations, Rights and Guarantees (arts. 1-43) * Second part: Authorities of the Nation (arts. 44–129). The following international human rights instruments —treaties an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underemployment
Underemployment is the underuse of a worker because their job does not use their skills, offers them too few hours, or leaves the worker idle. It is contrasted with unemployment, where a person lacks a job at all despite wanting one. Examples of workers who may be considered underemployed include those who hold a part-time job but wish to work more hours, part-time workers who wish to work full-time, and overqualified workers who have education, experience, or skills beyond their role's requirements. Underemployment has been studied from a variety of perspectives, including economics, management, psychology, and sociology. In economics, underemployment has three different distinct meanings and applications. Policy-makers may under-research these meanings when assessing the economy as they focus on unemployment instead: # " Overqualification" or "overeducation", the employment of workers with high education, skill levels, or experience in jobs that do not require such abilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Currency Board
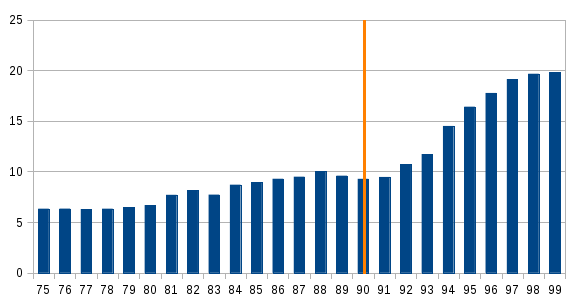
The Convertibility plan was a plan by the Argentine Currency Board that pegged the Argentine peso to the U.S. dollar between 1991 and 2002 in an attempt to eliminate hyperinflation and stimulate economic growth. While it initially met with considerable success, the board's actions ultimately failed. The peso was only pegged to the dollar until 2002. Background For most of the period between 1975 and 1990, Argentina experienced hyperinflation (averaging 325% a year), poor or negative GDP growth, a severe lack of confidence in the national government and the Central Bank, and low levels of capital investment. After eight currency crises since the early 1970s, inflation peaked in 1989, reaching 5,000% that year. GDP was 10% lower than in 1980 and per capita GDP had fallen by over 20%. Fixed investment fell by over half and, by 1989, could not cover yearly depreciation - particularly in the industrial sector. Social indicators deteriorated seriously: real wages collapsed to ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Bank Of Argentina
The Central Bank of the Argentine Republic (, BCRA) is the central bank of Argentina, being an autarchic entity. Article 3 of the Organic Charter lists the objectives of this Institution: “The bank aims to promote, to the extent of its powers and within the framework of the policies established by the national government, monetary stability, financial stability, employment, and economic development with social equity." Establishment Established by six Acts of Congress enacted on May 28, 1935, the bank replaced Argentina's currency board, which had been in operation since 1899. Its first president was Ernesto Bosch, who served in that capacity from 1935 to 1945. The Central Bank's headquarters on San Martín Street (in the heart of Buenos Aires' financial district, known locally as the ''city''), was originally designed in 1872 by architects Henry Hunt and Hans Schroeder. Completed in 1876, the Italian Renaissance-inspired building initially housed the Mortgage Bank of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domingo Cavallo
Domingo Felipe Cavallo (born July 21, 1946) is an Argentine economist and politician. Between 1991 and 1996, he was the Minister of Economy during Carlos Menem's presidency. He is known for implementing the convertibility plan, which established a pseudo-currency board with the United States dollar and allowed the dollar to be used for legal contracts. This brought the inflation rate down from over 1,300% in 1990 to less than 20% in 1992 and nearly to zero during the rest of the 1990s. He implemented pro-market reforms which included privatizations of state enterprises. Productivity per hour worked during his five-years as minister of Menem increased by more than 100%. In 2001, he was the economy minister for nine months during the 1998–2002 Argentine great depression. During a bank run, he implemented a restriction on cash withdrawing, known as '' corralito''. This was followed by the December 2001 riots in Argentina and the fall of Fernando de la Rúa as president. Caval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of Argentina
This article deals with the diplomatic affairs, foreign policy and international relations of the Argentine Republic. At the political level, these matters are handled by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, also known as the ''Cancillería'', which answers to the President. The current Minister of Foreign Affairs, since December 2023, is Chancellor (es: ''Canciller'') Diana Mondino. History From isolation to nationhood Owing to its geographical remoteness, local authorities in what is today Argentina developed an early sense of autonomy. Based largely on economic needs, during colonial times their pragmatism led to a flourishing unofficial market in smuggled goods, out of the then-small port of Buenos Aires, in blatant contravention of the Spanish mercantilist laws. With the Enlightened despotism of the late-eighteenth-century Bourbon kings and the creation of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776, trade increased as the political importance of the port-city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a business entity created or owned by a national or local government, either through an executive order or legislation. SOEs aim to generate profit for the government, prevent private sector monopolies, provide goods at lower prices, implement government policies, or serve remote areas where private businesses are scarce. The government typically holds full or majority ownership and oversees operations. SOEs have a distinct legal structure, with financial and developmental goals, like making services more accessible while earning profit (such as a state railway). They can be considered as government-affiliated entities designed to meet commercial and state capitalist objectives. Terminology The terminology around the term state-owned enterprise is murky. All three words in the term are challenged and subject to interpretation. First, it is debatable what the term "state" implies (e.g., it is unclear whether municipally owned corporations and ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Perón
Juan Domingo Perón (, , ; 8 October 1895 – 1 July 1974) was an Argentine military officer and Statesman (politician), statesman who served as the History of Argentina (1946-1955), 29th president of Argentina from 1946 to Revolución Libertadora, his overthrow in 1955 and again as the 40th president from 1973 to his death in 1974. He is the only Argentine president elected three times and holds the September 1973 Argentine presidential election, highest percentage of votes in clean elections with universal suffrage. Perón is arguably the most important and controversial Argentine politician of the 20th century and his influence extends to the present day. Perón's ideas, policies and movement are known as Peronism, which continues to be one of the major forces in Argentine politics. On 1 March 1911, Perón entered military college, graduating on 13 December 1913. Over the years, he rose through the military ranks. In 1930, Perón supported the coup against President Hipólito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |